
The swamp eels are a family (Synbranchidae) of freshwater eel-like fishes of the tropics and subtropics. Most species are able to breathe air and typically live in marshes, ponds and damp places, sometimes burying themselves in the mud if the water source dries up. They have various adaptations to suit this lifestyle; they are long and slender, they lack pectoral and pelvic fins, and their dorsal and anal fins are vestigial, making them limbless vertebrates. They lack scales and a swimbladder, and their gills open on the throat in a slit or pore. Oxygen can be absorbed through the lining of the mouth and pharynx, which is rich in blood vessels and acts as a "lung".

The Lumbricidae are a family of earthworms. About 33 lumbricid species have become naturalized around the world, but the bulk of the species are in the Holarctic region: from Canada and the United States and throughout Eurasia to Japan. An enigmatic species in Tasmania is Eophila eti. Currently, 670 valid species and subspecies in about 42 genera are recognized. This family includes the majority of earthworm species well known to Europeans.

Oligochaeta is a subclass of animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthworms, and freshwater or semiterrestrial microdrile forms, including the tubificids, pot worms and ice worms (Enchytraeidae), blackworms (Lumbriculidae) and several interstitial marine worms.

Belize is a country with a rich variety of wildlife, due to its unique position between North and South America, and a wide range of climates and habitats for plant and animal life. Belize's low human population, and approximately 8,867 square miles (22,970 km2) of undistributed land, provides an ideal home for more than 5000 species of plants, and vast numbers species of animals — with several hundred vertebrates including armadillos, snakes, and monkeys.

The Megascolecidae is a taxonomic family of earthworms which is native to Madagascar, Australia, New Zealand and both South East Asia and North America. All species of Megascolecidae belong to the Clitellata class. Megascolecidae are a large family of earthworms and they can grow up to 2 meters in length. The intercontinental distribution of Megascolecidae helps in favouring the Continental Drift theory.
The giant Gippsland earthworm, Megascolides australis, is one of Australia's 1,000 native earthworm species.

The Haplotaxida are one of two orders within the annelid subclass Oligochaeta, the other being the Lumbriculida. No real common name exists, but they are simply referred to as haplotaxids.

Sternotherus is a genus of turtles in the family Kinosternidae including six species commonly known as musk turtles. The genus is endemic to North America, occurring in the eastern third of the USA and southeast Ontario, Canada. Musk glands positioned near the bridge of the shell can produce foul smelling secretions when the turtles are threatened, although gentle handling does not normally provoke a response. Sternotherus are moderately small turtles, with the largest species in the genus, the razor-backed musk turtle, attaining a maximum of 17.6 cm. in shell length. The carapace is characteristically oval and domed, with most species having one or three keels on the back which may become smoother and obscure with age in some species. Musk turtles are generally drab in color, mostly black, gray, brown, olive, or ocher, which aid in camouflaging them in their natural habitats. The head is relatively large and stout, marked with spots, streaks, or strips. The plastron has only 10 or 11 scutes, as opposed to 12, a more common condition in North American turtles. The tail is short, with males having a horny claw like tip.
The Eudrilidae are a family of earthworms, mostly of Africa. One species, Eudrilus eugeniae, is widely distributed around the warmer parts of the world and historically cultured as the "African nightcrawler".
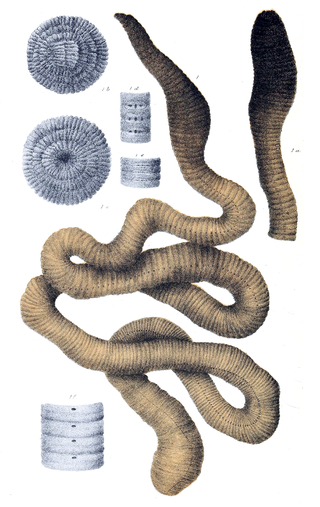
The animal family Almidae includes about six genera of segmented worms.

