
Apocynaceae is a family of flowering plants that includes trees, shrubs, herbs, stem succulents, and vines, commonly known as the dogbane family, because some taxa were used as dog poison. Members of the family are native to the European, Asian, African, Australian, and American tropics or subtropics, with some temperate members. The former family Asclepiadaceae is considered a subfamily of Apocynaceae and contains 348 genera. A list of Apocynaceae genera may be found here.

Catharanthus roseus, commonly known as bright eyes, Cape periwinkle, graveyard plant, Madagascar periwinkle, old maid, pink periwinkle, rose periwinkle, is a perennial species of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is native and endemic to Madagascar, but is grown elsewhere as an ornamental and medicinal plant, and now has a pantropical distribution. It is a source of the drugs vincristine and vinblastine, used to treat cancer. It was formerly included in the genus Vinca as Vinca rosea.

Voacangine is an alkaloid found predominantly in the root bark of the Voacanga africana tree, as well as in other plants such as Tabernanthe iboga, Tabernaemontana africana, Trachelospermum jasminoides, Tabernaemontana divaricata and Ervatamia yunnanensis. It is an iboga alkaloid which commonly serves as a precursor for the semi-synthesis of ibogaine. It has been demonstrated in animals to have similar anti-addictive properties to ibogaine itself. It also potentiates the effects of barbiturates. Under UV-A and UV-B light its crystals fluoresce blue-green, and it is soluble in ethanol.

Indole alkaloids are a class of alkaloids containing a structural moiety of indole; many indole alkaloids also include isoprene groups and are thus called terpene indole or secologanin tryptamine alkaloids. Containing more than 4100 known different compounds, it is one of the largest classes of alkaloids. Many of them possess significant physiological activity and some of them are used in medicine. The amino acid tryptophan is the biochemical precursor of indole alkaloids.

Tabernaemontana corymbosa is a species of plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is native to Brunei, China, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. Glossy green leaves and faintly sweet scented flower. Flowers continuously all year. Frost tolerant. Grows to about 2 metres. Likes full sun to part shade. A number of cultivars are available.
Strictosidine synthase (EC 4.3.3.2) is an enzyme in alkaloid biosynthesis that catalyses the condensation of tryptamine with secologanin to form strictosidine in a formal Pictet–Spengler reaction:

Coronaridine, also known as 18-carbomethoxyibogamine, is an alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga and related species, including Tabernaemontana divaricata for which it was named.

Ibogamine is an anti-convulsant, anti-addictive, CNS stimulant alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga and Crepe Jasmine. Basic research related to how addiction affects the brain has used this chemical.

Ajmalicine, also known as δ-yohimbine or raubasine, is an antihypertensive drug used in the treatment of high blood pressure. It has been marketed under numerous brand names including Card-Lamuran, Circolene, Cristanyl, Duxil, Duxor, Hydroxysarpon, Iskedyl, Isosarpan, Isquebral, Lamuran, Melanex, Raunatin, Saltucin Co, Salvalion, and Sarpan. It is an alkaloid found naturally in various plants such as Rauvolfia spp., Catharanthus roseus, and Mitragyna speciosa.
3α(S)-strictosidine β-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.105) is an enzyme with systematic name strictosidine β-D-glucohydrolase. It catalyses the following chemical reaction:

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.

Catharanthine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus and Tabernaemontana divaricata. Catharanthine is derived from strictosidine, but the exact mechanism by which this happens is currently unknown. Catharanthine is one of the two precursors that form vinblastine, the other being vindoline.

Strictosidine is a natural chemical compound and is classified as a glucoalkaloid and a vinca alkaloid. It is formed by the Pictet–Spengler condensation reaction of tryptamine with secologanin, catalyzed by the enzyme strictosidine synthase. Thousands of strictosidine derivatives are sometimes referred to by the broad phrase of monoterpene indole alkaloids. Strictosidine is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of numerous pharmaceutically valuable metabolites including quinine, camptothecin, ajmalicine, serpentine, vinblastine, vincristine and mitragynine.
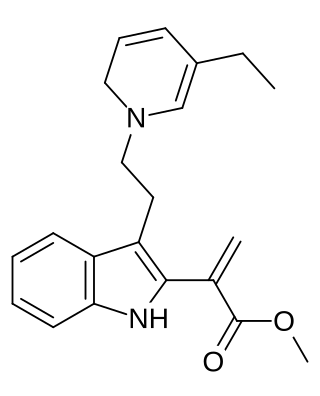
Dehydrosecodine is a terpene indole alkaloid. The compound is believed to be an unstable O-acetylated secodine type intermediate in the formation of catharanthine and tabersonine from stemmadenine. The enzymes involved forming dehydrosecodine or utilizing it as a substrate for further chemical reactions are currently unknown.

Apparicine is a monoterpenoid tricyclic indole alkaloid. It is named after Apparicio Duarte, a Brazilian botanist who studied the Aspidosperma species from which apparicine was first isolated. It was the first member of the vallesamine group of indole alkaloids to be isolated and have its structure established, which was first published in 1965. It has also been known by the synonyms gomezine, pericalline, and tabernoschizine.

Tabernaemontanine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Tabernaemontana divaricata.

Vobasine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Tabernaemontana divaricata.

Voacristine is a indole alkaloid occurring in Voacanga and Tabernaemontana genus. It is also an iboga type alkaloid.
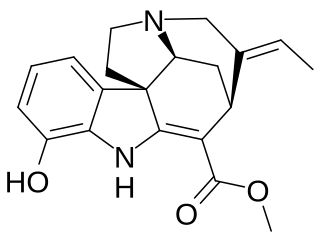
Vinervine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is a derivative of akuammicine, with one additional hydroxy (OH) group in the indole portion, hence it is also known as 12-hydroxyakuammicine.

Conopharyngine is the major alkaloid present in the leaves and stem-bark of Tabernaemontana pachysiphon and Conopharyngia durissima. It is closely related voacangine and coronaridine. Conopharyngine pseudoindoxyl, a derivative of it, is also found in the same plant Tabernaemontana pachysiphon.


















