Aquaculture, also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants. Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water, and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Aquaculture is also a practice used for restoring and rehabilitating marine and freshwater ecosystems. Mariculture, commonly known as marine farming, is aquaculture in seawater habitats and lagoons, as opposed to freshwater aquaculture. Pisciculture is a type of aquaculture that consists of fish farming to obtain fish products as food.

Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place. Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies and the oceans. About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem, causing declines in some populations.

Whiteleg shrimp, also known as Pacific white shrimp or King prawn, is a species of prawn of the eastern Pacific Ocean commonly caught or farmed for food.

The black carp or Chinese black roach is a species of cyprinid freshwater fish and the sole extant species of the genus Mylopharyngodon. It is native to lakes and rivers in East Asia, ranging from the Amur Basin across China to Vietnam. One of the largest cyprinids in the world, the black carp has a typical length of 60–120 cm (23.5–47 in), though it can reach up to 1.9 m in length and 109 kg (240 lb) in weight. It is carnivorous and generally feeds on invertebrates such as snails, clams and mussels.

Procambarus clarkii, known variously as the red swamp crayfish, Louisiana crawfish or mudbug, is a species of cambarid crayfish native to freshwater bodies of northern Mexico, and southern and southeastern United States, but also introduced elsewhere, where it is often an invasive pest.

Ark clam is the common name for a family of small to large-sized saltwater clams or marine bivalve molluscs in the family Arcidae. Generally less than 80 mm long, ark clams vary both in shape and size. They number about 200 species worldwide.

Fishing in India is a major sector within the economy of India contributing 1.07% of its total GDP. The fishing sector in India supports the livelihood of over 28 million people in the country, especially within the marginalized and vulnerable communities. India is the third largest fish producing country in the world accounting for 7.96% of the global production and second largest producer of fish through aquaculture, after China. The total fish production during the FY 2020-21 is estimated at 14.73 million metric tonnes. According to the National Fisheries Development Board the Fisheries Industry generates an export earnings of Rs 334.41 billion. Centrally sponsored schemes will increase exports by Rs 1 lakh crore in FY25. 65,000 fishermen have been trained under these schemes from 2017 to 2020. Freshwater fishing consists of 55% of total fish production.

The global commercial production for human use of fish and other aquatic organisms occurs in two ways: they are either captured wild by commercial fishing or they are cultivated and harvested using aquacultural and farming techniques.

Crab fisheries are fisheries which capture or farm crabs. True crabs make up 20% of all crustaceans caught and farmed worldwide, with about 1.4 million tonnes being consumed annually. The horse crab, Portunus trituberculatus, accounts for one quarter of that total. Other important species include flower crabs, snow crabs (Chionoecetes), blue crabs, edible or brown crabs, Dungeness crab, and mud crabs, each of which provides more than 20,000 tonnes annually.

Tegillarca granosa is a species of ark clam known as the blood cockle or blood clam due to the red haemoglobin liquid inside the soft tissues. It is found throughout the Indo-Pacific region from the eastern coast of South Africa northwards and eastwards to Southeast Asia, Australia, Polynesia, and up to northern Japan. It lives mainly in the intertidal zone at one to two metres water depth, burrowed down into sand or mud. Adult size is about 5 to 6 cm long and 4 to 5 cm wide.
Aquaculture in the Marshall Islands is governed by the Marshall Islands Marine Resources Authority. A hatchery for giant clams has been established by the national government in Likiep Atoll, and at least one other clam farm is in operation in Mili Atoll. At the CSD-16 Partnerships Fair in 2008, Erik Hagberg suggested that Holothuroidea cultivation is a viable option for developing aquaculture in the country.

China, with one-fifth of the world's population, accounts for two-thirds of the world's reported aquaculture production.
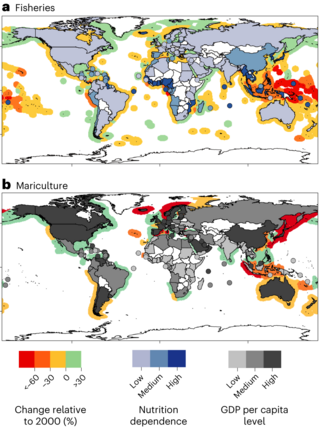
Fisheries are affected by climate change in many ways: marine aquatic ecosystems are being affected by rising ocean temperatures, ocean acidification and ocean deoxygenation, while freshwater ecosystems are being impacted by changes in water temperature, water flow, and fish habitat loss. These effects vary in the context of each fishery. Climate change is modifying fish distributions and the productivity of marine and freshwater species. Climate change is expected to lead to significant changes in the availability and trade of fish products. The geopolitical and economic consequences will be significant, especially for the countries most dependent on the sector. The biggest decreases in maximum catch potential can be expected in the tropics, mostly in the South Pacific regions.
Organic aquaculture is a holistic method for farming fish and other marine species in line with organic principles. The ideals of this practice established sustainable marine environments with consideration for naturally occurring ecosystems, use of pesticides, and the treatment of aquatic life. Managing aquaculture organically has become more popular since consumers are concerned about the harmful impacts of aquaculture on themselves and the environment.

Shuitou is a town of Nan'an City, in southern Fujian province, China.
The Araucanian herring is a species of fish in the family Clupeidae. It is an epipelagic fish, silvery below and dark blue above, which schools in coastal waters off the west coast of South America. It ranges along the Chilean coast from Valparaiso south to Talcahuano. It schools at depths from 0 to 70 meters in nearshore areas.

Geoduck aquaculture or geoduck farming is the practice of cultivating geoducks for human consumption. The geoduck is a large edible saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusk, that is native to the Pacific Northwest.

The Shijing River is a small river in the Fujian Province of China. The tidal estuary it forms when entering the Weitou Bay of the Taiwan Strait is known as the Anhai Bay. Most of the Shijing River's basin is within the prefecture-level city of Quanzhou.

Novaculina chinensis is a species of fresh water razor clam in the family Pharidae.

















