Togo is divided into 5 regions, which are subdivided in turn into 30 prefectures and 1 commune, which are further subdivided in turn into 300+ cantons.
Togo is divided into 5 regions, which are subdivided in turn into 30 prefectures and 1 commune, which are further subdivided in turn into 300+ cantons.
ISO 3166-2:TG assigns codes for the 5 regions.
Administrative divisions are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divided. Such a unit usually has an administrative authority with the power to take administrative or policy decisions for its area.
An arrondissement is any of various administrative divisions of France, Belgium, Haiti, certain other Francophone countries, as well as the Netherlands.
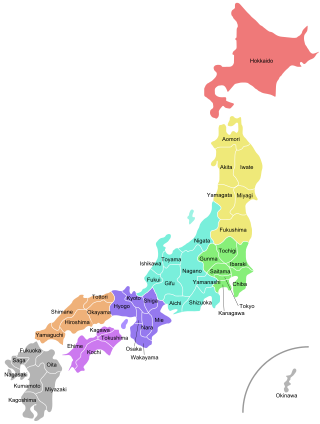
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one regional prefecture and one metropolis. In 1868, the Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.

The administrative divisions of France are concerned with the institutional and territorial organization of French territory. These territories are located in many parts of the world. There are many administrative divisions, which may have political, electoral (districts), or administrative objectives. All the inhabited territories are represented in the National Assembly, Senate and Economic and Social Council and their citizens have French citizenship and elect the President of France.

Namibia uses regions as its first-level subnational administrative divisions. Since 2013, it has 14 regions which in turn are subdivided into 121 constituencies.

Administratively, Tajikistan is divided into:

The Republic of the Congo is divided into twelve departments. These departments replaced former regions in 2002:

Guinea is divided into 8 regions among which the national capital Conakry ranks as a special zone. The other 7 regions are further subdivided into 33 prefectures and thence into sub-prefectures; which are later subdivided into local units and further subdivided into smaller units.
The administrative divisions of Peru have changed from time to time since the nation gained independence from Spain in the early 19th century. The old territorial subdivisions have split or merged due to several reasons, the most common ones being the need for decentralization and population increase, especially in Lima.

An oblast in Ukraine, sometimes translated as region or province, is the main type of first-level administrative division of the country. Ukraine's territory is divided into 24 oblasts, as well as one autonomous republic and two cities with special status. Ukraine is a unitary state, thus the oblasts do not have much legal scope of competence other than that which is established in the Ukrainian Constitution and devolved by law. Articles 140–146 of Chapter XI of the constitution deal directly with local authorities and their competence.

Regions are the first-level administrative divisions of Togo. They are subdivided into prefectures, which can be further broken down into communes. Each region has an elected regional government and a capital city that acts as its administrative seat. The regional governments have jurisdiction over some local affairs, but most powers are shared with the national government.

The districts of Peru are the third-level country subdivisions of Peru. They are subdivisions of the provinces, which in turn are subdivisions of the larger regions or departments. There are 1,838 districts in total.

The regions of Ivory Coast are the second-level subdivisions of Ivory Coast. There are 31 regions, and each region is subdivided into two or more departments, the third-level division in Ivory Coast. Two to four regions are combined to make up an autonomous district, the first-level subdivision. The autonomous districts of Abidjan and Yamoussoukro are not divided into regions.

Somalia is officially divided into 18 administrative regions. These are in turn subdivided into seventy-two districts
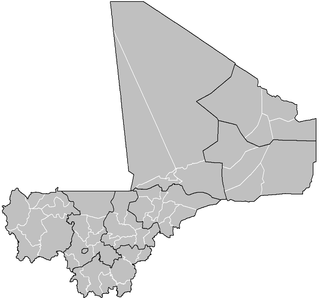
A cercle is the second-level administrative unit in Mali. Mali is divided into eight régions and one capital district (Bamako); the régions are subdivided into 49 cercles. These subdivisions bear the name of their principal city.

As of 2020, the regions of Tajikistan are subdivided into 47 districts, not including 4 districts belonging to the capital city Dushanbe, and 18 cities of regional subordination. Before ca. 2017, there were 58 districts. The districts are further subdivided into municipal units: either as urban municipalities called either as cities or towns, or as rural municipalities called jamoats, which in turn are further subdivided into villages.

Districts are the second-level administrative divisions of Myanmar. They are the subdivisions of the regions and states of Myanmar. According to the Myanmar Information Management Unit (MIMU), as of December 2015, there are 76 districts in Myanmar, which in turn are subdivided into townships, then towns, wards and villages.
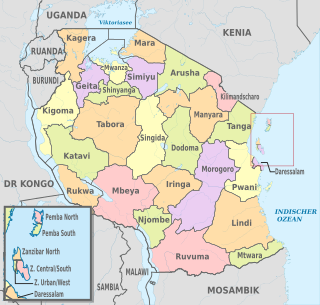
The administrative divisions of Tanzania are controlled by Part I, Article 2.2 of the Constitution of Tanzania. Tanzania is divided into thirty-one regions. Each region is subdivided into districts. The districts are sub-divided into divisions and further into local wards. Wards are further subdivided for management purposes: for urban wards into streets and for rural wards into villages. The villages may be further subdivided into hamlets.
Guinea-Bissau is divided into eight regions and one autonomous sector. These, in turn are subdivided into 37 sectors ; which are further subdivided into smaller groups called sections ; which are further subdivided into populated places. Here are the following listed below:

Namibia is divided into 14 regions subdivided, which are further subdivided into 121 constituencies. The administrative divisions of Namibia are tabled by Delimitation Commissions and accepted or declined by the National Assembly.