
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering ports in the cylinder.

A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the niche application Stirling engine. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.

The Wankel engine is a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion.

A two-strokeengine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes of the piston during only one crankshaft revolution. This is in contrast to a "four-stroke engine", which requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust functions occurring at the same time.

Petrol engine or gasoline engine is an internal combustion engine with spark-ignition, designed to run on petrol (gasoline) and similar volatile fuels.
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process.

The Ford 335 engine family was a group of engines built by the Ford Motor Company between 1969 and 1982. The "335" designation reflected Ford management's decision to produce an engine of that size with room for expansion during its development. This engine family began production in late 1969 with a 351 cu in (5.8 L) engine, commonly called the 351C. It later expanded to include a 400 cu in (6.6 L) engine which used a taller version of the engine block, commonly referred to as a tall deck engine block, a 351 cu in (5.8 L) tall deck variant, called the 351M, and a 302 cu in (4.9 L) engine which was exclusive to Australia.
Indirect injection in an internal combustion engine is fuel injection where fuel is not directly injected into the combustion chamber. In the last decade, gasoline engines equipped with indirect injection systems, wherein a fuel injector delivers the fuel at some point before the intake valve, have mostly fallen out of favor to direct injection. However, certain manufacturers such as Volkswagen, Toyota and Ford have developed a 'dual injection' system, combining direct injectors with port (indirect) injectors, combining the benefits of both types of fuel injection. Direct injection allows the fuel to be precisely metered into the combustion chamber under high pressure which can lead to greater power, fuel efficiency. The issue with direct injection is that it typically leads to greater amounts of particulate matter and with the fuel no longer contacting the intake valves, carbon can accumulate on the intake valves over time. Adding indirect injection keeps fuel spraying on the intake valves, reducing or eliminating the carbon accumulation on intake valves and in low load conditions, indirect injection allows for better fuel-air mixing. This system is mainly used in higher cost models due to the added expense and complexity.
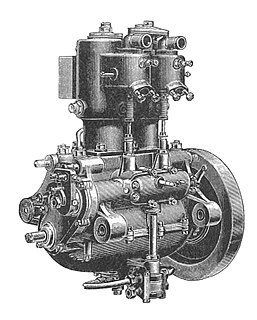
A crankcase is the housing for the crankshaft in a reciprocating internal combustion engine. In most modern engines, the crankcase is integrated into the engine block.
In the context of an internal combustion engine, the term stroke has the following related meanings

The Bourke engine was an attempt by Russell Bourke, in the 1920s, to improve the two-stroke engine. Despite finishing his design and building several working engines, the onset of World War II, lack of test results, and the poor health of his wife compounded to prevent his engine from ever coming successfully to market. The main claimed virtues of the design are that it has only two moving parts, is lightweight, has two power pulses per revolution, and does not need oil mixed into the fuel.

Axial engines are a type of reciprocating engine with pistons arranged around an output shaft with their axes parallel to the shaft. Barrel refers to the cylindrical shape of the cylinder group whilst the Z-crank alludes to the shape of the crankshaft.
A swing-piston engine is a type of internal combustion engine in which the pistons move in a circular motion inside a ring-shaped "cylinder", moving closer and further from each other to provide compression and expansion. Generally two sets of pistons are used, geared to move in a fixed relationship as they rotate around the cylinder. In some versions the pistons oscillate around a fixed center, as opposed to rotating around the entire engine. The design has also been referred to as a oscillating piston engine, vibratory engine when the pistons oscillate instead of rotate, or toroidal engine based on the shape of the "cylinder".
The split-cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine.
The term six-stroke engine has been applied to a number of alternative internal combustion engine designs that attempt to improve on traditional two-stroke and four-stroke engines. Claimed advantages may include increased fuel efficiency, reduced mechanical complexity and/or reduced emissions. These engines can be divided into two groups based on the number of pistons that contribute to the six strokes.

The Hornsby-Akroyd oil engine, named after its inventor Herbert Akroyd Stuart and the manufacturer Richard Hornsby & Sons, was the first successful design of an internal combustion engine using heavy oil as a fuel. It was the first to use a separate vapourising combustion chamber and is the forerunner of all hot-bulb engines, which are considered predecessors of the similar Diesel engine, developed a few years later.
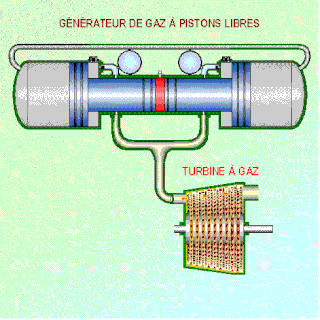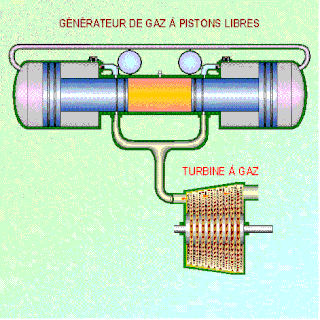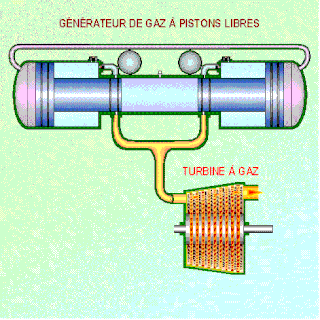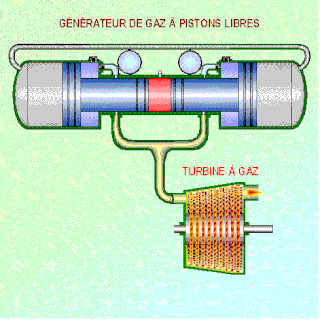
A free-piston engine is a linear, 'crankless' internal combustion engine, in which the piston motion is not controlled by a crankshaft but determined by the interaction of forces from the combustion chamber gases, a rebound device and a load device.

Squish is an effect in internal combustion engines which creates sudden turbulence of the air-fuel mixture as the piston approaches top dead centre (TDC).

An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is applied typically to pistons, turbine blades, rotor or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into useful work. This replaced the external combustion engine for applications where weight or size of the engine is important.
The free-piston linear generator (FPLG) uses chemical energy from fuel to drive magnets through a stator and converts this linear motion into electric energy. Because of its versatility, low weight and high efficiency, it can be used in a wide range of applications, although it is of special interest to the mobility industry as range extenders for electric vehicles.












