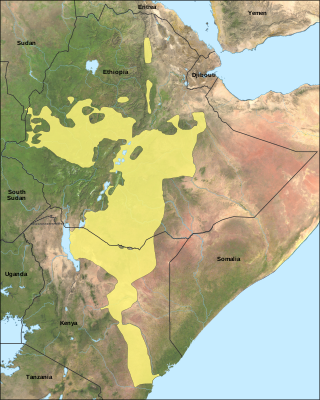
Oromo, historically also called Galla, is an Afroasiatic language that belongs to the Cushitic branch. It is native to the Ethiopian state of Oromia and Northern Kenya and is spoken predominantly by the Oromo people and neighboring ethnic groups in the Horn of Africa. It is used as a lingua franca particularly in the Oromia Region and northeastern Kenya.
Hurrian is an extinct Hurro-Urartian language spoken by the Hurrians (Khurrites), a people who entered northern Mesopotamia around 2300 BC and had mostly vanished by 1000 BC. Hurrian was the language of the Mitanni kingdom in northern Mesopotamia and was likely spoken at least initially in Hurrian settlements in modern-day Syria.
This article describes the grammar of Afrikaans, a language spoken in South Africa and Namibia which originated from 17th century Dutch.

Mount Moroto, also Moroto Mountain, is a mountain in the Northeastern part of Uganda.
Yakkha is a language spoken in parts of Nepal, Darjeeling district and Sikkim. The Yakkha-speaking villages are located to the East of the Arun river, in the southern part of the Sankhuwasabha district and in the northern part of the Dhankuta district of Nepal. About 14,000 people still speak the language, out of 17,003 ethnic Yakkha in Nepal. Genealogically, Yakkha belongs to the Eastern Kiranti languages and is in one subgroup with several Limbu languages, e.g. Belhare, Athpare, Chintang and Chulung. Ethnically however, the Yakkha people perceive themselves as distinct from the other Kiranti groups such as Limbu.

Hindustani, the lingua franca of Northern India and Pakistan, has two standardised registers: Hindi and Urdu. Grammatical differences between the two standards are minor but each uses its own script: Hindi uses Devanagari while Urdu uses an extended form of the Perso-Arabic script, typically in the Nastaʿlīq style.
Apma is the language of central Pentecost island in Vanuatu. Apma is an Oceanic language. Within Vanuatu it sits between North Vanuatu and Central Vanuatu languages, and combines features of both groups.
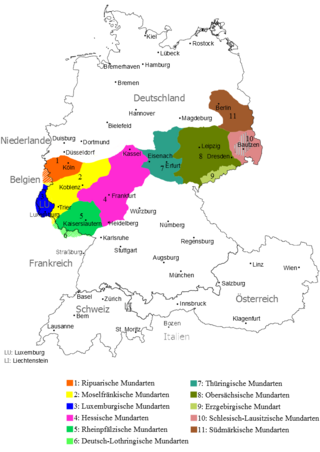
Erzgebirgisch is a (East) Central German dialect, spoken mainly in the central Ore Mountains in Saxony. It has received relatively little academic attention. Due to the high mobility of the population and the resulting contact with Upper Saxon, the high emigration rate and its low mutual intelligibility with other dialects, the number of speakers is decreasing.
The verb is one of the most complex parts of Basque grammar. It is sometimes represented as a difficult challenge for learners of the language, and many Basque grammars devote most of their pages to lists or tables of verb paradigms. This article does not give a full list of verb forms; its purpose is to explain the nature and structure of the system.
Dirasha is a member of the Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic family. It is spoken in the Omo region of Ethiopia, in the hills west of Lake Chamo, around the town of Gidole.
Nambikwara is an indigenous language spoken by the Nambikwara, who reside on federal reserves covering approximately 50,000 square kilometres of land in Mato Grosso and neighbouring parts of Rondonia in Brazil. Due to the fact that the Nambikwara language has such a high proportion of speakers, and the fact that the community has a positive attitude towards the language, it is not considered to be endangered despite the fact that its speakers constitute a small minority of the Brazilian population. For these reasons, UNESCO instead classifies Nambikwara as vulnerable.
Standard Kannada grammar is primarily based on Keshiraja's Shabdamanidarpana which provides the fullest systematic exposition of Kannada language. The earlier grammatical works include portions of Kavirajamarga of 9th century, Kavyavalokana and Karnatakabhashabhushana both authored by Nagavarma II in first half of the 12th century.
This article deals with the grammar of the Udmurt language.

Yolmo (Hyolmo) or Helambu Sherpa, is a Tibeto-Burman language of the Hyolmo people of Nepal. Yolmo is spoken predominantly in the Helambu and Melamchi valleys in northern Nuwakot District and northwestern Sindhupalchowk District. Dialects are also spoken by smaller populations in Lamjung District and Ilam District and also in Ramecchap District. It is very similar to Kyirong Tibetan and less similar to Standard Tibetan and Sherpa. There are approximately 10,000 Yolmo speakers, although some dialects have larger populations than others.
The Kadam people inhabit Mount Kadam in Nakapiripirit District in the Karamoja sub-region, located in north-eastern Uganda.

The Yukulta language, also spelt Yugulda, Yokula, Yukala, Jugula, and Jakula, and also known as Ganggalidda, is an extinct Tangkic language spoken in Queensland and Northern Territory, Australia. It was spoken by the Yukulta people, whose traditional lands lie on the southern coast of the Gulf of Carpentaria.
Zotung (Zobya) is a language spoken by the Zotung people, in Rezua Township, Chin State, Burma. It is a continuum of closely related dialects and accents. The language does not have a standard written form since it has dialects with multiple variations on its pronunciations. Instead, Zotung speakers use a widely accepted alphabet for writing with which they spell using their respective dialect. However, formal documents are written using the Lungngo dialect because it was the tongue of the first person to prescribe a standard writing, Sir Siabawi Khuamin.
Turkmen grammar is the grammar of the Turkmen language, whose dialectal variants are spoken in Turkmenistan, Iran, Afghanistan, Russia, China, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and others. Turkmen grammar, as described in this article, is the grammar of standard Turkmen as spoken and written by Turkmen people in Turkmenistan.
Ubykh was a polysynthetic language with a high degree of agglutination that had an ergative-absolutive alignment.

So (Tepeth) are a tribe living in the mountain ranges of mountain Moroto in the northeast part of Uganda and North western Kenya in the Turkana region. Traditionally, the So (Tepeth) were hunters and fruit gatherers, the decline in wild animals in the region made them resort to agriculture for sustainable living between 1970 and 1980. Tepeth are believed as original occupants of Karamoja plains unfortunately the current settlers (Karamojong people) pushed the Tepeth up on the mountain.







