
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants also known as lycopods or lycophytes. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching stems bearing simple leaves called microphylls and reproduce by means of spores borne in sporangia on the sides of the stems at the bases of the leaves. Although living species are small, during the Carboniferous, extinct tree-like forms (Lepidodendrales) formed huge forests that dominated the landscape and contributed to coal deposits.

The lycophytes, when broadly circumscribed, are a group of vascular plants that include the clubmosses. They are sometimes placed in a division Lycopodiophyta or Lycophyta or in a subdivision Lycopodiophytina. They are one of the oldest lineages of extant (living) vascular plants; the group contains extinct plants that have been dated from the Silurian. Lycophytes were some of the dominating plant species of the Carboniferous period, and included the tree-like Lepidodendrales, some of which grew over 40 metres (130 ft) in height, although extant lycophytes are relatively small plants.

Paleobotany, also spelled as palaeobotany, is the branch of botany dealing with the recovery and identification of plant remains from geological contexts, and their use for the biological reconstruction of past environments (paleogeography), and the evolutionary history of plants, with a bearing upon the evolution of life in general. A synonym is paleophytology. It is a component of paleontology and paleobiology. The prefix palaeo- or paleo- means "ancient, old", and is derived from the Greek adjective παλαιός, palaios. Paleobotany includes the study of terrestrial plant fossils, as well as the study of prehistoric marine photoautotrophs, such as photosynthetic algae, seaweeds or kelp. A closely related field is palynology, which is the study of fossilized and extant spores and pollen.

Adolphe-Théodore Brongniart FRS FRSE FGS was a French botanist. He was the son of the geologist Alexandre Brongniart and grandson of the architect, Alexandre-Théodore Brongniart. Brongniart's pioneering work on the relationships between extinct and existing plants has earned him the title of father of paleobotany. His major work on plant fossils was his Histoire des végétaux fossiles (1828–37). He wrote his dissertation on the Buckthorn family (Rhamnaceae), an extant family of flowering plants, and worked at the Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle in Paris until his death. In 1851, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. This botanist is denoted by the author abbreviation Brongn. when citing a botanical name.

Lepidodendron is an extinct genus of primitive lycopodian vascular plants belonging the order Lepidodendrales. It is well preserved and common in the fossil record. Like other Lepidodendrales, species of Lepidodendron grew as large-tree-like plants in wetland coal forest environments. They sometimes reached heights of 50 metres, and the trunks were often over 1 m in diameter. They are often known as "scale trees", due to their bark having been covered in diamond shaped leaf-bases, from which leaves grew during earlier stages of growth. However, they are correctly defined as arborescent lycophytes. They thrived during the Carboniferous Period, and persisted until the end of the Permian around 252 million years ago. Sometimes erroneously called "giant club mosses", the genus was actually more closely related to modern quillworts than to modern club mosses. In the form classification system used in paleobotany, Lepidodendron is both used for the whole plant as well as specifically the stems and leaves.

Joggins is a rural community located in western Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, Canada. On July 7, 2008 a 15-km length of the coast constituting the Joggins Fossil Cliffs was officially inscribed on the World Heritage List.

The zosterophylls are a group of extinct land plants that first appeared in the Silurian period. The taxon was first established by Banks in 1968 as the subdivision Zosterophyllophytina; they have since also been treated as the division Zosterophyllophyta or Zosterophyta and the class or plesion Zosterophyllopsida or Zosteropsida. They were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and had a world-wide distribution. They were probably stem-group lycophytes, forming a sister group to the ancestors of the living lycophytes. By the late Silurian a diverse assemblage of species existed, examples of which have been found fossilised in what is now Bathurst Island in Arctic Canada.
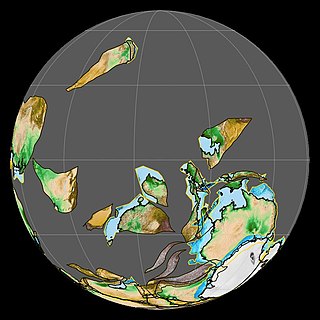
The Tournaisian is in the ICS geologic timescale the lowest stage or oldest age of the Mississippian, the oldest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Tournaisian age lasted from 358.9 Ma to 346.7 Ma. It is preceded by the Famennian and is followed by the Viséan. In global stratigraphy, the Tournaisian contains two substages: the Hastarian and Ivorian. These two substages were originally designated as European regional stages.

Arthropleura is a genus of massive millipedes that lived in what is now North America and Europe around 345 to 290 million years ago, from the Viséan stage of the lower Carboniferous Period to the Sakmarian stage of the lower Permian Period. The species of the genus are the largest known land invertebrates of all time, and would have had few, if any, predators.

