
Staurosporine is a natural product originally isolated in 1977 from the bacterium Streptomyces staurosporeus. It was the first of over 50 alkaloids to be isolated with this type of bis-indole chemical structure. The chemical structure of staurosporine was elucidated by X-ray analysis of a single crystal and the absolute stereochemical configuration by the same method in 1994.
Streptomyces spectabilis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces spectabilis produces hangtaimycin, gentamicin, kanamycin, neomycin B, sisomycin, tobramycin, paromomycin, spectinabilin, spectinomycin, aminocyclitol, actinospectacin, prodigiosine and the streptovaricin complex.

Callystatin A is a polyketide natural product from the leptomycin family of secondary metabolites. It was first isolated in 1997 from the marine sponge Callyspongia truncata which was collected from the Goto Islands in the Nagasaki Prefecture of Japan by the Kobayashi group. Since then its absolute configuration has been elucidated and callystatin A was discovered to have anti-fungal and anti-tumor activities with extreme potency against the human epidermoid carcinoma KB cells (IG50 = 10 pg/ml) and the mouse lymphocytic leukemia Ll210 cells (IG50 = 20 pg/ml).

Lavendamycin is a naturally occurring chemical compound discovered in fermentation broth of the soil bacterium Streptomyces lavendulae. Lavendamycin has antibiotic properties and anti-proliferative effects against several cancer cell lines. The use of lavendamycin as a cytotoxic agent in cancer therapy failed due to poor water solubility and non-specific cytotoxicity. The study of lavendamycin-based analogs designed to overcome these liabilities has been an area of research.

The cyclothiazomycins are a group of natural products, classified as thiopeptides, which are produced by various Streptomyces species of bacteria.
Streptomyces candidus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Russia. Streptomyces candidus produces lemonomycin, enterocin, pyrazofurin and avoparcin.
Streptomyces coeruleorubidus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from marine sediment. Streptomyces coeruleorubidus produces the following medications: pacidamycin 1, baumycin B1, baumycin B2, baumycin C1, feudomycin A, feudomycin B, feudomycin C, ficellomycin, feudomycinone A, and rubomycin.
Streptomyces corchorusii is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces corchorusii produces butalactin.
Streptomyces gardneri is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces gardneri produces thiopeptide A, proactinomycin A, proactinomycin B, proactinomycin C.
Streptomyces glomeratus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces glomeratus produces beromycin and nogalamycin.
Streptomyces nitrosporeus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from garden soil in Japan. Streptomyces nitrosporeus produces Benzastatin E, Benzastatin F, Benzastatin G Nitrosporeusine A and Nitrosporeusine B and the antibiotics nitrosporin and virantomycin and the inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme foroxymithine. Streptomyces nitrosporeus can degrade cellulose.
Streptomyces prunicolor is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Russia. Streptomyces prunicolor produces Pironetin and the free radical scavengers benthocyanin A, benthocyanin B and benthocyanin C.
Streptomyces violaceus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces violaceus produces rhodomycine, violamycin-B5 and violarin B.

A jadomycin is a natural product produced by Streptomyces venezuelae ISP5230 (ATCC10712), the organism which is most well known for making the antibiotic chloramphenicol. The name jadomycin is applied to a family of related angucyclines which are distinguished by the E ring, which is derived from an amino acid. The amino acid incorporation which forms the E-ring is a chemical reaction, rather than enzymatic, an uncommon occurrence in biosynthesis. As such a number of jadomycins incorporating different amino acids have been discovered. Jadomycin A was the first compound of this family to be isolated and constitutes the angucylic backbone with L-isoleucine incorporated into the E-ring. A related analog, jadomycin B, is modified by glycosylation with a 2,6-dideoxy sugar, L-digitoxose. Jadomycins have cytotoxic and antibacterial properties.

C-1027 or Lidamycin is an antitumor antibiotic consisting of a complex of an enediyne chromophore and an apoprotein. It shows antibiotic activity against most Gram-positive bacteria. It is one of the most potent cytotoxic molecules known, due to its induction of a higher ratio of DNA double-strand breaks than single-strand breaks.
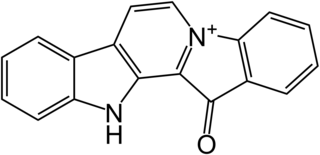
Fascaplysin is a marine alkaloid based on 12H-pyrido[1–2-a:3,4-b′]diindole ring system. It was first isolated as a red pigment from the marine sponge Fascaplysinopsis bergquist collected in the South Pacific near Fiji in 1988. Fascaplysin possesses a broad range of in vitro biological activities including analgesic, antimicrobial, antifungal, antiviral, antimalarial, anti-angiogenic, and antiproliferative activity against numerous cancer cell lines.

Abikoviromycin is an antiviral antibiotic piperidine alkaloid with the molecular formula C10H11ON which is produced by the bacteria Streptomyces abikoensis and Streptomyces rubescens.

Angustmycin A is a purine antibiotic and metabolite from Streptomyces bacteria with the molecular formula C11H13N5O4. Angustmycin A is also a cytokinin.

Capomycin is an antitumor antibiotic with the molecular formula C35H38O10 which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces capoamus.

Pyrrolostatin is a lipid peroxidation inhibitor with the molecular formula C15H21NO2 which has been isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces chrestomyceticus.











