In biology a section (Latin : sectio) is a taxonomic rank that is applied differently in botany and zoology.

In biology a section (Latin : sectio) is a taxonomic rank that is applied differently in botany and zoology.
Within flora (plants), 'section' refers to a botanical rank below the genus, but above the species:
Within fauna (animals), 'section' refers to an uncommonly used zoological rank below the order, but above the family:
The rank of Superfamily is commonly adopted instead.
The International Code of Nomenclature for Bacteria states that the Section rank is an informal one, between the subgenus and species (as in botany). [1]

Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts:
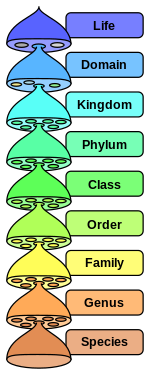
In biology, taxonomy is the scientific study of naming, defining (circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms.

Genus is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature, also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name, a binomen, binominal name, or a scientific name; more informally it is also historically called a Latin name. In the ICZN, the system is also called binominal nomenclature, "binomi'N'al" with an "N" before the "al", which is not a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system".

Order is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families.
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.

In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated as subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same.

In biology, a subgenus is a taxonomic rank directly below genus.

In biology, a taxon is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based ("Linnaean") nomenclature. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping.

In biology, a tribe is a taxonomic rank above genus, but below family and subfamily. It is sometimes subdivided into subtribes. By convention, all taxa ranked above species are capitalized, including both tribe and subtribe.

In zoological nomenclature, a type species is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen. A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus.

In biology, a type is a particular specimen of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally associated. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage, a type was a taxon rather than a specimen.

A botanical name is a formal scientific name conforming to the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and, if it concerns a plant cultigen, the additional cultivar or Group epithets must conform to the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP). The code of nomenclature covers "all organisms traditionally treated as algae, fungi, or plants, whether fossil or non-fossil, including blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria), chytrids, oomycetes, slime moulds and photosynthetic protists with their taxonomically related non-photosynthetic groups ."
Nomenclature codes or codes of nomenclature are the various rulebooks that govern the naming of living organisms. Standardizing the scientific names of biological organisms allows researchers to discuss findings.
In zoological nomenclature, author citation is the process in which a person is credited with the creation of the scientific name of a previously unnamed taxon. When citing the author of the scientific name, one must fulfill the formal requirements listed under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. According to Article 51.1 of the Code, "The name of the author does not form part of the name of a taxon and its citation is optional, although customary and often advisable." However, recommendation 51A suggests, "The original author and date of a name should be cited at least once in each work dealing with the taxon denoted by that name. This is especially important and has a unique character between homonyms and in identifying species-group names which are not in their native combinations." For the sake of information retrieval, the author citation and year appended to the scientific name, e.g. genus-species-author-year, genus-author-year, family-author-year, etc., is often considered a "de-facto" unique identifier, although this usage may often be imperfect.
In botanical nomenclature, author citation is the way of citing the person or group of people who validly published a botanical name, i.e. who first published the name while fulfilling the formal requirements as specified by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN). In cases where a species is no longer in its original generic placement, both the authority for the original genus placement and that for the new combination are given.

Priority is a fundamental principle of modern botanical nomenclature and zoological nomenclature. Essentially, it is the principle of recognising the first valid application of a name to a plant or animal. There are two aspects to this:

In biology, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system of biological classification (taxonomy) consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain. While older approaches to taxonomic classification were phenomenological, forming groups on the basis of similarities in appearance, organic structure and behaviour, methods based on genetic analysis have opened the road to cladistics.

This is a list of terms and symbols used in scientific names for organisms, and in describing the names. For proper parts of the names themselves, see List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. Note that many of the abbreviations are used with or without a stop.

The Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera (IRMNG) is a taxonomic database which attempts to cover published genus names for all domains of life, from 1758 in zoology up to the present, arranged in a single, internally consistent taxonomic hierarchy, for the benefit of Biodiversity Informatics initiatives plus general users of biodiversity (taxonomic) information. In addition to containing just over 500,000 published genus name instances as at May 2023, the database holds over 1.7 million species names, although this component of the data is not maintained in as current or complete state as the genus-level holdings. IRMNG can be queried online for access to the latest version of the dataset and is also made available as periodic snapshots or data dumps for import/upload into other systems as desired. The database was commenced in 2006 at the then CSIRO Division of Marine and Atmospheric Research in Australia and, since 2016, has been hosted at the Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ) in Belgium.