Related Research Articles

An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection.

An epidemic is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in excess of 15 cases per 100,000 people for two consecutive weeks is considered an epidemic.

Incubation period is the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, a chemical, or radiation, and when symptoms and signs are first apparent. In a typical infectious disease, the incubation period signifies the period taken by the multiplying organism to reach a threshold necessary to produce symptoms in the host.

Melioidosis is an infectious disease caused by a gram-negative bacterium called Burkholderia pseudomallei. Most people exposed to B. pseudomallei experience no symptoms; however, those who do experience symptoms have signs and symptoms that range from mild such as fever and skin changes, to severe with pneumonia, abscesses, and septic shock that could cause death. Approximately 10% of people with melioidosis develop symptoms that last longer than two months, termed "chronic melioidosis".

An asymptomatic carrier is a person or other organism that has become infected with a pathogen, but shows no signs or symptoms.

Blastomycosis, also known as Gilchrist's disease, is a fungal infection, typically of the lungs, which can spread to brain, stomach, intestine and skin, where it appears as crusting purplish warty plaques with a roundish bumpy edge and central depression. Only about half of people with the disease have symptoms, which can include fever, cough, night sweats, muscle pains, weight loss, chest pain, and feeling tired. Symptoms usually develop between three weeks and three months after breathing in the spores. In 25% to 40% of cases, the infection also spreads to other parts of the body, such as the skin, bones or central nervous system. Although blastomycosis is especially dangerous for those with weak immune systems, most people diagnosed with blastomycosis have healthy immune systems.
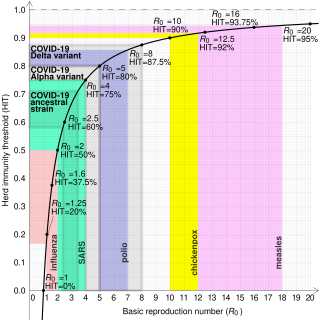
In epidemiology, the basic reproduction number, or basic reproductive number, denoted , of an infection is the expected number of cases directly generated by one case in a population where all individuals are susceptible to infection. The definition assumes that no other individuals are infected or immunized. Some definitions, such as that of the Australian Department of Health, add the absence of "any deliberate intervention in disease transmission". The basic reproduction number is not necessarily the same as the effective reproduction number , which is the number of cases generated in the current state of a population, which does not have to be the uninfected state. is a dimensionless number and not a time rate, which would have units of time−1, or units of time like doubling time.
Mathematical models can project how infectious diseases progress to show the likely outcome of an epidemic and help inform public health and plant health interventions. Models use basic assumptions or collected statistics along with mathematics to find parameters for various infectious diseases and use those parameters to calculate the effects of different interventions, like mass vaccination programs. The modelling can help decide which intervention(s) to avoid and which to trial, or can predict future growth patterns, etc.
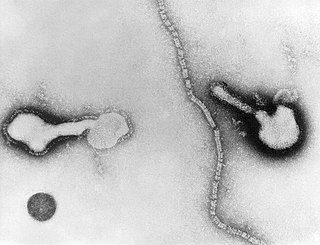
Human parainfluenza viruses (HPIVs) are the viruses that cause human parainfluenza. HPIVs are a paraphyletic group of four distinct single-stranded RNA viruses belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family. These viruses are closely associated with both human and veterinary disease. Virions are approximately 150–250 nm in size and contain negative sense RNA with a genome encompassing about 15,000 nucleotides.
A slow virus is a virus, or a viruslike agent, etiologically associated with a slow virus disease. A slow virus disease is a disease that, after an extended period of latency, follows a slow, progressive course spanning months to years, frequently involves the central nervous system, and in most cases progresses to death. Examples of slow virus diseases include HIV/AIDS, caused by the HIV virus, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis, the rare result of a measles virus infection, and Paget's disease of bone, which may be associated with paramyxoviruses, especially the measles virus and the human respiratory syncytial virus.

A subclinical infection—sometimes called a preinfection or inapparent infection—is an infection by a pathogen that causes few or no signs or symptoms of infection in the host. Subclinical infections can occur in both humans and animals. Depending on the pathogen, which can be a virus or intestinal parasite, the host may be infectious and able to transmit the pathogen without ever developing symptoms; such a host is called an asymptomatic carrier. Many pathogens, including HIV, typhoid fever, and coronaviruses such as COVID-19 spread in their host populations through subclinical infection.

Kuru is a rare, incurable, and fatal neurodegenerative disorder that was formerly common among the Fore people of Papua New Guinea. Kuru is a form of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) caused by the transmission of abnormally folded proteins (prions), which leads to symptoms such as tremors and loss of coordination from neurodegeneration.
Rickettsia typhi is a small, aerobic, obligate intracellular, rod shaped gram negative bacterium. It belongs to the typhus group of the Rickettsia genus, along with R. prowazekii. R. typhi has an uncertain history, as it may have long gone shadowed by epidemic typhus. This bacterium is recognized as a biocontainment level 2/3 organism. R. typhi is a flea-borne disease that is best known to be the causative agent for the disease murine typhus, which is an endemic typhus in humans that is distributed worldwide. As with all rickettsial organisms, R. typhi is a zoonotic agent that causes the disease murine typhus, displaying non-specific mild symptoms of fevers, headaches, pains and rashes. There are two cycles of R. typhi transmission from animal reservoirs containing R. typhi to humans: a classic rat-flea-rat cycle that is most well studied and common, and a secondary periodomestic cycle that could involve cats, dogs, opossums, sheep, and their fleas.

