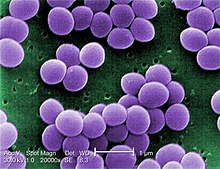
Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although S. aureus usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. S. aureus is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). The bacterium is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine. Despite much research and development, no vaccine for S. aureus has been approved.

Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a group of gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths worldwide attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019.
Bloodstream infections (BSIs) are infections of blood caused by blood-borne pathogens. The detection of microbes in the blood is always abnormal. A bloodstream infection is different from sepsis, which is characterized by severe inflammatory or immune responses of the host organism to pathogens.

Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) are strains of Staphylococcus aureus that have acquired resistance to the glycopeptide antibiotic vancomycin. Bacteria can acquire resistant genes either by random mutation or through the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another. Resistance genes interfere with the normal antibiotic function and allow bacteria to grow in the presence of the antibiotic. Resistance in VRSA is conferred by the plasmid-mediated vanA gene and operon. Although VRSA infections are uncommon, VRSA is often resistant to other types of antibiotics and a potential threat to public health because treatment options are limited. VRSA is resistant to many of the standard drugs used to treat S. aureus infections. Furthermore, resistance can be transferred from one bacterium to another.

Ceftazidime, sold under the brand name Fortaz among others, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. Specifically it is used for joint infections, meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, urinary tract infections, malignant otitis externa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection, and vibrio infection. It is given by injection into a vein, muscle, or eye.

Staphylococcus epidermidis is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. It is part of the normal human microbiota, typically the skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although S. epidermidis is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. S. epidermidis is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, S. epidermidis is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory.

Cefepime is a fourth-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Cefepime has an extended spectrum of activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, with greater activity against both types of organism than third-generation agents. A 2007 meta-analysis suggested when data of trials were combined, mortality was increased in people treated with cefepime compared with other β-lactam antibiotics. In response, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) performed their own meta-analysis which found no mortality difference.

Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. It has found use in biochemical research because of its ability to bind immunoglobulins. It is composed of five homologous Ig-binding domains that fold into a three-helix bundle. Each domain is able to bind proteins from many mammalian species, most notably IgGs. It binds the heavy chain within the Fc region of most immunoglobulins and also within the Fab region in the case of the human VH3 family. Through these interactions in serum, where IgG molecules are bound in the wrong orientation, the bacteria disrupts opsonization and phagocytosis.

Panton–Valentine leukocidin (PVL) is a cytotoxin—one of the β-pore-forming toxins. The presence of PVL is associated with increased virulence of certain strains (isolates) of Staphylococcus aureus. It is present in the majority of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) isolates studied and is the cause of necrotic lesions involving the skin or mucosa, including necrotic hemorrhagic pneumonia. PVL creates pores in the membranes of infected cells. PVL is produced from the genetic material of a bacteriophage that infects Staphylococcus aureus, making it more virulent.

Hemolysins or haemolysins are lipids and proteins that cause lysis of red blood cells by disrupting the cell membrane. Although the lytic activity of some microbe-derived hemolysins on red blood cells may be of great importance for nutrient acquisition, many hemolysins produced by pathogens do not cause significant destruction of red blood cells during infection. However, hemolysins are often capable of lysing red blood cells in vitro.

Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are part of the gut flora present in the digestive tract.

A staphylococcal infection or staph infection is an infection caused by members of the Staphylococcus genus of bacteria.

Bacterial cellular morphologies are the shapes that are characteristic of various types of bacteria and often key to their identification. Their direct examination under a light microscope enables the classification of these bacteria.

Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms.
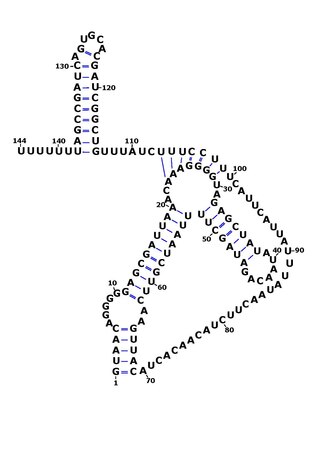
RsaOG is a non-coding RNA that was discovered in the pathogenic bacteria Staphylococcus aureus N315 using a large scale computational screening based on phylogenetic profiling. It was first identified, but not named, in 2005. RsaOG has since been identified in other strains of Staphylococcus aureus under the name of RsaI, it has also been discovered in other members of the Staphylococcus genus but in no other bacteria.
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is a gram positive coccus bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus found worldwide. It is primarily a pathogen for domestic animals, but has been known to affect humans as well. S. pseudintermedius is an opportunistic pathogen that secretes immune modulating virulence factors, has many adhesion factors, and the potential to create biofilms, all of which help to determine the pathogenicity of the bacterium. Diagnoses of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius have traditionally been made using cytology, plating, and biochemical tests. More recently, molecular technologies like MALDI-TOF, DNA hybridization and PCR have become preferred over biochemical tests for their more rapid and accurate identifications. This includes the identification and diagnosis of antibiotic resistant strains.
ESKAPE is an acronym comprising the scientific names of six highly virulent and antibiotic resistant bacterial pathogens including: Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter spp. The acronym is sometimes extended to ESKAPEE to include Escherichia coli. This group of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria can evade or 'escape' commonly used antibiotics due to their increasing multi-drug resistance (MDR). As a result, throughout the world, they are the major cause of life-threatening nosocomial or hospital-acquired infections in immunocompromised and critically ill patients who are most at risk. P. aeruginosa and S. aureus are some of the most ubiquitous pathogens in biofilms found in healthcare. P. aeruginosa is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium, commonly found in the gut flora, soil, and water that can be spread directly or indirectly to patients in healthcare settings. The pathogen can also be spread in other locations through contamination, including surfaces, equipment, and hands. The opportunistic pathogen can cause hospitalized patients to have infections in the lungs, blood, urinary tract, and in other body regions after surgery. S. aureus is a Gram-positive, cocci-shaped bacterium, residing in the environment and on the skin and nose of many healthy individuals. The bacterium can cause skin and bone infections, pneumonia, and other types of potentially serious infections if it enters the body. S. aureus has also gained resistance to many antibiotic treatments, making healing difficult. Because of natural and unnatural selective pressures and factors, antibiotic resistance in bacteria usually emerges through genetic mutation or acquires antibiotic-resistant genes (ARGs) through horizontal gene transfer - a genetic exchange process by which antibiotic resistance can spread.
Necrotizing pneumonia (NP), also known as cavitary pneumonia or cavitatory necrosis, is a rare but severe complication of lung parenchymal infection. In necrotizing pneumonia, there is a substantial liquefaction following death of the lung tissue, which may lead to gangrene formation in the lung. In most cases patients with NP have fever, cough and bad breath, and those with more indolent infections have weight loss. Often patients clinically present with acute respiratory failure. The most common pathogens responsible for NP are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae. Diagnosis is usually done by chest imaging, e.g. chest X-ray, CT scan. Among these CT scan is the most sensitive test which shows loss of lung architecture and multiple small thin walled cavities. Often cultures from bronchoalveolar lavage and blood may be done for identification of the causative organism(s). It is primarily managed by supportive care along with appropriate antibiotics. However, if patient develops severe complications like sepsis or fails to medical therapy, surgical resection is a reasonable option for saving life.

Fabimycin is an newly developed antibiotic candidate which is effective against gram-negative bacterias, an unusually problematic class of bacteria that uses thicker cell walls and molecular efflux pumps to protect themselves by preventing the antibiotics reaching inside the cells.