
Silphium is an unidentified plant that was used in classical antiquity as a seasoning, perfume, aphrodisiac, and medicine. It also was used as a contraceptive by ancient Greeks and Romans. It was the essential item of trade from the ancient North African city of Cyrene, and was so critical to the Cyrenian economy that most of their coins bore a picture of the plant. The valuable product was the plant's resin.

Silphium is a genus of North American plants in the tribe Heliantheae within the family Asteraceae.

Silphium laciniatum is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known commonly as compassplant or compass plant. It is native to North America, where it occurs in Ontario in Canada and the eastern and central United States as far west as New Mexico. Other common names include prairie compass plant, pilotweed, polarplant, gum weed, cut-leaf silphium, and turpentine plant. It is a rosinweed of genus Silphium.

Cumberland University is a private university in Lebanon, Tennessee. It was founded in 1842. The campus's current historic buildings were constructed between 1892 and 1896.
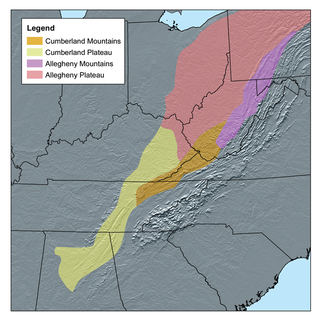
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms "Allegheny Plateau" and the "Cumberland Plateau" both refer to the dissected plateau lands lying west of the main Appalachian Mountains. The terms stem from historical usage rather than geological difference, so there is no strict dividing line between the two. Two major rivers share the names of the plateaus, with the Allegheny River rising in the Allegheny Plateau and the Cumberland River rising in the Cumberland Plateau in Harlan County, Kentucky.

The Cumberland Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern section of the Appalachian Mountains. They are located in western Virginia, southwestern West Virginia, the eastern edges of Kentucky, and eastern middle Tennessee, including the Crab Orchard Mountains. Their highest peak, with an elevation of 4,223 feet (1,287 m) above mean sea level, is High Knob, which is located near Norton, Virginia.

Silphium asteriscus, commonly called starry rosinweed, is an herbaceous plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the eastern United States, from Oklahoma and Texas east to Florida and Pennsylvania. It is a widespread species found in a variety of open habitats, such as prairies and woodlands.

Silphium perfoliatum, the cup plant or cup-plant, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, native to eastern and central North America. It is an erect herbaceous perennial with triangular toothed leaves, and daisy-like yellow composite flower heads in summer.

Silphium integrifolium is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. Its common names include rosinweed, whole-leaf rosinweed, entire-leaf rosinweed, prairie rosinweed, and silflower. It is native to eastern North America, including Ontario in Canada and the eastern and central United States as far west as New Mexico.

Tebenna silphiella, the rosinweed moth, is a moth of the family Choreutidae. It is known from the central part of the United States, including Wisconsin, Illinois and Colorado. The habitat consists of prairies and meadows.

Silphium pinnatifidum, the tansy rosinweed or cutleaf prairie dock, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the Southeastern United States where it is found in Alabama, Georgia, Kentucky, and Tennessee. Its habitat is prairies, barrens, and cedar glades.

Silphium mohrii, known by the common names Mohr's rosinweed and shaggy rosinweed, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the Southeastern United States, where it is native only to northern Alabama, southern Tennessee, and extreme northwest Georgia. It is native to prairie remnants and rocky limestone openings. Because of its restricted range and severely declined habitat, it is considered a vulnerable species.

Silphium terebinthinaceum is a member of the Asteraceae, a family that includes sunflowers, commonly referred to as prairie dock or prairie rosinweed. "Rosinweed" became one of the plant's common names due to the fact that upon injury, resin flows from the wound, giving the plant a sweet smell. Tea brewed from the roots of the prairie dock have a variety of medical applications in Native American culture. The smoke from this plant has also been used as a treatment for congestion and rheumatism.

Silphium trifoliatum, commonly known as whorled rosinweed, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the eastern United States, where it is found east of the Mississippi River. Its natural habitat is open, grassy areas such as prairies, river cobble bars, and roadsides. It is a tall perennial that produces heads of yellow flowers in mid-summer through fall.

Silphium albiflorum, commonly known as white rosinweed, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the United States, where it is endemic to the state of Texas. Its natural habitat is in open, calcareous prairies.

Silphium radula, commonly known as roughstem rosinweed, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native North America, where it is found in the South Central region of the United States. Its natural habitat is prairies over sandy or calcareous soil.
Silphium wasiotense, commonly called Appalachian rosinweed, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native eastern to North America, where it is endemic to the Cumberland Plateau of Kentucky and Tennessee. Its natural habitat is in dry open woodlands. It is considered rare throughout its range.
Silphium compositum, the kidney-leaf rosinweed, is a flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. A perennial in the Silphium genus, it has yellow flowers and is deciduous. It grows in the southeastern United States. It has divided basal leaves.
Silphium is an unidentified plant recorded in classical antiquity, believed extinct.
Silphium perplexum is a prairie species in the family Asteraceae, it is endemic to the state of Alabama. S. perplexum is commonly known as Old Cahaba rosinweed, a reference to the Cahaba River near which all populations of this species are found.















