Nigeria is a federation of thirty-six states and one Federal Capital Territory, which are divided into 774 Local Government Areas (LGAs) in total. [1] [2]
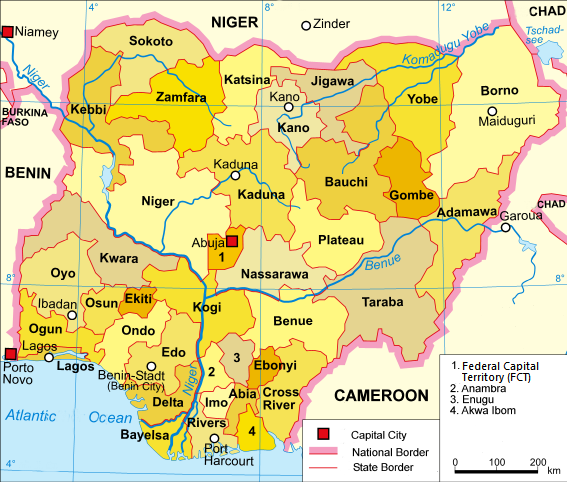
Nigeria is a federation of thirty-six states and one Federal Capital Territory, which are divided into 774 Local Government Areas (LGAs) in total. [1] [2]


Biafra, officially the Republic of Biafra, was a partially recognised state in West Africa that declared independence from Nigeria and existed from 1967 until 1970. Its territory consisted of the former Eastern Region of Nigeria, predominantly inhabited by the Igbo ethnic group. Biafra was established on 30 May 1967 by Igbo military officer and Eastern Region governor C. Odumegwu Ojukwu under his presidency, following a series of ethnic tensions and military coups after Nigerian independence in 1960 that culminated in the 1966 anti-Igbo pogrom. The Nigerian military proceeded in an attempt to reclaim the territory of Biafra, resulting in the start of the Nigerian Civil War. Biafra was officially recognised by Gabon, Haiti, Ivory Coast, Tanzania, and Zambia while receiving de facto recognition and covert military support from France, Portugal, Israel, South Africa and Rhodesia. After nearly three years of war, during which around two million Biafran civilians died, President Ojukwu fled into exile in Ivory Coast as the Nigerian military approached the capital of Biafra. Philip Effiong became the second president of Biafra, and he oversaw the surrender of Biafran forces to Nigeria.

Abuja is the capital and eighth most populous city of Nigeria. Situated in the middle of the country within the Federal Capital Territory (FCT), it is a planned city built mainly in the 1980s based on a master plan by International Planning Associates (IPA), a consortium of three American planning and architecture firms made up of Wallace, Roberts, McHarg & Todd as the lead, Archi systems International, and Planning Research Corporation. The Central Business District of Abuja was designed by Japanese architect Kenzo Tange. It replaced Lagos, the country's most populous city, as the capital on 12 December 1991.
A federal district is a specific administrative division in one of various federations. These districts may be under the direct jurisdiction of a federation's national government, as in the case of federal territory, or they may function as ordinary federated units. Federal districts often include capital districts.

Nigeria is a federation of 36 states. Each of the 36 states is a semi-autonomous political unit that shares powers with the federal government as enumerated under the Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria. The Federal Capital Territory (FCT), is the capital territory of Nigeria, and it is in this territory that the capital city of Abuja is located. The FCT is not a state. It is a territory of the Federal Government, administered by Ministers of Government appointed by the President who supervises by the administration of the territory. Each state is subdivided into local government areas (LGAs). There are 774 local governments in Nigeria. Under the constitution, the 36 states are co-equal but not supreme because sovereignty resides with the federal government. The constitution can be amended by the National Assembly, but each amendment must be ratified by two-thirds of the 36 states of the federation.

Murtala Ramat Muhammed ; 8 November 1938 – 13 February 1976) was a Nigerian general and head of state, who led the 1966 Nigerian counter-coup in overthrowing the Johnson Aguiyi-Ironsi military regime and featured prominently during the Nigerian Civil War and thereafter ruled Nigeria from 29 July 1975 until his assassination on 13 February 1976. This period in Nigerian history, from the Northern counter-coup victory to Murtala's death, is commonly associated with the institutionalization of the military in Nigerian politics.