Airborne transmission or aerosol transmission is transmission of an infectious disease through small particles suspended in the air. Infectious diseases capable of airborne transmission include many of considerable importance both in human and veterinary medicine. The relevant infectious agent may be viruses, bacteria, or fungi, and they may be spread through breathing, talking, coughing, sneezing, raising of dust, spraying of liquids, flushing toilets, or any activities which generate aerosol particles or droplets. This is the transmission of diseases via transmission of an infectious agent, and does not include diseases caused by air pollution.
Hantavirus hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) is a group of clinically similar illnesses caused by species of hantaviruses. It is also known as Korean hemorrhagic fever and epidemic hemorrhagic fever. It is found in Europe, Asia, and Africa. The species that cause HFRS include Hantaan orthohantavirus, Dobrava-Belgrade orthohantavirus, Saaremaa virus, Seoul orthohantavirus, Puumala orthohantavirus and other orthohantaviruses. Of these species, Hantaan River virus and Dobrava-Belgrade virus cause the most severe form of the syndrome and have the highest morbidity rates. When caused by the Puumala virus, it is also called nephropathia epidemica. This infection is known as sorkfeber in Swedish, myyräkuume in Finnish, and musepest in Norwegian.

A superspreading event (SSEV) is an event in which an infectious disease is spread much more than usual, while an unusually contagious organism infected with a disease is known as a superspreader. In the context of a human-borne illness, a superspreader is an individual who is more likely to infect others, compared with a typical infected person. Such superspreaders are of particular concern in epidemiology.
Allison Joan McGeer is a Canadian infectious disease specialist in the Sinai Health System, and a professor in the Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathobiology at the University of Toronto. She also appointed at the Dalla Lana School of Public Health and a Senior Clinician Scientist at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute, and is a partner of the National Collaborating Centre for Infectious Diseases. McGeer has led investigations into the severe acute respiratory syndrome outbreak in Toronto and worked alongside Donald Low. During the COVID-19 pandemic, McGeer has studied how SARS-CoV-2 survives in the air and has served on several provincial committees advising aspects of the Government of Ontario's pandemic response.
In epidemiology, particularly in the discussion of infectious disease dynamics (modeling), the latent period is the time interval between when an individual or host is infected by a pathogen and when they become infectious, i.e. capable of transmitting pathogens to other susceptible individuals.

In epidemiology, particularly in the discussion of infectious disease dynamics, the infectious period is the time interval during which a host is infectious, i.e. capable of directly or indirectly transmitting pathogenic infectious agents or pathogens to another susceptible host. The infectious period can start before, during or after the onset of symptoms, and it may stop before or after the symptoms stop showing. It is also known in the literature by a variety of synonymous terms such as the infective period, the period of infectiousness, communicability period, the period of communicability, contagious period, the period of contagiousness, transmission period or transmissibility period. The degree of infectiousness is not constant but varies through the infectious period.
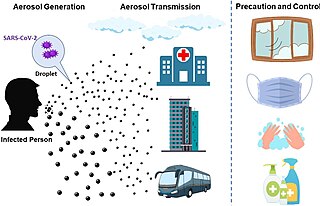
The transmission of COVID-19 is the passing of coronavirus disease 2019 from person to person. COVID-19 is mainly transmitted when people breathe in air contaminated by droplets/aerosols and small airborne particles containing the virus. Infected people exhale those particles as they breathe, talk, cough, sneeze, or sing. Transmission is more likely the more physically close people are. However, infection can occur over longer distances, particularly indoors.
References
- ↑ Last J.M. (2001) A Dictionary of Epidemiology, Oxford University Press.
- ↑ Fine, P. E. M. (2003). "The Interval between Successive Cases of an Infectious Disease". American Journal of Epidemiology. 158 (11): 1039–1047. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwg251 . PMID 14630599.
- ↑ Lipsitch, M.; Cohen, T.; Cooper, B.; Robins, J. M.; Ma, S.; James, L.; Gopalakrishna, G.; Chew, S. K.; Tan, C. C.; Samore, M. H.; Fisman, D.; Murray, M. (2003). "Transmission Dynamics and Control of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome" (PDF). Science. 300 (5627): 1966–1970. Bibcode:2003Sci...300.1966L. doi:10.1126/science.1086616. PMC 2760158 . PMID 12766207.
- ↑ Park, Minah; Cook, Alex R.; Lim, Jue Tao; Sun, Yinxiaohe; Dickens, Borame L. (2020-03-31). "A Systematic Review of COVID-19 Epidemiology Based on Current Evidence". Journal of Clinical Medicine. 9 (4): 967. doi: 10.3390/jcm9040967 . ISSN 2077-0383. PMC 7231098 . PMID 32244365.