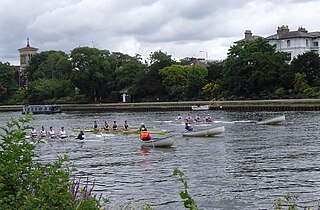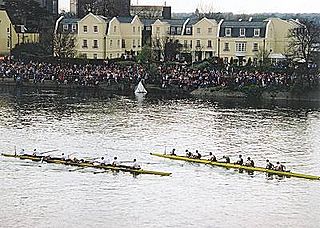Rowing, sometimes called crew in the United States, is the sport of racing boats using oars. It differs from paddling sports in that rowing oars are attached to the boat using oarlocks, while paddles are not connected to the boat. Rowing is divided into two disciplines: sculling and sweep rowing. In sculling, each rower holds two oars, one in each hand, while in sweep rowing each rower holds one oar with both hands. There are several boat classes in which athletes may compete, ranging from single sculls, occupied by one person, to shells with eight rowers and a coxswain, called eights. There are a wide variety of course types and formats of racing, but most elite and championship level racing is conducted on calm water courses 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) long with several lanes marked using buoys.

Sculling is the use of oars to propel a boat by moving them through the water on both sides of the craft, or moving one oar over the stern. A long, narrow boat with sliding seats, rigged with two oars per rower may be referred to as a scull, its oars may be referred to as sculls and a person rowing it referred to as sculler.

Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically attached to the boat, and the rower drives the oar like a lever, exerting force in the same direction as the boat's travel; while paddles are completely hand-held and have no attachment to the boat, and are driven like a cantilever, exerting force opposite to the intended direction of the boat.

In watercraft, a racing shell is an extremely narrow, and often comparatively long, rowing boat specifically designed for racing or exercise. It is equipped with long oars, outriggers to hold the oarlocks away from the boat, and sliding seats. The boat's long length and semicircular cross-section reduce drag to a minimum. This makes the boat both fast and unstable. It must be balanced by the rowers to avoid tipping. Being able to balance – or "set" – the boat while putting maximum effort into the oars is therefore an essential skill of sport rowing.
In competitive rowing, the following specialized terms are important in the corresponding aspects of the sport:

Coastal and offshore rowing is a rowing sport performed at sea. In North America, this sport is often called open water rowing.

In rowing, oars are used to propel the boat. Oars differ from paddles in that they use a fixed or sliding fulcrum, an oarlock or rowlock attached to the side of the boat, to transfer power from the handle to the blade, rather than using the athlete's shoulders or hands as the pivot-point as in canoeing and kayaking.

A coxless pair, abbreviated as a 2- and also known as a straight pair, is a racing shell used in the sport of competitive rowing. It is designed for two rowers, who propel the boat with sweep oars.

Skiffing refers to the sporting and leisure activity of rowing a Thames skiff. The skiff is a traditional hand built clinker-built wooden craft of a design which has been seen on the River Thames and other waterways in England and other countries since the 19th century. Sculling is the act of propelling the boat with a pair of oars, as opposed to rowing which requires both hands on a single oar.
The Thames is one of the main rowing rivers in Europe. Several annual competitions are held along its course, including the Henley Royal Regatta, The Boat Race and other long-distance events, called Head of the River races (Heads).

A double scull, also abbreviated as a 2x, is a rowing boat used in the sport of competitive rowing. It is designed for two persons who propel the boat by sculling with two oars each, one in each hand.

A quadruple sculling boat, often simply called a quad and abbreviated as a 4x, is a racing shell used in the sport of competitive rowing. It is designed for four people who propel the boat by sculling with two oars, or "sculls", one in each hand.
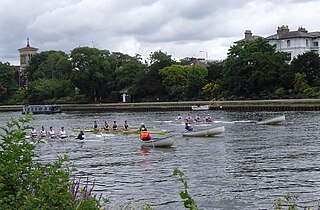
A coxed four, abbreviated as a 4+, is a racing shell used in the sport of competitive rowing. It is designed for four persons who propel the boat with sweep oars and is steered by a coxswain.

A coxless four, abbreviated as a 4- and also called a straight four, is a racing shell used in the sport of competitive rowing. It is designed for four persons who propel the boat with sweep oars, without a coxswain.

A coxed pair, abbreviated as a 2+, is a racing shell used in the sport of competitive rowing. It is designed for two persons who propel the boat with sweep oars and is steered by a coxswain (cox).
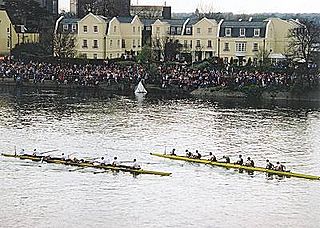
An eight, abbreviated as an 8+, is a racing shell used in competitive rowing (crew). It is designed for eight rowers, who propel the boat with sweep oars, and is steered by a coxswain, or "cox".

Sweep rowing is one of two disciplines of the sport of rowing. In sweep rowing each rower has one oar, usually held with both hands. As each rower has only one oar, the rowers have to be paired so that there are equal numbers of oars on each side of the boat. In the United Kingdom, rowing generally refers to sweep rowing only. The term pulling was also used historically. In the other rowing discipline, sculling, each rower holds two oars, one in each hand.

An octuple sculling shell, often simply called an oct and abbreviated as an 8x or 8x+, is a racing shell used in the sport of rowing.

Human-powered watercraft are watercraft propelled only by human power, instead of being propelled by wind power or an engine.

Stern sculling is the use of a single oar over the stern of a boat to propel it with side-to-side motions that create forward lift in the water. The strict terminology of propulsion by oar is complex and contradictory, and varies by context. Stern sculling may also simply be referred to as "sculling", most commonly so in a maritime situation. In fresh water, and particularly in sport rowing, sculling is use of two oars on either side of the boat by each person, in contrast to sweep rowing, whereby each boat crew member employs a single oar, complemented by another crew member working on the opposite side with their oar.