
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.

A V12 engine is a twelve-cylinder piston engine where two banks of six cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V12 engines are more common than V10 engines. However, they are less common than V8 engines.

A two-strokeengine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes of the piston in one revolution of the crankshaft. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust functions occurring at the same time.

A V16 engine is a sixteen-cylinder piston engine where two banks of eight cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V16 engines are less common than engines with fewer cylinders, such as V8 and V12 engines. Each bank of a V16 engine can be thought of as a straight-eight, a design that can be inherently balanced. Most V16 engines have a 45° bank angle.

A straight-four engine is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
A V20 engine is a twenty-cylinder piston engine where two banks of ten cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. Large diesel V20 engines have been used in diesel locomotives, haul trucks, electric generators and marine applications.

An opposed-piston engine is a piston engine in which each cylinder has a piston at both ends, and no cylinder head. Petrol and diesel opposed-piston engines have been used mostly in large-scale applications such as ships, military tanks, and factories. Current manufacturers of opposed-piston engines include Cummins, Achates Power and Fairbanks-Morse Defense (FMDefense).
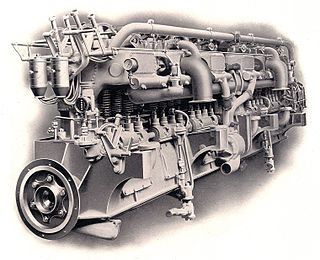
A straight-12 engine or inline-12 engine is a twelve-cylinder piston engine with all twelve cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankcase.

A W18 engine is an eighteen-cylinder piston engine with three banks of six cylinders in a W configuration.

Cummins Inc. is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and distributes engines, filtration, and power generation products. Cummins also services engines and related equipment, including fuel systems, controls, air handling, filtration, emission control, electrical power generation systems, and trucks.

The Cummins B Series is a family of diesel engines produced by American manufacturer Cummins. In production since 1984, the B series engine family is intended for multiple applications on and off-highway, light-duty, and medium-duty. In the automotive industry, it is best known for its use in school buses, public service buses in the United Kingdom, and Dodge/Ram pickup trucks.

The term turbo-diesel, also written as turbodiesel and turbo diesel, refers to any diesel engine equipped with a turbocharger. As with other engine types, turbocharging a diesel engine can significantly increase its efficiency and power output, especially when used in combination with an intercooler.

A V8 engine is an eight-cylinder piston engine in which two banks of four cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.

A two-stroke diesel engine is a diesel engine that uses compression ignition in a two-stroke combustion cycle. It was invented by Hugo Güldner in 1899.

Buda Engine was founded in 1881 by George Chalender in Buda, Illinois, to make equipment for railways. Later based in Harvey, Illinois, Buda from 1910 manufactured engines for industrial, truck, and marine applications. Early Buda engines were gasoline fueled. Later, diesel engines were introduced, utilizing proprietary Lanova cylinder head designs, injection pumps and nozzles. These were known as Buda-Lanova diesel engines. Buda Engine Company was acquired by Allis-Chalmers in 1953. The Buda-Lanova models were re-christened "Allis-Chalmers diesel".
The Komatsu 960E-1 (960E) is an off-highway, ultra-class, rigid-frame, two-axle, diesel/AC electric powertrain haul truck designed and manufactured by Komatsu in Peoria, Illinois, United States. The 960E-1 has been Komatsu's largest, highest capacity haul truck, offering a payload capacity of up to 360 short tons (327 t). The 960-E1 is the first generation of the 960E series of haul trucks and is alternately referred to by Komatsu specifically as the 960E-1 or generally as the 960E.

A straight-seven engine or inline-seven engine is a straight engine with seven cylinders. It is more common in marine applications because these engines are usually based on a modular design, with individual heads per cylinder.
Jacobs Vehicle Systems, Inc. is an American company that engineers, develops and manufacturers commercial vehicle retarding and valve actuation technologies. The company produces light-duty, medium-duty, and heavy-duty engine brakes, recreational vehicle exhaust brakes, aftermarket parts and tune-up kits to heavy-duty diesel engine manufacturers in its domestic market in America, as well as in Asia and Europe.

An internal combustion engine is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance. This process transforms chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to.

OSE class A-450, also known as 450άρα or Καναδέζα is a series of diesel-electric locomotives used by TrainOSE. They were built and put into operation by OSE in 1973. Construction was made by Montreal Locomotive Works in Canada. Outwardly they look like the class A.501, with the basic difference that they are of lesser strength and have different appearance, before rebuilding, as in the elevated head-ons they housed the steam heating boiler. This allowed them to be used in passenger routes during the winter.
