The president of Nigeria, officially the president of the Federal Republic of Nigeria is the head of state and head of government of the Federal Republic of Nigeria. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the Nigerian Armed Forces.
ISO 3166-2:NG is the entry for Nigeria in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.
A federal capital is a political entity, often a municipality or capital city, that serves as the seat of the federal government. A federal capital is typically a city that physically encompasses the offices and meeting places of its respective government, where its location and relationship to subnational states are fixed by law or federal constitution. Federal capitals may or may not be considered states in themselves, and either exercise significant political autonomy from the federation or are directly ruled by the national government located within their premises, as federal districts.
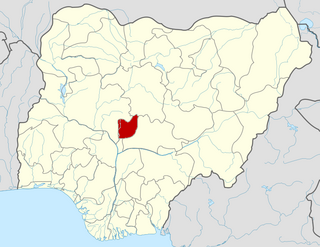
The Federal Capital Territory (FCT) is a federal territory in central Nigeria. Abuja, the capital city of Nigeria, is located in this territory. The FCT was formed in 1976 from parts of the states of old Kaduna, Kwara, Niger, and Plateau states, with the bulk of land mass carved out of Niger state. The Federal Capital Territory is within the North Central region of the country. Unlike other states of Nigeria, which are headed by elected Governors, it is administered by the Federal Capital Territory Administration, headed by a minister, who is appointed by the president.
A capital district, capital region, or capital territory is normally a specially designated administrative division where a country's seat of government is located. As such, in a federal model of government, no state or territory has any political or economic advantage relative to the others because of the national capital lying within its borders. A capital territory can be a specific form of federal district.

Nasarawa State is a state in the North Central region of Nigeria, bordered to the east by the states of Taraba and Plateau, to the north by Kaduna State, to the south by the states of Benue and Kogi, and to the west by the Federal Capital Territory. Named for the historic Nasarawa Emirate, the state was formed from the west of Plateau State on 1 October 1996. The state has thirteen local government areas and its capital is Lafia, located in the east of the state, while a key economic centre of the state is the Karu Urban Area—suburbs of Abuja—along the western border with the FCT.

The Senate is the upper chamber of Nigeria's bicameral legislature, the National Assembly. The National Assembly is the nation's legislature and has the power to make laws, as summarized in chapter one, section four of the 1999 Constitution of Nigeria. The lower chamber is the House of Representatives.

The House of Representatives is the lower chamber of Nigeria's bicameral National Assembly. The Senate is the upper chamber.
Jeremiah Timbut Useni is a retired Nigerian army lieutenant general, who served as minister responsible for the administration of the Federal Capital Territory, Abuja under the Sani Abacha military junta. He served Nigeria in various capacities such as Minister for Transport and Quarter-Master General of the Nigeria Army. Useni also served as Deputy Chairman of one of the significant parties in Nigeria, the All Nigeria Peoples Party. He was elected Senator for the Plateau South constituency of Plateau State, Nigeria in the March 2015 national elections. Useni was running on the People's Democratic Party (PDP) platform.
Philips Tanimu Aduda is a Nigerian politician. He served two terms in the Nigerian House of Representatives between 2003 and 2011, and was elected to the Senate for the Abuja Federal Capital Territory in the 9 April 2011 elections, running on the People's Democratic Party (PDP) ticket.

Mohammed Ali Ndume is a Nigerian politician who has served as the senator representing Borno South senatorial district since 2011. He was a member of the House of Representatives of Nigeria from 2003 to 2011. He is currently a member of the All Progressives Congress.
The table below lists the Nigerian senators of the 8th National Assembly. The Senate included three senators from each of the 36 states, plus one senator for the Federal Capital Territory. The Senate president was Sen. Bukola Saraki of the All Progressives Congress and the deputy Senate president was Ike Ekweremadu. The Senate president and his deputy were assisted by the principal officers including the majority leader, deputy majority leader, minority leader, deputy minority leader, chief whip, deputy chief whip, minority whip and deputy minority whip.

Ibrahim Mohammed Bomai is a Nigerian politician. He currently serves as the Senator representing Yobe South Senatorial District in the 10th National Assembly. He was initially elected in 2019 and was reelected in the 2023 Yobe South Senatorial District Election.