
Causantín mac Áeda was an early King of Scotland, known then by the Gaelic name Alba. The Kingdom of Alba, a name which first appears in Constantine's lifetime, was situated in modern-day Northern Scotland.

The Picts were a group of peoples in what is now Scotland north of the Firth of Forth, in the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and details of their culture can be gleaned from early medieval texts and Pictish stones. The name Picti appears in written records as an exonym from the late third century AD. They are assumed to have been descendants of the Caledonii and other northern Iron Age tribes. Their territory is referred to as "Pictland" by modern historians. Initially made up of several chiefdoms, it came to be dominated by the Pictish kingdom of Fortriu from the seventh century. During this Verturian hegemony, Picti was adopted as an endonym. This lasted around 160 years until the Pictish kingdom merged with that of Dál Riata to form the Kingdom of Alba, ruled by the House of Alpin. The concept of "Pictish kingship" continued for a few decades until it was abandoned during the reign of Caustantín mac Áeda.
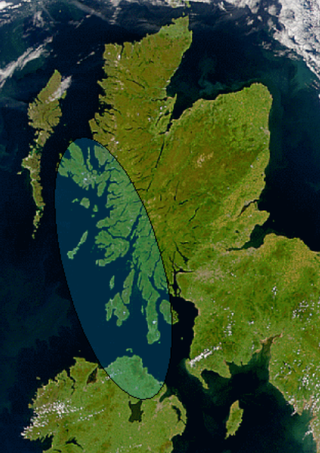
Dál Riata or Dál Riada was a Gaelic kingdom that encompassed the western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is now Argyll in Scotland and part of County Antrim in Northern Ireland. After a period of expansion, Dál Riata eventually became associated with the Gaelic Kingdom of Alba.
Pictish is an extinct Brittonic Celtic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited number of geographical and personal names found on monuments and early medieval records in the area controlled by the kingdoms of the Picts. Such evidence, however, shows the language to be an Insular Celtic language related to the Brittonic language then spoken in most of the rest of Britain.

Atholl or Athole is a large historical division in the Scottish Highlands, bordering Marr, Gowrie, Perth, Strathearn, Breadalbane, Lochaber, and Badenoch. Historically it was a Pictish kingdom, becoming one of the original provinces of the Kingdom of Alba before being incorporated into the sheriffdom and later county of Perthshire. Today it forms the northern part of Perth and Kinross, Scotland.
The House of Alpin, also known as the Alpínid dynasty, Clann Chináeda, and Clann Chinaeda meic Ailpín, was the kin-group which ruled in Pictland, possibly Dál Riata, and then the kingdom of Alba from the advent of Kenneth MacAlpin in the 840s until the death of Malcolm II in 1034.

Óengus son of Fergus was king of the Picts from 732 until his death in 761. His reign can be reconstructed in some detail from a variety of sources. The unprecedented territorial gains he made from coast to coast, and the legacy he left, mean Óengus can be considered the first king of what would become Scotland.

Fortriu was a Pictish kingdom recorded between the 4th and 10th centuries. It was traditionally believed to be located in and around Strathearn in central Scotland, but is more likely to have been based in the north, in the Moray and Easter Ross area. Fortriu is a term used by historians as it is not known what name its people used to refer to their polity. Historians also sometimes use the name synonymously with Pictland in general.
Uuen son of Onuist, commonly referred to by the hypocoristic Eóganán, was king of the Picts between AD 837–839.
The Battle of Corbridge took place on the banks of the River Tyne near the village of Corbridge in Northumberland in the year 918.

The origins of the Kingdom of Alba pertain to the origins of the Kingdom of Alba, or the Gaelic Kingdom of Scotland, either as a mythological event or a historical process, during the Early Middle Ages.
Caittil Find was the leader of a contingent of Norse-Gaels, recorded as being defeated in battle in 857 CE. Some historians have considered him to be identical to Ketill Flatnose, a prominent Norse sea-king who had strong associations with the Hebrides of Scotland and Olaf the White. This view is however not shared by all.

Scotland was divided into a series of kingdoms in the early Middle Ages, i.e. between the end of Roman authority in southern and central Britain from around 400 AD and the rise of the kingdom of Alba in 900 AD. Of these, the four most important to emerge were the Picts, the Gaels of Dál Riata, the Britons of Alt Clut, and the Anglian kingdom of Bernicia. After the arrival of the Vikings in the late 8th century, Scandinavian rulers and colonies were established on the islands and along parts of the coasts. In the 9th century, the House of Alpin combined the lands of the Scots and Picts to form a single kingdom which constituted the basis of the Kingdom of Scotland.

Ewan is an anglicisation of the Scottish Gaelic name Eòghann. It is possibly a derivative of the Pictish name, Uuen, "The Warrior" or "born of the mountain". It is most common as a male given name in Scotland and Canada. It is also, less commonly, a surname, especially among the Scottish Clans, examples of variation in spelling include McEwan’s beer and MacEwan University.

The Rulers of Bamburgh were significant regional potentates in what is now northern England and south-eastern Scotland during the Viking Age. Sometimes referred to in modern sources as the Earldom of Bamburgh, their polity existed for roughly two centuries, beginning after the attacks on the Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of Northumbria by the Vikings in the later ninth century, and ending after the Norman Conquest later in the eleventh century. In Scottish and Irish sources of the period the Bamburgh 'earldom' is referred to as the kingship of the Northern English, or simply of the 'Saxons'.
Angus is a masculine given name in English. It is an Anglicised form of the Scottish Gaelic and Irish Aonghas, which is composed of Celtic elements meaning "one" and "choice". A variant spelling of the Scottish Gaelic name is Aonghus. The Irish form of the Scottish Gaelic name is Aengus. A pet form of the given name Angus is Angie, pronounced "an-ghee", which represents the Scottish Gaelic Angaidh. A short form of the given name Angus is Gus, which may be lengthened to Gussie. The feminine form of Angus is Angusina.
Sorley and Somerled are masculine given names in the English language, Anglicizations of Scottish Gaelic Somhairle and Norse Sumarlidi.
Aonghas is a masculine given name in Scottish Gaelic. Derived from the Old Irish given name Oíngus, it is composed of Celtic elements meaning "one" and "choice". A variant spelling of the Scottish Gaelic name is Aonghus. The Irish form of the Scottish Gaelic names is Aengus. A pet form of the Scottish Gaelic name is Angaidh, which is represented in English as Angie.

The modern names of Scottish islands stem from two main influences. There are many names that derive from the Scottish Gaelic language in the Hebrides and Firth of Clyde. In the Northern Isles most place names have a Norse origin. There are also some island place names that originate from three other influences, including a limited number that are essentially English language names, a few that are of Brittonic origin and some of an unknown origin that may represent a pre-Celtic language. These islands have all been occupied by the speakers of at least three and in many cases four or more languages since the Iron Age, and many of the names of these islands have more than one possible meaning as a result.










