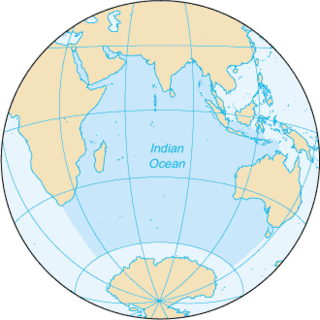
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering 70,560,000 km2 (27,240,000 sq mi) or 19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, the Laccadive Sea, the Somali Sea, Bay of Bengal, and the Andaman Sea.

Mumbai is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second-most populous city in India after Delhi and the seventh-most populous city in the world with a population of roughly 20 million. As per the Indian government population census of 2011, Mumbai was the most populous city in India with an estimated city proper population of 12.5 million living under Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai. Mumbai is the centre of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, the sixth most populous metropolitan area in the world with a population of over 23 million. Mumbai lies on the Konkan coast on the west coast of India and has a deep natural harbour. In 2008, Mumbai was named an alpha world city. It has the highest number of millionaires and billionaires among all cities in India. Mumbai is home to three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Elephanta Caves, Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus, and the city's distinctive ensemble of Victorian and Art Deco buildings designed in the 19th and 20th centuries.

Seychelles, officially the Republic of Seychelles, is an archipelagic island country in the Indian Ocean at the eastern edge of the Somali Sea. It consists of 115 islands. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, is 1,500 kilometres (932 mi) east of mainland Africa. Other nearby island countries and territories include the Comoros, Madagascar, Mauritius, and the French overseas regions of Mayotte and Réunion to the south; and Maldives and the Chagos Archipelago to the east. It is the least populous sovereign African country, with an estimated 2020 population of 98,462.

Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India consisting of 572 islands, of which 38 are inhabited, at the junction of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea.

Languages spoken in India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians, both families together are sometimes known as Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino–Tibetan, Tai–Kadai and a few other minor language families and isolates. India has the world's fourth highest number of languages (447), after Nigeria (524), Indonesia (710) and Papua New Guinea (840). The Indian subcontinent is home to the third most spoken language in the world, Hindi-Urdu; the sixth most spoken language, Bengali; and the thirteenth most spoken language, Punjabi.

Tourism in India is important for the country's economy and is growing rapidly. The World Travel and Tourism Council calculated that tourism generated ₹16.91 lakh crore (US$220 billion) or 9.2% of India's GDP in 2018 and supported 42.673 million jobs, 8.1% of its total employment. The sector is predicted to grow at an annual rate of 6.9% to ₹32.05 lakh crore (US$430 billion) by 2028. In October 2015, India's medical tourism sector was estimated to be worth US$3 billion, and it is projected to grow to US$7–8 billion by 2020. In 2014, 184,298 foreign patients travelled to India to seek medical treatment.

India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.

Lakshadweep, also known as Laccadives, is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located 200 to 440 km off of Malabar Coast.

The West Indies are a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago.

The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) is the first and only tri-service theater command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. It was created in 2001 to safeguard India's strategic interests in Southeast Asia and the Strait of Malacca by increasing rapid deployment of military assets in the region. It provides logistical and administrative support to naval ships which are sent on deployment to East Asia and the Pacific Ocean.

The Indian subcontinent, or simply the subcontinent, is a physiographical region in South Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate and projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. It generally includes Bangladesh, Bhutan, the British Indian Ocean Territory, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. The terms Indian subcontinent and South Asia are sometimes used interchangeably to denote the region, although the geopolitical term of South Asia generally also includes Afghanistan. The United Nations geoscheme for Asia includes both Afghanistan and Iran in Southern Asia.

India-Nauru relations refers to the international relations that exist between India and Nauru. These have been established since the island's independence in 1968.

Forum for India-Pacific Islands cooperation (FIPIC) is a multinational grouping developed in 2014 for cooperation between India and 14 Pacific Islands nations which include Cook Islands, Fiji, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Nauru, Niue, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Tonga, Tuvalu and Vanuatu. All heads of state or heads of government of the above countries met in Suva, Fiji in November 2014 for the first time where the annual summit was conceptualised.

India–Palau relations refers to the international relations that exist between India and Palau. The Embassy of India in Manila, Philippines is concurrently accredited to Palau.

India and Kiribati established diplomatic relations in 1985. The High Commission of India in Suva, Fiji is concurrently accredited to Kiribati. Kiribati maintains an Honorary Consulate in New Delhi.

Cayman Islands–India relations refers to the international relations that exist between the Cayman Islands and India. The foreign relations of the Cayman Islands are handled by the British Foreign Office. Therefore, India's foreign policy has focused on economic relations with the Cayman Islands, as well providing consular services to Indians and Caymanians. The High Commission of India in Kingston, Jamaica is concurrently accredited to the Cayman Islands.

Cook Islands–India relations refers to bilateral relations between the Cook Islands and India.
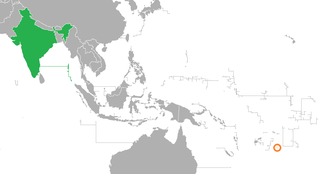
India–Niue relations refers to bilateral relations between India and Niue.

India–Solomon Islands relations refers to the international relations between India and the Solomon Islands. Neither country has a resident ambassador. The High Commission of India in Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea is concurrently accredited to the Solomon Islands


















