
The United States Department of State (DOS), commonly referred to as the State Department, is the federal executive department that advises the President and conducts international relations. Equivalent to the foreign ministry of other countries, it was established in 1789 as the nation's first executive department. The current Secretary of State is Mike Pompeo, who ascended to the office in April 2018 after Rex Tillerson resigned.
The Hague Convention Abolishing the Requirement of Legalisation for Foreign Public Documents, the Apostille Convention, or the Apostille Treaty, is an international treaty drafted by the Hague Conference on Private International Law. It specifies the modalities through which a document issued in one of the signatory countries can be certified for legal purposes in all the other signatory states. A certification under the terms of the convention is called an apostille or Hague Apostille. It is an international certification comparable to a notarisation in domestic law, and normally supplements a local notarisation of the document. If the convention applies between two countries, such an apostille is sufficient to certify a document's validity, and removes the need for double-certification, by the originating country and then by the receiving country.
The Bureau of Consular Affairs (CA) is a bureau of the U.S. Department of State reporting to the Under Secretary of State for Management. The mission of the Bureau is to administer laws, formulate regulations and implement policies relating to the broad range of consular services and immigration. As of 2017, the bureau is headed by the Assistant Secretary of State for Consular Affairs, Carl Risch.
The Office of the Official Solicitor is a part of the Ministry of Justice of the Government of the United Kingdom. The Official Solicitor acts for people who, because they lack mental capacity and cannot properly manage their own affairs, are unable to represent themselves and no other suitable person or agency is able or willing to act. The Official Solicitor acts for England & Wales only, as Scotland and Northern Ireland have separate legal systems and judiciaries.

The National Center for Missing & Exploited Children (NCMEC) is a private, nonprofit organization established in 1984 by the United States Congress. In September 2013, the United States House of Representatives, United States Senate, and the President of the United States reauthorized the allocation of $40 million in funding for the National Center for Missing & Exploited Children as part of Missing Children's Assistance Reauthorization Act of 2013. The current chair of the organization is child safety advocate Patty Wetterling, mother of Jacob Wetterling.

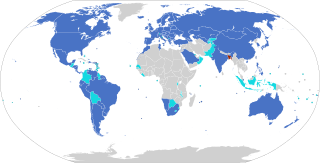
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction or Hague Abduction Convention is a multilateral treaty developed by the Hague Conference on Private International Law (HCCH) that provides an expeditious method to return a child internationally abducted by a parent from one member country to another.

International child abduction in Japan refers to the illegal international abduction or removal of children from their country of habitual residence by an acquaintance or family member to Japan or their retention in Japan in contravention to the law of another country. Most cases involve a Japanese mother taking her children to Japan in defiance of visitation or joint custody orders issued by Western courts. The issue is a growing problem as the number of international marriages increases. Barring exceptional circumstances, the effects of child abduction are generally detrimental to the welfare of children. Parental abduction often has a particularly devastating effect on parents who may never see their children again.
Child laundering is a scheme whereby intercountry adoptions are effected by illegal and fraudulent means. It may involve the trafficking of children, the acquisition of children through monetary arrangements, deceit and/or force. The children may then be held in sham orphanages while formal international adoption processes are used to send the children to adoptive parents in another country.
The Ministry of Women, Family and Human Rights (MMFDH), former Ministry of Human Rights (2016-2018) and Secretariat for Human Rights of the Presidency of the Republic (1997-2015) is an office attached to the Presidency of Brazil. Its purpose is to implement, promote, and protect human rights, civic rights, and the rights of children, adolescents, women, families, the elderly, and the disabled.
Catherine Irene Jacqueline Meyer, Baroness Meyer, CBE is a British life peer and the wife of Sir Christopher Meyer, the former British Ambassador to the United States. She was the founder and chief executive of the charity PACT, now, Action Against Abduction.

Mexico is amongst the world's most popular sources and destinations for international child abduction while also being widely regarded as having one of the least effective systems of protecting and returning internationally abducted children within its borders.
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction, commonly referred to as the Hague Abduction Convention, is a multilateral treaty developed by the Hague Conference on Private International Law. The treaty provides an expeditious method of returning a child taken illegally from one country to another. It was concluded on October 25, 1980

International child abduction in Brazil comprises cases in which the removal of a child by one of the joint holders of custody or non-custodial or contested parents to Brazil in contravention of other laws of other countries and/or the desires of other custody claimants. The phenomenon of international child abduction is defined in international law and legislated on by the Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction, which entered into force in Brazil on January 1, 2000 and aims to trace abducted children, secure their prompt return to the country of habitual residence and organize or secure effective rights of access. In 2010 Brazil was accused by the US State Department of being non-compliant with the Hague Convention.
Abbott v. Abbott, 560 U.S. 1 (2010), was a decision by the Supreme Court of the United States holding that a parent's ne exeat right is a "right to custody" under the Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction and the US International Child Abduction Remedies Act. The child thus should have been returned to Chile, the country of "habitual residence" because the mother violated the ne exeat right of the father when taking the child to the United States without the father's consent.
The Convention of 1961 Concerning the Powers of Authorities and the Law Applicable in Respect of the Protection of Infants, French: Convention du 5 octobre 1961 concernant la compétence des autorités et la loi applicable en matière de protection des mineurs, or Hague Protection of Minors Convention is a multilateral convention of the Hague Conference on Private International Law. The 1961 Convention emphasized the concept of the "interests of the child" as a basis for authorities of the child's nationality to overrule the authorities of the child's habitual residence. It built upon prior efforts to create successful multilateral treaties and brought an innovation in terminology by creating a compromise between advocates of "nationality" as the determining factor for jurisdiction and advocates for the modern fact-centric model of "habitual residence." The convention also included expanded language to encompass both judicial and administrative authorities in response to the Boll case. Of particularly special note, the drafters of the 1961 Convention expressly considered a provision addressing the removal of a child from their habitual residence with an intent to evade rightful jurisdiction—primarily for child custody reasons. This first attempt to codify international child abduction failed due to an inability to agree on a definition or manner of describing the phenomenon, with a number of countries that adhered to the principle of nationality regulating personal child and family law unable to classify their nationals removing children from foreign countries to their home state as illegal.










