The Bell UH-1 Iroquois is a utility military helicopter designed and produced by the American aerospace company Bell Helicopter. It is the first member of the prolific Huey family, as well as the first turbine-powered helicopter in service with the United States military.

The Bell X-1 is a rocket engine–powered aircraft, designated originally as the XS-1, and was a joint National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics–U.S. Army Air Forces–U.S. Air Force supersonic research project built by Bell Aircraft. Conceived during 1944 and designed and built in 1945, it achieved a speed of nearly 1,000 miles per hour in 1948. A derivative of this same design, the Bell X-1A, having greater fuel capacity and hence longer rocket burning time, exceeded 1,600 miles per hour in 1954. The X-1 aircraft #46-062, nicknamed Glamorous Glennis and flown by Chuck Yeager, was the first piloted airplane to exceed the speed of sound in level flight and was the first of the X-planes, a series of American experimental rocket planes designed for testing new technologies.

The Hiller YH-32 Hornet was an American ultralight helicopter built by Hiller Aircraft in the early 1950s. It was a small and unique design because it was powered by two Hiller 8RJ2B ramjet engines mounted on the rotor blade tips which weigh 13 lb (5.9 kg) each and deliver an equivalent of 45 hp (34 kW) for a total of 90 hp (67 kW). Versions of the HJ-1 Hornet were built for the United States Army and the United States Navy in the early 1950s.

The Piasecki HUP Retriever or H-25 Army Mule, later UH-25, is a compact single radial engine, twin overlapping tandem rotor utility helicopter developed by the Piasecki Helicopter Corporation of Morton, Pennsylvania. Designed to a United States Navy specification, the helicopter was produced from 1949 to 1954, and was also used by the United States Army and foreign navies. The HUP/H-25 was the first helicopter to be produced with an autopilot and also the first to perform a loop.

The Bell XV-3 is an American tiltrotor aircraft developed by Bell Helicopter for a joint research program between the United States Air Force and the United States Army in order to explore convertiplane technologies. The XV-3 featured an engine mounted in the fuselage with driveshafts transferring power to two-bladed rotor assemblies mounted on the wingtips. The wingtip rotor assemblies were mounted to tilt 90 degrees from vertical to horizontal, designed to allow the XV-3 to take off and land like a helicopter but fly at faster airspeeds, similar to a conventional fixed-wing aircraft.

The Bell 533 was a research helicopter built by Bell Helicopter under contract with the United States Army during the 1960s, to explore the limits and conditions experienced by helicopter rotors at high airspeeds. The helicopter was a YH-40—a preproduction version of the UH-1 Iroquois—modified and tested in several helicopter and compound helicopter configurations. The Bell 533 was referred to as the High Performance Helicopter (HPH) by the Army, and reached a top speed of 274.6 knots in 1969, before being retired.

The Seibel S-4 was a two-bladed, single-engine helicopter built by Seibel Helicopter. Designed by Charles Seibel, the S-4 was evaluated by the United States Army under the designation YH-24 Sky Hawk, but would be rejected for service. The S-4B would serve as the basis for the design of the Cessna CH-1 Skyhook, the only helicopter Cessna ever produced.

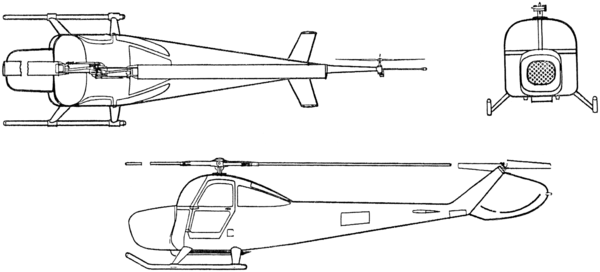
The Bell R-12 was an American 1940s military utility helicopter built by the Bell Helicopter company. The design did not go into full production, but over a dozen prototypes were used for various tests and projects.

The Bell UH-1 Iroquois military helicopter, first introduced in 1959, is the first production member of the prolific Huey family of helicopters, and was itself developed in over twenty variants, which are listed below.

The Platt-LePage XR-1, also known by the company designation PL-3, was an early American transverse rotors helicopter, built by the Platt-LePage Aircraft Company of Eddystone, Pennsylvania. The winner of a United States Army Air Corps design competition held in early 1940, the XR-1 was the first helicopter tested by the USAAF, flying in 1941. The flight testing of the XR-1 proved troublesome, and although continued testing showed that the design had promise, other, improved helicopters were becoming available before the XR-1 was ready for service. As a result, the development of the aircraft was terminated in 1945.

The Doman LZ-5 was a utility helicopter developed in the United States in the early 1950s by Doman Helicopters Inc. of Danbury, Connecticut. Despite the procurement of international manufacturing agreements, no series production of the aircraft ever occurred, and only three prototypes were built. Two of these were purchased by the United States Army as the YH-31, but eventually becoming VH-31.

The McDonnell XV-1 is an experimental Convertiplane developed by McDonnell Aircraft for a joint research program between the United States Air Force and the United States Army to explore technologies to develop an aircraft that could take off and land like a helicopter but fly at faster airspeeds, similar to a conventional airplane. The XV-1 would reach a speed of 200 mph, faster than any previous rotorcraft, but the program was terminated due to the tip-jet noise and complexity of the technology which gave only a modest gain in performance.

The United States Army Aviation Museum is an aviation museum located on Fort Novosel near Daleville, Alabama. It has the largest collection of helicopters held by a museum in the world. The museum features some 50 aircraft on public display with aviation artifacts ranging from a replica of the Wright brothers' Model B military biplane to an RAH-66 Comanche. The museum has over 160 aircraft in its collection and holds 3,000 historical items.

The Sikorsky XH-39, developed by Sikorsky Aircraft in 1954, was the U.S. Army's first turbine-powered helicopter. It was fast and innovative, but ultimately rejected by the United States Army in favor of the Bell UH-1 Iroquois.

The Sikorsky S-52 is a utility helicopter developed by Sikorsky Aircraft in the late 1940s. It was used by the U.S. Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. The S-52 was the first US helicopter with all-metal rotor blades. Initially a two-seater, it was developed into the four-seat S-52-2 and S-52-3. It was designated HO5S-1 by the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps, HO5S-1G by the Coast Guard, and YH-18A by the U.S. Army, and was used extensively by civil operators after being retired by the military.

The Bell Huey family of helicopters includes a wide range of civil and military aircraft produced since 1956 by Bell Helicopter. This H-1 family of aircraft includes the utility UH-1 Iroquois and the derivative AH-1 Cobra attack helicopter series and ranges from the XH-40 prototype, first flown in October 1956, to the 21st-century UH-1Y Venom and AH-1Z Viper. Although not flown in military service in the USA, the Bell 412 served in Canada and Japan and, like the UH-1Y, is a twin engine four rotor design based on the Bell 212.

The Piasecki H-16 Transporter was a tandem-rotor transport or rescue helicopter designed by Frank Piasecki and built by Piasecki Helicopter. The prototypes were evaluated by the United States Air Force and Army, but the crash of the second test aircraft led to cancelling the project.

The Bell 30 was the prototype for the first commercial helicopter, and the first helicopter built by the Bell Aircraft Company. Designed by Arthur M. Young, the type served as a demonstration testbed for the successful Bell 47.
The I.P.D BF-1 Beija-Flôr was a two-seat light helicopter designed by Henrich Focke.

The Kayaba Heliplane Type-1 was a gyrodyne designed by Shiro Kayaba and prototyped by Kayaba Industry in Japan during the early 1950s.