The yellow mud turtle, also commonly known as the yellow-necked mud turtle, is a species of mud turtle in the family Kinosternidae. The species is endemic to the Central United States and Mexico.

The mud salamander, is a bright red salamander of the family Plethodontidae. It is found in streams, seeps and swamps and underneath logs, rocks and leaves. It is endemic to the eastern half of the United States with one isolated population in central Mississippi. Mud salamanders have short stocky bodies ranging from 7.5 to 16 cm long. Body color ranges with age and locality with coastal mud salamanders being more dark and drab whilst inland mud salamanders are brighter and have more contrast against the black polka dots that sporadically pattern their bodies. In the earlier years of a mud salamanders life, they tend to have crimson colored body and unspotted stomachs, as they age the salamander becomes a dark red almost purple color and acquires a spotted stomach. mud salamanders have 16 to 17 costal grooves found along the sides of the salamanders body. These salamanders are ectothermic meaning that they cannot control their body temperature and it fluctuates with the temperature. The mud salamander is readily confused with two other species, the red salamander and the spring salamander. It can be distinguished from the Red salamander by having golden pupils and a shorter snout, and can be distinguished from the spring salamander by having a shorter body length and missing the nasal ridge associated with this species. There are four subspecies in the mud salamander complex, these are the Gulf Coast mud salamander, rusty mud salamander, Midland mud salamander and the eastern mud salamander.

The red salamander is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae endemic to the eastern United States. Its skin is orange/red with random black spots. Its habitats are temperate forests, small creeks, ponds, forests, temperate shrubland, rivers, intermittent rivers, freshwater, trees springs. Overall this species is common and widespread, but locally it has declined because of habitat loss and it is considered threatened in Indiana. Red salamanders eat insects, earthworms, spiders, small crustaceans, snails and smaller salamanders. The red salamander, as a member of the family Plethodontidae, lacks lungs and respires through its skin.

Pheretima is a genus of earthworms found mostly in New Guinea and parts of Southeast Asia.

The family Criodrilidae is represented by genus Criodrilus comprising limicolous (mud-dwelling) and/or aquatic earthworms endemic to the Palaearctic currently known only from Europe and Japan, respectively. Only three or four species are described, and the type, Criodrilus lacuum, has been introduced into North and South Americas, and is found rarely in plant pots or paddy fields.

An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. They occur worldwide where soil, water, and temperature allow.

Invasive species of earthworms from the suborder Lumbricina have been expanding their range in North America. Their introduction can have marked effects on the nutrient cycles in temperate forests. These earthworms increase the cycling and leaching of nutrients by breaking up decaying organic matter and spreading it into the soil. Since plants native to these northern forests are evolutionarily adapted to the presence of thick layers of decaying organic matter, the introduction of worms can lead to loss of biodiversity as young plants face less nutrient-rich conditions. Some species of trees and other plants may be incapable of surviving such changes in available nutrients. This change in the plant diversity in turn affects other organisms and often leads to increased invasions of other exotic species as well as overall forest decline. They do not require a mate to reproduce, allowing them to spread faster.
Microchaetus rappi, the African giant earthworm, is a large earthworm in the Microchaetidae family, the largest of the segmented worms. It averages about 1.4 m (4.5 ft) in length, but can reach a length of as much as 6.7 m (22 ft) and can weigh over 1.5 kg (3.3 lb).
Diplocardia longa is a species of earthworm native to North America. It was first described by the American zoologist John Percy Moore in 1904. The type locality is Hawkinsville, Georgia. This worm has bioluminescent properties; its body fluids and the sticky slime it exudes when stimulated emit a bluish glow.

Amynthas mekongianus, the Mekong worm or Mekong giant earthworm, previously known as Megascolex mekongianus, is a species of earthworm in the family Megascolecidae. It is native to the vicinity of the River Mekong in southeastern Asia and may have more than 500 segments and grow to a length of 2.9 m (10 ft).















