
Psychological statistics is application of formulas, theorems, numbers and laws to psychology. Statistical methods for psychology include development and application statistical theory and methods for modeling psychological data. These methods include psychometrics, factor analysis, experimental designs, and Bayesian statistics. The article also discusses journals in the same field.
Simultaneous equations models are a type of statistical model in which the dependent variables are functions of other dependent variables, rather than just independent variables. This means some of the explanatory variables are jointly determined with the dependent variable, which in economics usually is the consequence of some underlying equilibrium mechanism. Take the typical supply and demand model: whilst typically one would determine the quantity supplied and demanded to be a function of the price set by the market, it is also possible for the reverse to be true, where producers observe the quantity that consumers demand and then set the price.
In statistics, path analysis is used to describe the directed dependencies among a set of variables. This includes models equivalent to any form of multiple regression analysis, factor analysis, canonical correlation analysis, discriminant analysis, as well as more general families of models in the multivariate analysis of variance and covariance analyses.
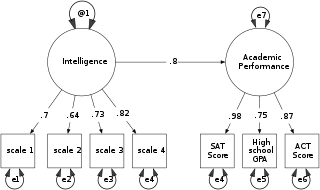
Structural equation modeling (SEM) is a diverse set of methods used by scientists doing both observational and experimental research. SEM is used mostly in the social and behavioral sciences but it is also used in epidemiology, business, and other fields. A definition of SEM is difficult without reference to technical language, but a good starting place is the name itself.
Latent growth modeling is a statistical technique used in the structural equation modeling (SEM) framework to estimate growth trajectories. It is a longitudinal analysis technique to estimate growth over a period of time. It is widely used in the field of psychology, behavioral science, education and social science. It is also called latent growth curve analysis. The latent growth model was derived from theories of SEM. General purpose SEM software, such as OpenMx, lavaan, AMOS, Mplus, LISREL, or EQS among others may be used to estimate growth trajectories.
Timothy Zook Keith is an American psychologist. His research is focused on the nature and measurement of intelligence, understanding school learning, and on the methodologies of confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modelling, and he is considered a leading authority on in the use of structural equation modeling and confirmatory factor analysis in school psychology. He has been a Fellow of the American Psychological Association since 1991.
In statistics, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) is a special form of factor analysis, most commonly used in social science research. It is used to test whether measures of a construct are consistent with a researcher's understanding of the nature of that construct. As such, the objective of confirmatory factor analysis is to test whether the data fit a hypothesized measurement model. This hypothesized model is based on theory and/or previous analytic research. CFA was first developed by Jöreskog (1969) and has built upon and replaced older methods of analyzing construct validity such as the MTMM Matrix as described in Campbell & Fiske (1959).
LISREL is a proprietary statistical software package used in structural equation modeling (SEM) for manifest and latent variables. It requires a "fairly high level of statistical sophistication".
Karl Gustav Jöreskog is a Swedish statistician. Jöreskog is a professor emeritus at Uppsala University, and a co-author of the LISREL statistical program. He is also a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Jöreskog received his bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees at Uppsala University. He is also a former student of Herman Wold. He was a statistician at Educational Testing Service (ETS) and a visiting professor at Princeton University.
Measurement invariance or measurement equivalence is a statistical property of measurement that indicates that the same construct is being measured across some specified groups. For example, measurement invariance can be used to study whether a given measure is interpreted in a conceptually similar manner by respondents representing different genders or cultural backgrounds. Violations of measurement invariance may preclude meaningful interpretation of measurement data. Tests of measurement invariance are increasingly used in fields such as psychology to supplement evaluation of measurement quality rooted in classical test theory.
In statistics, econometrics, epidemiology, genetics and related disciplines, causal graphs are probabilistic graphical models used to encode assumptions about the data-generating process.
The partial least squares path modeling or partial least squares structural equation modeling is a method for structural equation modeling that allows estimation of complex cause-effect relationships in path models with latent variables.

SmartPLS is a software with graphical user interface for variance-based structural equation modeling (SEM) using the partial least squares (PLS) path modeling method. Users can estimate models with their data by using basic PLS-SEM, weighted PLS-SEM (WPLS), consistent PLS-SEM (PLSc-SEM), and sumscores regression algorithms. The software computes standard results assessment criteria and it supports additional statistical analyses . Since SmartPLS is programmed in Java, it can be executed and run on different computer operating systems such as Windows and Mac.
JASP is a free and open-source program for statistical analysis supported by the University of Amsterdam. It is designed to be easy to use, and familiar to users of SPSS. It offers standard analysis procedures in both their classical and Bayesian form. JASP generally produces APA style results tables and plots to ease publication. It promotes open science via integration with the Open Science Framework and reproducibility by integrating the analysis settings into the results. The development of JASP is financially supported by several universities and research funds.

WarpPLS is a software with graphical user interface for variance-based and factor-based structural equation modeling (SEM) using the partial least squares and factor-based methods. The software can be used in empirical research to analyse collected data and test hypothesized relationships. Since it runs on the MATLAB Compiler Runtime, it does not require the MATLAB software development application to be installed; and can be installed and used on various operating systems in addition to Windows, with virtual installations.

Structural Equations with Latent Variables is a statistics textbook authored by Kenneth Bollen, published in 1989. It provides a framework for understanding and applying structural equation modelling. It is commonly used in graduate-level courses that focus on structural equation modelling within the social sciences.
Jeffrey Scott Tanaka was an American psychologist and statistician, known for his work in educational psychology, social psychology and various fields of statistics including structural equation modeling.
Patrick James Curran is an American statistician and professor of quantitative psychology at the University of North Carolina, where he is also a faculty member at the Center for Developmental Science.

In statistics (classical test theory), average variance extracted (AVE) is a measure of the amount of variance that is captured by a construct in relation to the amount of variance due to measurement error.

Marko Sarstedt is a German academic and a marketing researcher. He is a Full Professor at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich and Adjunct Research Professor at Babeș-Bolyai-University.








