| Siege of Nuremberg | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Thirty Years' War | |||||||
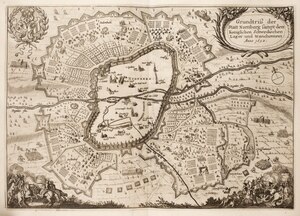 Siege of Nuremberg (engraving by Matthäus Merian, 1642) | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| | | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 45,000 175 guns [1] | 50,000 [2] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 2,500 killed and wounded 10,000 died from disease 11,000 deserted | 900 killed and wounded [3] Heavy amount of mean dead from disease Unknown total | ||||||
The siege of Nuremberg was a campaign that took place in 1632 about the Imperial City of Nuremberg during the Thirty Years' War.
In July 1632, rather than face the numerically superior combined Imperial and Catholic League army under the command of Albrecht von Wallenstein and Bavarian Elector Maximilian I, Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden ordered a tactical retreat into the city of Nuremberg. Wallenstein's army immediately started to invest Nuremberg and laid siege to the city, waiting for hunger and epidemics to cripple the Swedish force. [2]
It proved difficult for the besiegers to maintain the siege because the city was large and needed a large force to man the circumvallation. In Wallenstein's camp, there were 50,000 soldiers, 15,000 horses and 25,000 camp followers. [2] Foraging to supply such a large static besieging force proved to be extremely difficult. Gustavus' army grew through reinforcements from 18,500 to 45,000 men with 175 field guns, the largest army he ever led in person. [4]
With poor sanitation and inadequate supplies, both sides suffered from hunger, typhus and scurvy. To try to break the deadlock, 25,000 men under Gustavus attacked the Imperial entrenchments in the Battle of the Alte Veste on 3 September but failed to break through, having lost 2,500 men compared to 900 Imperials. [3] Eventually, the siege ended after eleven weeks when the Swedes and their allies withdrew. Disease killed 10,000 Swedish and allied troops, with an additional 11,000 deserters. [3] Gustavus was so weakened by the struggle that he sent peace proposals to Wallenstein, who dismissed them. [3]