
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.

A two-strokeengine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust functions occurring at the same time.

A V16 engine is a sixteen-cylinder piston engine where two banks of eight cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V16 engines are less common than engines with fewer cylinders, such as V8 and V12 engines.
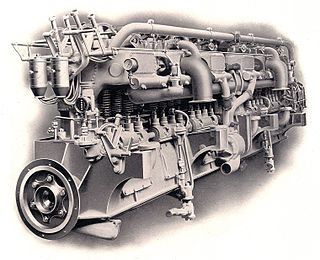
A straight-12 engine or inline-12 engine is a twelve-cylinder internal combustion engine with all twelve cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankcase.
The Wärtsilä RT-flex96C is a two-stroke turbocharged low-speed diesel engine designed by the Finnish manufacturer Wärtsilä. It is designed for large container ships that run on heavy fuel oil. Its largest 14-cylinder version is 13.5 metres (44 ft) high, 26.59 m (87 ft) long, weighs over 2,300 tons, and produces 80,080 kW (107,390 hp). The engine is the largest reciprocating engine in the world.

The Chevrolet "big block" engine is a term for a series of large-displacement, naturally-aspirated, 90°, overhead valve, gasoline-powered, V-8 engines; that were developed and produced by the Chevrolet Division of General Motors, from the 1950s until present.

Wärtsilä Oyj Abp, trading internationally as Wärtsilä Corporation, is a Finnish company which manufactures and services power sources and other equipment in the marine and energy markets. The core products of Wärtsilä include technologies for the energy sector, including gas, multi-fuel, liquid fuel and biofuel power plants and energy storage systems; and technologies for the marine sector, including cruise ships, ferries, fishing vessels, merchant ships, navy ships, special vessels, tugs, yachts and offshore vessels. Ship design capabilities include ferries, tugs, and vessels for the fishing, merchant, offshore and special segments. Services offerings include online services, underwater services, turbocharger services, and also services for the marine, energy, and oil and gas markets. At the end of June 2018, the company employed more than 19,000 workers.

The Chrysler Hemi engines, known by the trademark Hemi, are a series of American I6 and V8 gasoline engines built by Chrysler with overhead valve hemispherical combustion chambers. Three different types of Hemi engines have been built by Chrysler for automobiles: the first from 1951 to 1958, the second from 1964 to 1971, and the third beginning in 2003. Although Chrysler is most identified with the use of "Hemi" as a marketing term, many other auto manufacturers have incorporated similar designs. The engine block and cylinder heads were cast and manufactured at Indianapolis Foundry.

The Toyota S Series engines are a family of straight-4 petrol or CNG engines with displacement from 1.8 L to 2.2 L produced by Toyota Motor Corporation from January 1980 to August 2007. The series has cast iron engine blocks and alloy cylinder heads.
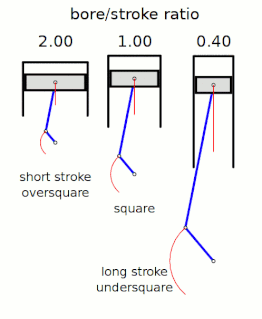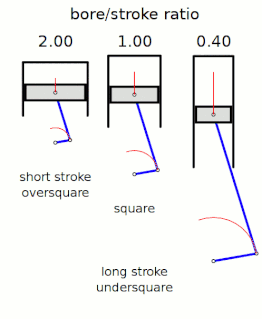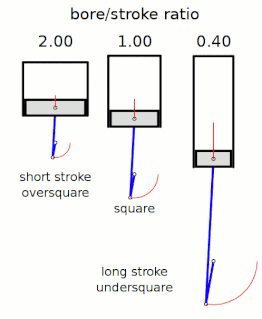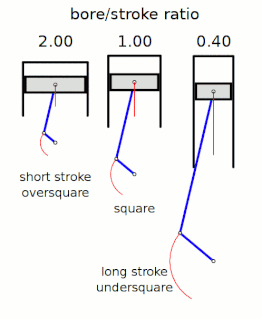
In a reciprocating piston engine, the stroke ratio, defined by either bore/stroke ratio or stroke/bore ratio, is a term to describe the ratio between cylinder bore diameter and piston stroke length. This can be used for either an internal combustion engine, where the fuel is burned within the cylinders of the engine, or external combustion engine, such as a steam engine, where the combustion of the fuel takes place outside the working cylinders of the engine.
The MAN B&W K108ME-C is a low speed two-stroke turbocharged diesel engine for marine engineering applications. It is designed by the Danish department of the German diesel engine supplier: MAN Diesel SE, the former MAN B&W Diesel group, and part of the larger MAN SE.

An inboard motor is a marine propulsion system for boats. As opposed to an outboard motor where an engine is mounted outside the hull of the craft, an inboard motor is an engine enclosed within the hull of the boat, usually connected to a propulsion screw by a driveshaft.
A straight-nine engine or inline-nine engine is a straight engine with nine cylinders. Straight-nine engines are usually diesel engines used for ship propulsion. Rolls-Royce Marine Engines, Pielstick and Wärtsilä have made this type of engine.

Wärtsilä is the second largest diesel engine company in the world. Wärtsilä released the Vasa engine series in 1977 and remained in production until 2010. These popular medium speed diesels were produced in Vasa, Finland; hence their name, Vasa. The lead designer of the first engine was Wilmer Wahlstedt. The series comprises three models, the Vasa 22, 32, and 46, with the number denoting the bore size of the engine. Vasa 32 engines are the most popular of the series and can still be found throughout the marine and power generation industries.

A straight-seven engine or inline-seven engine is a straight engine with seven cylinders. Wärtsilä, with their RTA96-C, and MAN Diesel produce crosshead two-stroke diesel engines in this configuration. Wärtsilä also produces regular trunk engines in this configuration. It is more common in marine applications because marine engines are usually based on a modular design, with individual heads per cylinder.
A V14 engine is a V engine with 14 cylinders mounted on the crankcase in two banks of seven. It is a relatively rare layout, which is used on large medium-speed diesel engines used for power generation and marine propulsion.

SSCV Sleipnir is a semi-submersible crane vessel (SSCV) owned and operated by Heerema Marine Contractors. It is named for Sleipnir, the eight-legged horse ridden by Odin in Norse mythology. The vessel is equipped with two revolving cranes built by Huisman Equipment B.V., each with a capacity of 10,000 t ; the main cranes can be operated in tandem to jointly lift 20,000 t. It was ordered in 2015 and built in Singapore by Sembcorp Marine. After its completion in 2019, SSCV Sleipnir succeeded Heerema's earlier SSCV Thialf as the largest crane vessel in the world.

The Chevrolet Turbo-Thrift engine is a straight-six produced from 1962 to 2001 by the Chevrolet Division of General Motors. The entire series of engines was commonly called Turbo-Thrift, although the name was first used on the 230 cubic inch version that debuted in 1963. The new engine featured seven main bearings in lieu of the four bearing design of its predecessor, the "Stovebolt" engine, and was considerably smaller and approximately 100 lbs lighter.













