
Barbados is an up-and-coming tourist country that provides reliable and safe transportation for natives and visitors alike. The country is very small with a length of 21 miles (34 km) and a width of 14 miles (23 km). Barbados has 1,600 kilometres (990 mi) of public paved roads, two active marine ports in, remnants of a railway system, and one airport; the Sir Grantley Adams International Airport, located in Christ Church.

Ahmedabad is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 makes it the fifth-most populous city in India, and the encompassing urban agglomeration population estimated at 6,357,693 is the seventh-most populous in India. Ahmedabad is located near the banks of the Sabarmati River, 25 km (16 mi) from the capital of Gujarat, Gandhinagar, also known as its twin city.
This page provides a historical timeline of Ahmedabad, the sixth largest city in India.

The Metropolitan Transport Corporation (Chennai) Ltd. - (MTC), is the agency that operates the public bus service in Chennai, India. In 2022 the MTC has a total fleet of 3,448 buses with 3,233 scheduled services, with on average 2.832 million passengers per day. On March 22, 2016, the Union Ministry of Road Transport and Highways reported that Chennai had the most crowded buses in the country with 1300 passengers per bus in each direction per day. During peak hours, in some routes, a bus with a capacity to accommodate 80 persons carries twice the number of people due to the extensiveness of the system. It has an operating area of 3,929 square kilometres (1,517 sq mi). MTC has a total of 604 routes with its largest terminus being Broadway in Central Chennai.

The Société de transport de Montréal is a public transport agency that operates transit bus and rapid transit services in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Established in 1861 as the "Montreal City Passenger Railway Company", it has grown to comprise four subway lines with a total of 68 stations, as well as over 186 bus routes and 23 night routes. The STM was created in 2002 to replace the Société de transport de la communauté urbaine de Montréal. The STM operates the most heavily used urban mass transit system in Canada, and one of the most heavily used rapid transit systems in North America. As of 2019, the average daily ridership is 2,297,600 passengers: 977,400 by bus, 1,306,500 by rapid transit and 13,700 by paratransit service.

Motera is a neighbourhood in the northwestern part of the metropolis of Ahmedabad in Gujarat, India. It lies west of the Sabarmati River. It falls under the West Zone of Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation and under the Gandhinagar South constituency of Gujarat Legislative Assembly and under the Gandhinagar constituency of the Lok Sabha. The chief attraction in Motera is the world's largest sports stadium, Narendra Modi Stadium. The stadium is the venue for the international cricket matches held in Ahmedabad. In 2015, old stadium was demolished and new stadium was built which got the honour of world's largest stadium.

Pune Mahanagar Parivahan Mahamandal Ltd (PMPML) is the public transport bus service provider for the city of Pune, India.

The transport system of Kolkata, a city in India, is a mix of modern mass rapid transport and old transport modalities like rickshaws. Kolkata is connected to the rest of India by the National Highways, the extensive network of the Indian Railways, National Waterways and by air. The most traffic to Northeast India route via Kolkata.

The Amdavad Municipal Corporation, or the AMC, established in July 1950 under the Bombay Provincial Corporation Act (1949), is responsible for the civic infrastructure and administration of the city of Ahmedabad.
Amit Popatlal Shah is an Indian politician who served as the mayor of the city of Ahmedabad, in the state of Gujarat, India from 23 October 2005 to 23 April 2008. He is affiliated with the BJP. Presently he is president in BJP of Ahmedabad City.
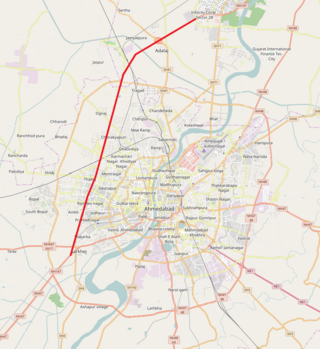
The Sarkhej–Gandhinagar Highway, colloquially the S.G. Road or S.G. Highway, connects the city of Ahmedabad with Gandhinagar, the capital of the state of Gujarat, India. It forms the major part of NH 8C that connects Sarkhej with Chiloda near Gandhinagar. It is a major artery road for commercial and public transport and is witnessing a major construction boom along its route towards Gandhinagar.

Ahmedabad Junction railway station is the main railway station of Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. It is also the biggest railway station within Gujarat and also one of the major railway station in India. It is the highest income-generating division in Western Railways. It connects to Mumbai, Chennai, Delhi, Howrah and other major cities of India. Also it is central railway station of Gujarat which connects to Saurashtra, Kutch, Vadodara, Surat, Himmatnagar, Bhavnagar, Palanpur, etc.

The Ellis Bridge is a century-old bridge in Ahmedabad, Gujarat. It bridges the western and eastern parts of the city across the Sabarmati river. This bowstring arch truss bridge was the first bridge in Ahmedabad, constructed in 1892. Concrete wings were added on either side in 1997 and it was renamed the Swami Vivekananda Bridge.

The Brihanmumbai Electricity Supply and Transport Undertaking (BEST) is a civic transport and electricity provider public body based in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It was originally set up in 1873 as a tramway company called "Bombay Tramway Company Limited". The company set up a captive thermal power station at the Wadi bunder in November 1905 to generate electricity for its trams and positioned it to also supply electricity to the city and re-branded itself to "Bombay Electric Supply & Tramways (BEST)" Company. In 1926, BEST also became an operator of motor buses. In 1947, the BEST became an undertaking of the Municipal Corporation and rebranded itself to "Bombay Electric Supply & Transport (BEST)". In 1995 the organisation was renamed to "Brihanmumbai Electric Supply & Transport (BEST)" alongside Mumbai. It now operates as an autonomous body under the Municipal Corporation.

Indore City Bus is a road transport system run by Atal Indore City Transport Services Limited or AICTSL. This transport system runs through 277 kilometers of road network in the Indore city and surrounding areas. The city bus service has 6 private partners along with the city administration and the total investment has gone more than 40 Crores.
Public transport in Invercargill, New Zealand is by bus.

Janmarg, also known as Ahmedabad BRTS, is a bus rapid transit system in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. It is operated by Ahmedabad Janmarg Limited, a subsidiary of Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation and others. It is designed by CEPT University. It was inaugurated in October 2009. The network expanded to 89 kilometres (55 mi) by December 2017 with daily ridership of 3,49,000 passengers. BRTS won several nation and international awards for design, implementation and operation. It was rated Silver on BRT Standard in 2013.

The Indore BRTS or Ahilya Path Designed by Resident Engineer Shrilal Prasad NiralaTeam Leader of TCPL Indore is the bus rapid transit system for the city of Indore, Madhya Pradesh by AICTSL also called i-Bus(Intelligent Bus), became operational from 10 May 2013. The Indore BRTS project started in 2007 under the Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (JNNURM). It involves the participation of the Governments of India and Madhya Pradesh, and the World Bank.
Surat City Bus is the name under which city buses are operated in Surat, Gujarat, India. It is operated by a private entity-‘Sitilink’ under a public private partnership model for the Surat Municipal Corporation (SMC). The model is based on an earlier model by the Ahmedabad Municipal Transport Service (AMTS) which operated bus services in Ahmedabad on a public-private partnership, but subsequently failed. In 2012, the Government of Gujarat announced that it would set up similar transport facilities in 180 cities across the state under a public-private partnership.


















