
A raven is any of several larger-bodied passerine bird species in the genus Corvus. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between crows and ravens. Names are assigned to different species chiefly based on their size.

Banksia is a genus of around 170 species of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes, and woody fruiting "cones" and heads. Banksias range in size from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up to 30 metres (100 ft) tall. They are found in a wide variety of landscapes: sclerophyll forest, (occasionally) rainforest, shrubland, and some more arid landscapes, though not in Australia's deserts.

Phalangeriformes is a paraphyletic suborder of about 70 species of small to medium-sized arboreal marsupials native to Australia, New Guinea, and Sulawesi. The species are commonly known as possums, gliders, and cuscus. The common name "possum" for various Phalangeriformes species derives from the creatures' resemblance to the opossums of the Americas. However, although opossums are also marsupials, Australasian possums are more closely related to other Australasian marsupials such as kangaroos.

The family Psittacidae or holotropical parrots is one of three families of true parrots. It comprises the 12 species of subfamily Psittacinae and 167 of subfamily Arinae including several species that have gone extinct in recent centuries. Some of the most iconic birds in the world are represented here, such as the blue-and-yellow macaw among the New World parrots and the grey parrot among the Old World parrots.

Columbidae is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They primarily feed on plants, and can be taxonomically divided amongst granivores, that feed mostly on the ground on seeds, and frugivores, that feed mostly on fruits, from branches. The family occurs worldwide, often in close proximity with humans, but the greatest variety is in the Indomalayan and Australasian realms.

A wallaby is a small or middle-sized macropod native to Australia and New Guinea, with introduced populations in New Zealand, Hawaii, the United Kingdom and other countries. They belong to the same taxonomic family as kangaroos and sometimes the same genus, but kangaroos are specifically categorised into the four largest species of the family. The term "wallaby" is an informal designation generally used for any macropod that is smaller than a kangaroo or a wallaroo that has not been designated otherwise.

In biology, a subgenus is a taxonomic rank directly below genus.

Macropodidae is a family of marsupials that includes kangaroos, wallabies, tree-kangaroos, wallaroos, pademelons, quokkas, and several other groups. These genera are allied to the suborder Macropodiformes, containing other macropods, and are native to the Australian continent, New Guinea and nearby islands.

Chelidae is one of three living families of the turtle suborder Pleurodira, and are commonly called Austro-South American side-neck turtles. The family is distributed in Australia, New Guinea, parts of Indonesia, and throughout most of South America. It is a large family of turtles with a significant fossil history dating back to the Cretaceous. The family is entirely Gondwanan in origin, with no members found outside Gondwana, either in the present day or as a fossil.
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa.

The Pterophoridae or plume moths are a family of Lepidoptera with unusually modified wings, giving them the shape of a narrow winged airplane. Though they belong to the Apoditrysia like the larger moths and the butterflies, unlike these they are tiny and were formerly included among the assemblage called "microlepidoptera".

The Old World rats and mice, part of the subfamily Murinae in the family Muridae, comprise at least 519 species. Members of this subfamily are called murines. In terms of species richness, this subfamily is larger than all mammal families except the Cricetidae and Muridae, and is larger than all mammal orders except the bats and the remainder of the rodents.

Livistona is a genus of palms, the botanical family Arecaceae, native to southeastern and eastern Asia, Australasia, and the Horn of Africa. They are fan palms, the leaves with an armed petiole terminating in a rounded, costapalmate fan of numerous leaflets.

Acacia, commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about 1,084 species of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Australasia, but the taxonomic name has been redefined to now be reserved for species mainly from Australia, with others from New Guinea, Southeast Asia, and the Indian Ocean. The genus name is neo-Latin, borrowed from the Greek ἀκακία, a term used in antiquity to describe a preparation extracted from Vachellia nilotica, the original type species.
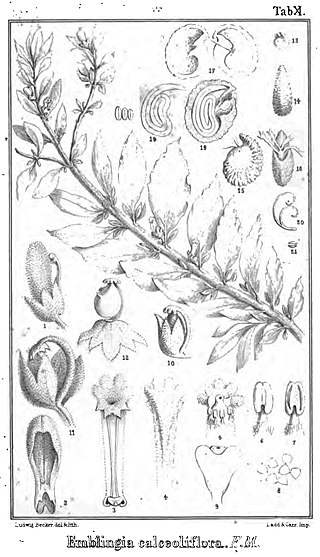
Emblingia is a monospecific plant genus containing the species Emblingia calceoliflora, a herbaceous prostrate subshrub endemic to Western Australia. It has no close relatives, and is now generally placed alone in family Emblingiaceae.

Elseya is a genus of large side-necked turtles, commonly known as Australian snapping turtles, in the family Chelidae. Species in the genus Elseya are found in river systems in northern and northeastern Australia and throughout the river systems of New Guinea. They are identified by the presence of alveolar ridges on the triturating surfaces of the mouth and the presence of a complex bridge strut.

The Myuchelys is a genus of turtles, the Australian saw-shelled turtles, in the family Chelidae and subfamily Chelodininae. They inhabit the headwaters and tributaries of rivers within their range and this led to the name Myuchelys, which is formed from the Aboriginal word myuna meaning clear water and the Greek chelys meaning turtle. They have a short neck and the intergular scute completely separates the gular scutes. They have no alveolar ridge separating them from the snapping turtles of the genus Elseya.

Ledrinae is a relatively small subfamily within the very large and diverse leafhopper family Cicadellidae. Originally placed in its own family, the "Ledridae", it is based on the type genus Ledra.

The Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera (IRMNG) is a taxonomic database which attempts to cover published genus names for all domains of life, from 1758 in zoology up to the present, arranged in a single, internally consistent taxonomic hierarchy, for the benefit of Biodiversity Informatics initiatives plus general users of biodiversity (taxonomic) information. In addition to containing just over 500,000 published genus name instances as at May 2023, the database holds over 1.7 million species names, although this component of the data is not maintained in as current or complete state as the genus-level holdings. IRMNG can be queried online for access to the latest version of the dataset and is also made available as periodic snapshots or data dumps for import/upload into other systems as desired. The database was commenced in 2006 at the then CSIRO Division of Marine and Atmospheric Research in Australia and, since 2016, has been hosted at the Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ) in Belgium.


















