
Loranthaceae, commonly known as the showy mistletoes, is a family of flowering plants. It consists of about 75 genera and 1,000 species of woody plants, many of them hemiparasites. The three terrestrial species are Nuytsia floribunda, Atkinsonia ligustrina, and Gaiadendron punctatum Loranthaceae are primarily xylem parasites, but their haustoria may sometimes tap the phloem, while Tristerix aphyllus is almost holoparasitic. For a more complete description of the Australian Loranthaceae, see Flora of Australia online., for the Malesian Loranthaceae see Flora of Malesia.

The Santalaceae, sandalwoods, are a widely distributed family of flowering plants which, like other members of Santalales, are partially parasitic on other plants. Its flowers are bisexual or, by abortion, unisexual. Modern treatments of the Santalaceae include the family Viscaceae (mistletoes), previously considered distinct.

Nepenthes mollis, or the velvet pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant species natives to Kalimantan, Borneo. It used to be known only from a single dried herbarium specimen and is the sole recognised species in the genus Nepenthes of which the pitchers are unknown. In 2019 Global Wildlife Conservation announced the rediscovery of the species.
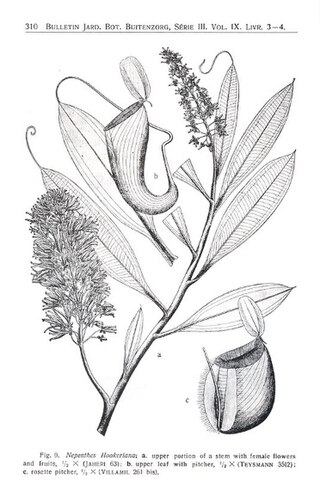
"The Nepenthaceae of the Netherlands Indies" is a seminal monograph by B. H. Danser on the tropical pitcher plants of the Dutch East Indies and surrounding regions. It was originally published in the Bulletin du Jardin Botanique de Buitenzorg in 1928, and reprinted by Natural History Publications (Borneo) in 2006.

Tapinanthus is a genus of mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, native to Africa. The name of the genus is derived from the Greek tapeinos meaning "low" or "humble" and anthos meaning flower.

Amyema is a genus of semi-parasitic shrubs (mistletoes) which occur in Malesia and Australia.

Dendrophthoe is a genus of hemiparasitic shrubs found in Asia and Australia known as mistletoes. The genus was described by German naturalist Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius in 1830. Species in this genus have a variety of reported uses in the medical traditions of the region, most notably in Nepal.

Macrosolen is a genus of plants in the family Loranthaceae. It includes about 83 species all over the world with ca. 40 species widely distributed in tropical South and Southeast Asia. Some species were described by de Loureiro, Lecomte, Danser (1938) and Hô (2003).

Macrosolen parasiticus is a species of parasitic shrub in the family Loranthaceae. It is commonly called parasite honeysuckle. It is widely distributed in tropical South and South West Indian regions especially in the Western Ghats. Macrosolen parasiticus species were described by Danser (1938).

Amyema nestor is a species of epiphytic hemiparasitic plant in the family Loranthaceae. It is native to Western Australia, and found growing only on acacias.
Thaumasianthes is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae.
Dendromyza is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Santalaceae. They are dioecious stem-parasitic shrubs.
Erianthemum is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae.
Elytranthe is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae.
Lepeostegeres is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae.

Plicosepalus is a genus of hemiparasitic flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae.
Globimetula is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae.
Distrianthes is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae.
Lepidaria is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae.

Cyne is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae.











