Related Research Articles

Gujarat is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about 1,600 km (990 mi) is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some 196,024 km2 (75,685 sq mi); and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million in 2011. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language.

Surat is a city in the western Indian state of Gujarat. The word Surat directly translates to face in Urdu, Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of the river Tapti near its confluence with the Arabian Sea, it used to be a large seaport. It is now the commercial and economic centre of South Gujarat, and one of the largest urban areas of western India. It has well-established diamond and textile industry, and is a major supply centre for apparels and accessories. About 90% of the world's diamonds are cut and polished in Surat. It is the second largest city in Gujarat after Ahmedabad and the eighth largest city by population and ninth largest urban agglomeration in India. It is the administrative capital of the Surat district.

Rajkot is the fourth-largest city in the Indian state of Gujarat after Ahmedabad, Vadodara, and Surat, and is in the centre of the Saurashtra region of Gujarat. Rajkot is the 35th-largest metropolitan area in India, with a population of more than 2 million as of 2021. Rajkot is the 6th cleanest city of India, and it is the 22nd fastest-growing city in the world as of March 2021. The city contains the administrative headquarters of the Rajkot District, 245 km from the state capital Gandhinagar, and is located on the banks of the Aji and Nyari rivers. Rajkot was the capital of the Saurashtra State from 15 April 1948 to 31 October 1956, before its merger with Bombay State on 1 November 1956. Rajkot was reincorporated into Gujarat State on 1 May 1960.

Mehsana, also spelled Mahesana, is a city and the headquarters of Mehsana district in the Indian state of Gujarat. Established in 14th century, the city was under Gaekwads of Baroda State from 18th century to the independence of India in 1947. Dairy, oil and natural gas are major industries in the city.

Navsari is an administrative district in the state of Gujarat in India, with its headquarters at the city of Navsari. The district covers an area of 2,211 square kilometres and was formed in 1997 after Valsad district was split into Valsad and Navsari districts. It is the largest producer of chikoos in India.
Botad, located in Gujarat's Saurashtra (region), is a significant city and district headquarters of the Botad district. Established as a separate district in 2013, Botad has developed into a key administrative and economic hub, connecting nearby towns and fostering growth across the region.

Hazira is a suburb and a transshipment port in the Surat City in the Gujarat state of India. It is the west most end of Surat.

Kalol is a city in Gandhinagar district in the Indian state of Gujarat, located alongside Gujarat State Highway 41 between the cities of Mehsana and Ahmedabad.
Una is a town and a municipality in Gir Somnath district of the Saurashtra region in the state of Gujarat, India.
Gujarat State Road Transport Corporation abbreviated (GSRTC), is a Government State Transport Undertaking of Gujarat for passengers facilitating with road public transport in moffusil / city services. GSRTC operates within the state of Gujarat, India and neighboring states. It has a fleet of 8322 buses.

Janmarg, also known as Ahmedabad BRTS, is a bus rapid transit system in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. It is operated by Ahmedabad Janmarg Limited, a subsidiary of Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation and others. It is designed by Centre for Environmental Planning and Technology. It was inaugurated in October 2009. The network expanded to 89 kilometres (55 mi) by December 2017 and 160 km by March 2023; with daily ridership of 349,000 passengers. BRTS won several nation and international awards for design, implementation and operation. It was rated Silver on BRT Standard in 2013.

Surat Municipal Corporation (SMC) is the local civic body responsible for the administration of Surat, Gujarat which has come into being under the Bombay Provincial Municipal Act, 1949. The Surat Municipal Corporation was established on 2 October 1966. Surat Municipal Corporation area 462.149 km2. It carries out all the obligatory functions and discretionary functions entrusted by the BPMC Act, 1949 with the following mission.
The Surat Metro is an under-construction rapid transit rail system for Surat in the Surat Metropolitan Region, Gujarat state of India. Two corridors with a combined length of 40.35 kilometers are under construction since 18 January 2021. The project is expected to be completed by December 2027 at an estimated cost of ₹12,020.32 crore (US$1.4 billion).
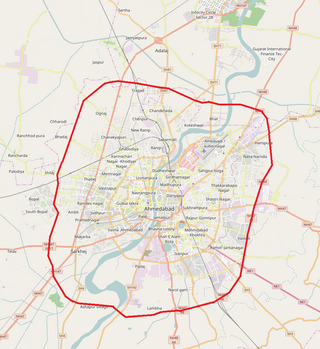
The Sardar Patel Ring Road is a 76 km long ring road encircling the city of Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. It is a toll road built by the Ahmedabad Urban Development Authority (AUDA). Built at a cost of ₹355 crore, it was opened in 2004.

Gandhinagar Municipal Corporation is the local civic body responsible for the administration of Gandhinagar, the capital of the Indian state of Gujarat. It was set up in 2010. Gandhinagar Municipal Corporation has 326 sq km area.

Kumbhariya is a village of historical, archaeological and religious importance with cultural heritage in Danta Taluka of Banaskantha district, Gujarat, India.

Gopi Talav or Gopi Lake is a lake in the Gopipura locality in the city of Surat in Gujarat state of India. It was built circa 1510 CE by Malik Gopi, who was an affluent merchant and governor of Surat during the Gujarat Sultanate. In 2012, the lake was renovated by Surat Municipal Corporation and the area surrounding redeveloped as a recreational facility.
Indian Railway Stations Development Corporation Limited (IRSDC) was a special purpose vehicle owned by the Rail Land Development Authority (RLDA), Ircon International and RITES. All three companies are owned by the Indian Ministry of Railways. IRSDC was incorporated on 12 April 2012.
Transport in Surat is shared by public, and private transport. Surat, India has Rapid Transport System with BRTS Surat, Surat Metro, Railways etc. Surat has 861 Buses
References
- 1 2 3 "180 Gujarat cities to get private bus service".
- 1 2 "No takers for Surat city bus service". The Indian Express . Surat. 20 March 2013. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ↑ Bhatt, Himansshu (26 October 2012). "Surat's public transport on verge of collapse". The Times of India . Surat. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ↑ John, Paul (16 June 2012). "180 Gujarat cities to get private bus service". The Times of India . Ahmedabad. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ↑ Rawat, Basant (21 August 1998). "Govt apathy hits bus project". The Indian Express . Surat. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ↑ "GSRTC bus office inaugurated". The Indian Express . Surat. 24 June 1999. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ↑ Thomas, Melvyn (21 August 2012). "Travelling in Surat's redline buses a harrowing experience". The Times of India . Surat. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ↑ "Surat buses back on roads". The Times of India . Surat. 21 September 2013. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ↑ Bhatt, Himansshu (10 May 2013). "No public transport for 45 days". The Times of India . Surat. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ↑ Bhatt, Himansshu (4 July 2013). "New bus service in Surat unlikely before August". The Times of India . Surat. Retrieved 28 June 2014.