
Loliginidae, commonly known as pencil squids, is an aquatic family of squid classified in the order Myopsida.

Doryteuthis plei, also known as the slender inshore squid or arrow squid, is a medium-sized squid belonging to the family Loliginidae. It occurs abundantly in coastal waters of the Atlantic Ocean, from Argentina northward to North Carolina.

Myopsida is one of the four orders of squid. It consists of two families: the monotypic Australiteuthis and the diverse and commercially important Loliginidae. Some taxonomists classify this taxon as a suborder of the order Teuthida, in which case it is known as Myopsina. This reclassification is due to Myopsina and Oegopsina not being demonstrated to form a clade.

The longfin inshore squid is a species of squid of the family Loliginidae.

Loligo is a genus of squid and one of the most representative and widely distributed groups of myopsid squid.

The European squid or common squid is a large squid belonging to the family Loliginidae. It occurs abundantly in coastal waters from the North Sea to at least the west coast of Africa. This species lives from sea level to depths of 500 m (1,600 ft). Its mantle is up to 40 cm (16 in) long. The species is extensively exploited by commercial fisheries.

Taningia danae, the Dana octopus squid, is a species of squid in the family Octopoteuthidae. It is one of the largest known squid species, reaching a mantle length of 1.7 m (5.6 ft) and total length of 2.3 m (7.5 ft). The largest known specimen, a mature female, weighed 161.4 kg (356 lb).
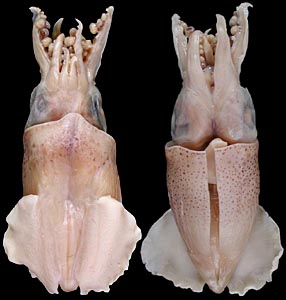
A. aldrichi is a small species of squid found in northern Australian waters. The species was described by Chung Cheng Lu in 2005 based on specimens collected in the inshore waters of Northern Australia. The largest known individual of this species is a mature female measuring 27.6 mm (1.09 in) in mantle length (ML). The holotype is a mature male of 21.3 mm (0.84 in) ML. A live specimen of A. aldrichi has yet to be recorded. A. aldrichi is a member of the class Cephalopoda and part of the subclass Coleodia. Within this class there are two orders, the Myopsida and Oegopsida, which both fall under the superorder Decapodiformes. A. aldrichi falls under the order of Myospida, and is the only member of its genus, Australiteuthis, and family, Australiteuthidae.
Loligo reynaudii, commonly known as the Cape Hope squid, is a 20–30 cm long squid belonging to the family Loliginidae. In South Africa it is known as either calamari or chokka.
Alloteuthis africana, also known as the African squid, is a species of squid in the family Loliginidae. This species of squid is restricted to the Guinean province. To identify the Alloteuthis africana from other Alloteuthis family members, it is highly recommended to measure the width of the squids head and the sucker size.
Pickfordiateuthis is a genus of tiny squid in the family Loliginidae. While four species have been assigned to the genus, only three have been named. No member is known to reach a maximum mantle length of more than 22 mm.

Alloteuthis subulata, the European common squid, is a species of squid in the genus Alloteuthis and the family Loliginidae.

The neon flying squid, sometimes called the red flying squid, akaika, and red squid is a species of large flying squid in the family Ommastrephidae. They are found in subtropical and temperate oceanic waters globally.

Sepioteuthis lessoniana, commonly known as the bigfin reef squid, glitter squid or oval squid, is a species of loliginid squid. It is one of the three currently recognized species belonging to the genus Sepioteuthis. Studies in 1993, however, have indicated that bigfin reef squids may comprise a cryptic species complex. The species is likely to include several very similar and closely related species.
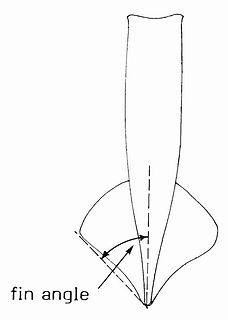
Cephalopod fins, sometimes known as wings, are paired flap-like locomotory appendages. They are found in ten-limbed cephalopods as well as in the eight-limbed cirrate octopuses and vampire squid. Many extinct cephalopod groups also possessed fins. Nautiluses and the more familiar incirrate octopuses lack swimming fins. An extreme development of the cephalopod fin is seen in the bigfin squid of the family Magnapinnidae.

Cephalopods exhibit various dermal structures on their mantles and other parts. These may take the form of conspicuous warts, cushions, papillae or scales, though in many species they are microscopic tubercles. The most elaborate forms are found among the oceanic squid of the order Teuthida.

Uroteuthis is a genus of 14 species of common inshore squids of the Indo-West Pacific and is further subdivided into 3 subgenera. The members of the genus Uroteuthis are the only squids of the family Loliginidae that possess photophores and all species in the genus have a pair of photophore organs on the ventral surface of their ink sac either side of their intestine.
Lolliguncula is a genus of squid from the family Loliginidae from the eastern Pacific and western Atlantic, known as brief squid. The genus is divided into two subgenera Lolliguncula and Loliolopsis. They are rather small squids with a maximum mantle length of 120mm, that inhabit shallow warm seas, although some species have been recorded in areas of low salinity. They are typified by having a short mantle, which is round at the posterior; and fins that are broader than long, but which have no posterior lobes. The males produce spermatophores with a long cement body and they lack a ventral crest on their hectocotylus. Their suckers have square teeth which ring the entire margin or are placed distally. The males do not have enlarged suckers on the left ventral arm. The tentacular club is expanded and contains suckers in four series. The two subgenera differ in the morphology of the hectocotylus.
Richard E. Young is a teuthologist. He is an Emeritus Professor of Oceanography at the University of Hawaii's School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology.
Gretta T. Pecl is an Australian marine ecologist and Director of the Centre for Marine Socioecology at the University of Tasmania. She is an Australian Research Council Future Fellow and on the Editorial Board of Springer Nature's Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries.