Coal forests were the vast swathes of swamps and riparian forests that covered much of the land on Earth's tropical regions during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) and Permian periods. As plant matter from these forests decayed, enormous deposits of peat accumulated, which later became buried and converted into coal over the subsequent eras.

Stigmaria is a form taxon for common fossils found in Carboniferous rocks. They represent the underground rooting structures of arborescent lycophytes such as Sigillaria and Lepidodendron under the order Lepidodendrales.

Dendrerpeton is a genus of an extinct group of temnospondyl amphibians. Its fossils have been found primarily in the Joggins Formation of Eastern Canada and in Ireland. It lived during the Carboniferous and is said to be around 309–316 million years of age, corresponding to more specifically the Westphalian (stage) age. Of terrestrial temnospondyl amphibians evolution, it represents the first stage. Although multiple species have been proposed, the species unanimously recognized is D. acadianum. This species name comes from “Acadia” which is a historical name for the Nova Scotia region as a French colony. It refers to the location of the coal field at which the fossil was found.

The Fossil Grove is a group of plant fossils located within Victoria Park, Glasgow, Scotland. It was discovered in 1887 and contains the fossilised stumps and the stigmarian system of eleven extinct Lepidodendron lycopsids, which are sometimes described as "giant club mosses" but are more closely related to quillworts. The Fossil Grove is managed as a museum and has been a popular tourist attraction since it opened for public viewing in 1890.

Lepidodendrales or arborescent lycophytes are an extinct order of primitive, vascular, heterosporous, arborescent (tree-like) plants belonging to Lycopodiopsida. Members of Lepidodendrales are the best understood of the fossil lycopsids due to the vast diversity of Lepidodendrales specimens and the diversity in which they were preserved; the extensive distribution of Lepidodendrales specimens as well as their well-preservedness lends paleobotanists exceptionally detailed knowledge of the coal-swamp giants’ reproductive biology, vegetative development, and role in their paleoecosystem. The defining characteristics of the Lepidodendrales are their secondary xylem, extensive periderm development, three-zoned cortex, rootlike appendages known as stigmarian rootlets arranged in a spiralling pattern, and megasporangium each containing a single functional megaspore that germinates inside the sporangium. Many of these different plant organs have been assigned both generic and specific names as relatively few have been found organically attached to each other. Some specimens have been discovered which indicate heights of 40 and even 50 meters and diameters of over 2 meters at the base. The massive trunks of some species branched profusely, producing large crowns of leafy twigs; though some leaves were up to 1 meter long, most were much shorter, and when leaves dropped from branches their conspicuous leaf bases remained on the surface of branches. Strobili could be found at the tips of distal branches or in an area at the top of the main trunk. The underground organs of Lepidodendrales typically consisted of dichotomizing axes bearing helically arranged, lateral appendages serving an equivalent function to roots. Sometimes called "giant club mosses", they are believed to be more closely related to extant quillworts based on xylem, although fossil specimens of extinct Selaginellales from the Late Carboniferous also had secondary xylem.
This article attempts to place key plant innovations in a geological context. It concerns itself only with novel adaptations and events that had a major ecological significance, not those that are of solely anthropological interest. The timeline displays a graphical representation of the adaptations; the text attempts to explain the nature and robustness of the evidence.

Psaronius is an extinct genus marattialean tree fern which grew to 10m in height, and is associated with leaves of the organ genus Pecopteris and other extinct tree ferns. Originally, Psaronius was a name for the petrified stems, but today the genus is used for the entire tree fern. Psaronius tree fern fossils are found from the Carboniferous through the Permian.
Calligenethlon is an extinct genus of embolomere tetrapodomorphs from the Late Carboniferous of Joggins, Nova Scotia. It is the only definitively identified embolomere from the Joggins Fossil Cliffs and is the largest tetrapod to have been found preserved in lycopod tree stumps.

The Joggins Formation is a geologic formation in Nova Scotia. It preserves fossils dating back to the Westphalian stage or Moscovian stage of the Upper Carboniferous period or Pennsylvanian period, including Hylonomus, the earliest known reptile. In addition to fossils, the Joggins Formation was a valuable source of coal from the 17th century until the mid-20th century.

Cyclopteris is an extinct genus of seed ferns in the extinct family †Cyclopteridaceae. Species are from the Carboniferous.
Leptophloeum is an extinct genus of vascular plants in the lycophyte clade. It is widely distributed being, known from the Laurasian and Gondwanan settings between the Devonian and Early Carboniferous periods.

































