An eating disorder is a mental disorder defined by abnormal eating behaviors that negatively affect a person's physical or mental health. Types of eating disorders include binge eating disorder, where the patient eats a large amount in a short period of time; anorexia nervosa, where the person has an intense fear of gaining weight and restricts food or overexercises to manage this fear; bulimia nervosa, where individuals eat a large quantity (binging) then try to rid themselves of the food (purging); pica, where the patient eats non-food items; rumination syndrome, where the patient regurgitates undigested or minimally digested food; avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), where people have a reduced or selective food intake due to some psychological reasons; and a group of other specified feeding or eating disorders. Anxiety disorders, depression and substance abuse are common among people with eating disorders. These disorders do not include obesity. People often experience comorbidity between an eating disorder and OCD. It is estimated 20-60% of patients with an ED have a history of OCD.

Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging or fasting, and excessive concern with body shape and weight. This activity aims to expel the body of calories eaten from the binging phase of the process. Binge eating refers to eating a large amount of food in a short amount of time. Purging refers to the attempts to get rid of the food consumed. This may be done by vomiting or taking laxatives.
Orthorexia nervosa (ON) is a proposed eating disorder characterized by an excessive preoccupation with eating healthy food. The term was introduced in 1997 by American physician Steven Bratman, M.D. He suggested that some people's dietary restrictions intended to promote health may paradoxically lead to unhealthy consequences, such as social isolation; anxiety; loss of ability to eat in a natural, intuitive manner; reduced interest in the full range of other healthy human activities; and, in rare cases, severe malnutrition or even death.
Appetite is the desire to eat food items, usually due to hunger. Appealing foods can stimulate appetite even when hunger is absent, although appetite can be greatly reduced by satiety. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to regulate adequate energy intake to maintain metabolic needs. It is regulated by a close interplay between the digestive tract, adipose tissue and the brain. Appetite has a relationship with every individual's behavior. Appetitive behaviour also known as approach behaviour, and consummatory behaviour, are the only processes that involve energy intake, whereas all other behaviours affect the release of energy. When stressed, appetite levels may increase and result in an increase of food intake. Decreased desire to eat is termed anorexia, while polyphagia is increased eating. Dysregulation of appetite contributes to anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, cachexia, overeating, and binge eating disorder.

Butthole Surfers is an American rock band formed in San Antonio, Texas, by singer Gibby Haynes and guitarist Paul Leary in 1981. The band has had numerous personnel changes, but its core lineup of Haynes, Leary, and drummer King Coffey has been consistent since 1983. Teresa Nervosa served as second drummer from 1983 to 1985, 1986 to 1989, and 2009. The band has also employed a variety of bass players, most notably Jeff Pinkus.
Binge eating disorder (BED) is an eating disorder characterized by frequent and recurrent binge eating episodes with associated negative psychological and social problems, but without the compensatory behaviors common to bulimia nervosa, OSFED, or the binge-purge subtype of anorexia nervosa.
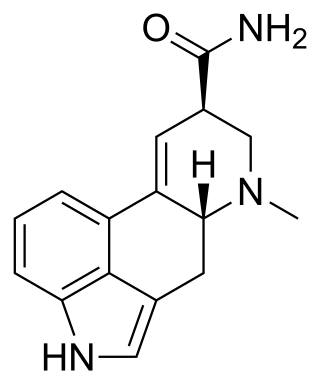
Ergine, also known as d-lysergic acid amide (LSA) and d-lysergamide, is an ergoline alkaloid that occurs in various species of vines of the Convolvulaceae and some species of fungi. The psychedelic properties in the seeds of ololiuhqui, Hawaiian baby woodrose and morning glories have been linked to ergine and/or isoergine, its epimer, as it is an alkaloid present in the seeds.

Argyreia nervosa is a perennial climbing vine native to the Indian subcontinent and introduced to numerous areas worldwide, including Hawaii, Africa, and the Caribbean. Though it can be invasive, it is often prized for its aesthetic and medicinal value. Common names include Hawaiian baby woodrose, adhoguda अधोगुडा or vidhara विधारा (Sanskrit), elephant creeper and woolly morning glory. Its seeds are known for their powerful entheogenic properties, greater or similar to those of Ipomoea species, with users reporting significant psychedelic and spiritual experiences. The two botanical varieties are A. n. var. nervosa described here, and A. n. var. speciosa, which are used in Ayurvedic medicine for their medicinal value.
Salvador Minuchin was a family therapist born and raised in San Salvador, Entre Ríos, Argentina. He developed structural family therapy, which addresses problems within a family by charting the relationships between family members, or between subsets of family. These charts represent power dynamics as well as the boundaries between different subsystems. The therapist tries to disrupt dysfunctional relationships within the family, and cause them to settle back into a healthier pattern.

Delta Phi Epsilon is an international sorority founded on March 17, 1917 at New York University Law School in Manhattan. It is one of 26 social sororities that form the National Panhellenic Conference. It has 110 active chapters, three of which are located in Canada, making the sorority an international organization.
The National Association of Anorexia Nervosa and Associated Disorders (ANAD) is the oldest organization aimed at fighting eating disorders in the United States. ANAD assists people struggling with eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa and also provides resources for families, schools and the eating disorder community. Headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, ANAD is a non-profit organization working in the areas of support, awareness, advocacy, referral, education, and prevention.

The gorse tip moth is a smallish moth species of the family Depressariidae.

Simyra is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae. The genus was described by Ochsenheimer in 1816.

Simyra albovenosa, the reed dagger, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in most of Europe, then Turkey, Iran, Transcaucasus and into the east Palearctic.

Acronicta insularis, the cattail caterpillar or Henry's marsh moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1868. It is found from coast to coast throughout the United States and southern Canada.

Anorexia nervosa (AN), often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by low weight, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. Anorexia is a term of Greek origin: an- (ἀν-, prefix denoting negation) and orexis (ὄρεξις, "appetite"), translating literally to "a loss of appetite"; the adjective nervosa indicating the functional and non-organic nature of the disorder. Anorexia nervosa was coined by Gull in 1873 but, despite literal translation, the feeling of hunger is frequently present and the pathological control of this instinct is a source of satisfaction for the patients.
Tell Kazel is an oval-shaped tell that measures 350 m × 325 m at its base, narrowing to 200 m × 200 m at its top. It is located in the Safita district of the Tartus Governorate in Syria in the north of the Akkar plain on the north of the al-Abrash river approximately 18 km (11 mi) south of Tartus.

Triphysa nervosa is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It is found in northern Transuralia, the mountains of southern Siberia, eastern Siberia, Amurland, the Russian Far East, Korea, northern and north-eastern China and Mongolia.
Simyra confusa is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Francis Walker in 1856. It is found in Sri Lanka.
Body image disturbance (BID) is a common symptom in patients with eating disorders and is characterized by an altered perception of one's own body.











