The Sikorsky H-19 Chickasaw is a multi-purpose piston-engined helicopter that was used by the United States Army and United States Air Force. It was also license-built by Westland Aircraft as the Westland Whirlwind in the United Kingdom. United States Navy and United States Coast Guard models were designated HO4S, while those of the U.S. Marine Corps were designated HRS. In 1962, the U.S. Navy, U.S. Coast Guard and U.S. Marine Corps versions were all redesignated as H-19s like their U.S. Army and U.S. Air Force counterparts.

The PA-20 Pacer and PA-22 Tri-Pacer, Caribbean, and Colt are an American family of light strut-braced high-wing monoplane aircraft built by Piper Aircraft from 1949 to 1964.

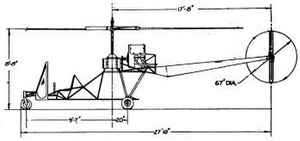
The Hiller YH-32 Hornet is an American ultralight helicopter built by Hiller Aircraft in the early 1950s. It was a small and unique design because it was powered by two Hiller 8RJ2B ramjet engines mounted on the rotor blade tips which weigh 13 lb (5.9 kg) each and deliver an equivalent of 45 hp (34 kW) for a total of 90 hp (67 kW). Versions of the HJ-1 Hornet were built for the United States Army and the United States Navy in the early 1950s.

The Sikorsky R-4 is a two-seat helicopter that was designed by Igor Sikorsky with a single, three-bladed main rotor and powered by a radial engine. The R-4 was the world's first large-scale mass-produced helicopter and the first helicopter used by the United States Army Air Forces, the United States Navy, the United States Coast Guard and the United Kingdom's Royal Air Force and Royal Navy. In U.S. Navy and U.S. Coast Guard service, the helicopter was known as the Sikorsky HNS-1. In British service it was known as the Hoverfly.

The Hiller OH-23 Raven is a two, three, or four-place, military light observation helicopter based on the Hiller Model 360. The Model 360 was designated by the company as the UH-12, which was first flown in 1948. Initially it was a two-place helicopter powered by a piston engine that entered service in the late 1940s, it went on to be a popular military and civilian light helicopter in the late 20th century.

The Hughes TH-55 Osage is a piston-powered light training helicopter produced for the United States Army. It was also produced as the Model 269 family of light utility helicopters, some of which were marketed as the Model 300. The Model 300C was produced and further developed by Schweizer after 1983.

The Cessna CH-1 Skyhook is the only helicopter ever built by the Cessna Aircraft Company. It was the first helicopter to land on the summit of Pike's Peak and the last piston-engined helicopter to set the helicopter altitude record. The CH-1 had a single, two-bladed main rotor, and a front-mounted reciprocating engine which gave the aircraft a stable center of gravity (CG). Its semi-monocoque airframe greatly resembles its light airplane siblings built by Cessna. The CH-1 was named Skyhook for the civil market, similar to the marketing names used in the Cessna single engine airplane line, such as Skyhawk, Skylane and Skywagon. The United States Army designated the CH-1C as the YH-41 Seneca. While the CH-1 achieved several helicopter firsts and set a world record, it never became a commercial or military success.

The Piasecki VZ-8 Airgeep was a prototype vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft developed by Piasecki Aircraft. The Airgeep was developed to fulfill a U.S. Army Transportation Research Command contract for a flying jeep in 1957. The flying jeep was envisioned to be smaller and easier to fly than a helicopter.

The Brantly B-2 is an American two-seat light helicopter produced by the Brantly Helicopter Corporation.

The Bell UH-1 Iroquois military helicopter, first introduced in 1959, is the first production member of the prolific Huey family of helicopters, and was itself developed in over twenty variants, which are listed below.

The Doman LZ-5 was a utility helicopter developed in the United States in the early 1950s by Doman Helicopters Inc. of Danbury, Connecticut. Despite the procurement of international manufacturing agreements, no series production of the aircraft ever occurred, and only three prototypes were built. Two of these were purchased by the United States Army as the YH-31, but eventually becoming VH-31.

The Firestone XR-9, also known by the company designation Model 45, was a 1940s American experimental helicopter built by the Firestone Aircraft Company for the United States Army Air Forces. Only two were built.

The McCulloch Model MC-4 was an American tandem-rotor helicopter and was the first helicopter developed by McCulloch Aircraft Corporation, a division of McCulloch Motors Corporation. It was evaluated by the United States Army as the YH-30 and the United States Navy as the XHUM-1.

The Sikorsky S-52 is a utility helicopter developed by Sikorsky Aircraft in the late 1940s. It was used by the U.S. Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. The S-52 was the first US helicopter with all-metal rotor blades. Initially a two-seater, it was developed into the four-seat S-52-2 and S-52-3. It was designated HO5S-1 by the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps, HO5S-1G by the Coast Guard, and YH-18A by the U.S. Army, and was used extensively by civil operators after being retired by the military.

The Piasecki H-16 Transporter was a tandem-rotor transport or rescue helicopter designed by Frank Piasecki and built by Piasecki Helicopter. The prototypes were evaluated by the United States Air Force and Army, but the crash of the second test aircraft led to cancelling the project.

The Kaman K-225 is an American experimental helicopter developed by Kaman Aircraft. One example was modified to become the world's first gas turbine-powered helicopter.

The Aero HC-2 Heli Baby is a two-seat general-purpose light utility helicopter, designed by engineer Jaroslav Šlechta, and produced by the Czechoslovak company Aero Vodochody in the 1950s. It has a three-blade main rotor, and a two-blade tail rotor. The helicopter has an entirely metal frame and cockpit, and windows made of Plexiglas. It was the first and the only Czechoslovak-designed helicopter to be produced.

The Matra-Cantinieau MC-101 was an early 1950s French experimental two seat helicopter of conventional tail rotor configuration but with its engine mounted close to the main rotor, above the seating.

The Transcendental Model 1-G was an experimental American tiltrotor prototype of the 1950s. It was a single-seat aircraft powered by a piston engine, and was the first tiltrotor to fly. A single example was built, which was destroyed in a crash in 1955.