Streptococcus equinus is a Gram-positive, nonhemolytic, nonpathogenic, lactic acid bacterium of the genus Streptococcus. It is the principal Streptococcus found in the alimentary canal of a horse, and makes up the majority of the bacterial flora in horse feces. S. equinus is seldom found in humans. Equivalence with Streptococcus bovis has been contested.

Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms.
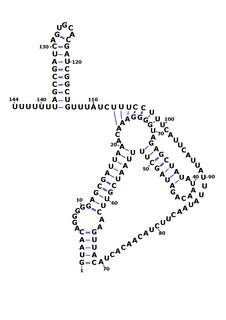
RsaOG is a non-coding RNA that was discovered in the pathogenic bacteria Staphylococcus aureus N315 using a large scale computational screening based on phylogenetic profiling. It was first identified, but not named, in 2005. RsaOG has since been identified in other strains of Staphylococcus aureus under the name of RsaI, it has also been discovered in other members of the Staphylococcus genus but in no other bacteria.
Staphylococcus condimenti is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of single, paired, and clustered cocci. Strains of this species were originally isolated from fermenting soy sauce mash and are positive for catalase, urease, arginine dihydrolase, nitrate reductase, beta-galactosidase, and phosphatase activity.
Staphylococcus vitulinus is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of clustered cocci. The species was originally isolated from food and animals and was named Staphylococcus vitulus. The name was later changed to Staphylococcus vitulinus for correct Latin grammar.
Staphylococcus stepanovicii is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of single, paired, and clustered cocci. The species is novobiocin-resistant and oxidase-positive. It was named in honor of Serbian microbiologist Srdjan Stepanović.
Staphylococcus simiae is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of clustered cocci. This species was originally isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of South American squirrel monkeys, Saimiri sciureus, and found to be genetically similar to S. aureus, but more biochemically similar to S. piscifermentans. A draft genome of S. simiae was sequenced.
Staphylococcus carnosus is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of single and paired cocci. Its genome has the highest GC content - 36.4% - of any sequenced staphylococcal species.
Staphylococcus lentus is a Gram-positive, oxidase-positive, coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of clustered cocci. The species was originally classified as a subspecies; its name is a combination derived from Staphylococcus sciuri subsp. lentus.
Staphylococcus delphini is a Gram-positive, coagulase-positive member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of single, paired, and clustered cocci. Strains of this species were originally isolated from aquarium-raised dolphins suffering from skin lesions.
Staphylococcus equorum is a gram-positive, coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of clustered cocci. Originally isolated from the skin of healthy horses, this species contains a cell wall similar to that of Staphylococcus xylosus.
Staphylococcus massiliensis is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of clustered cocci. Strains of this species were first isolated from a human brain abscess and were found to be most closely related to Staphylococcus piscifermentans, Staphylococcus condimenti, Staphylococcus carnosus subsp. carnosus, Staphylococcus carnosus subsp. utilis, and Staphylococcus simulans. A subsequent study found that S. massiliensis may actually be part of the human skin microbiome and may have been a contaminant of brain abscess-derived samples.
Staphylococcus intermedius is a Gram-positive, catalase positive member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of clustered cocci. Strains of this species were originally isolated from the anterior nares of pigeons, dogs, cats, mink, and horses. Many of the isolated strains show coagulase activity. Clinical tests for detection of methicillin-resistant S. aureus may produce false positives by detecting S. intermedius, as this species shares some phenotypic traits with methicillin-resistant S. aureus strains. It has been theorized that S. intermedius has previously been misidentified as S. aureus in human dog bite wound infections, which is why molecular technologies such as MALDI-TOF and PCR are preferred in modern veterinary clinical microbiology laboratories for their more accurate identifications over biochemical tests. S. intermedius is largely phenotypically indiscriminate from Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and Staphylococcus delphini, and therefore the three organisms are considered to be included in the more general 'Staphylococcus intermedius group'.
Campylobacter lanienae is a species of Campylobacter found in humans and other animals. Like other Campylobacter species, it is rod-shaped, non-glucose-fermenting, oxidase- and catalase-positive, Gram-negative and motile.
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is a gram positive coccus bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus found worldwide. It is primarily a pathogen for domestic animals, but has been known to affect humans as well.S. pseudintermedius is an opportunistic pathogen that secretes immune modulating virulence factors, has many adhesion factors, and the potential to create biofilms, all of which help to determine the pathogenicity of the bacterium. Diagnoses of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius have traditionally been made using cytology, plating, and biochemical tests. More recently, molecular technologies like MALDI-TOF, DNA hybridization and PCR have become preferred over biochemical tests for their more rapid and accurate identifications. This includes the identification and diagnosis of antibiotic resistant strains.
Ligilactobacillus acidipiscis is a species in the genus Ligilactobacillus. It is a homofermentative, rod-shaped lactic acid bacteria. Its type strain is FS60-1T.
Weissella thailandensis is a species of Gram-positive bacteria. It is a homofermentative, sphere-shaped lactic acid bacteria. Its type strain is FS61-1T. Its genome has been sequenced.
Virgibacillus salexigens is a species of Gram-positive bacteria. This species was formerly contained by the genus Salibacillus and before that by Bacillus. Strains of this species were originally isolated from salterns and saline soil samples in Spain. They are spore-forming, slightly aerobic, and moderately halophilic.
Victivallis vadensis is a Gram-negative, coccus-shaped, bacteria found in the human digestive tract. It measures approximately 0.5-1.3 micrometers in diameter, is non-motile and chemoorganotrophic, and does not form spores. Victivallis vadensis is strictly anaerobic, as are 90 percent of the bacteria in the human gastrointestinal system.
Staphylococcus agnetis is a Gram positive, coagulase-variable member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus. Strains of this species were originally isolated from the milk and teats of cows with mastitis. This species is not known to infect humans.


