
The Enxet are an indigenous people of about 17,000 living in the Gran Chaco region of western Paraguay. Originally hunter-gatherers, many are now forced to supplement their livelihood as laborers on the cattle ranches that have encroached upon their dwindling natural forest habitat. Nevertheless, the Enxet are still engaged in an ongoing conflict with the government and ranchers, who want to destroy what remains of the forest to open the land for massive settlement. Today, only a handful of Enxet are still able to maintain their traditional way of life, while the majority live in small settlements sponsored by various missionary organizations. The Enxet and Enlhet languages are still vigorous.

The papaya, papaw, or pawpaw is the plant species Carica papaya, one of the 21 accepted species in the genus Carica of the family Caricaceae. It was first domesticated in Mesoamerica, within modern-day southern Mexico and Central America. In 2020, India produced 43% of the world's supply of papayas.

Yerba mate or yerba-maté is a plant species of the holly genus Ilex native to South America. It was named by the French botanist Augustin Saint-Hilaire. The leaves of the plant can be steeped in hot water to make a beverage known as mate. Brewed cold, it is used to make tereré. Both the plant and the beverage contain caffeine.

Zinnia is a genus of plants of the tribe Heliantheae within the family Asteraceae. They are native to scrub and dry grassland in an area stretching from the Southwestern United States to South America, with a centre of diversity in Mexico. Members of the genus are notable for their solitary long-stemmed 12 petal flowers that come in a variety of bright colors. The genus name honors German master botanist Johann Gottfried Zinn (1727–59).

Victoria or giant waterlily is a genus of water-lilies, in the plant family Nymphaeaceae, with very large green leaves that lie flat on the water's surface. Victoria boliviana has a leaf that is up to 3 metres (9.8 ft) in width, on a stalk up to 8 metres (26 ft) in length. The genus name was given in honour of Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom. It pushes other water plants aside as it spreads out until only those of its kind remains. When this happens it has completely cut out the sunlight from getting to any plants below the water. All three species typically have four sepals each measuring 12 centimetres (4.7 in) long by 8 centimetres (3.1 in) wide. There are typically 50 to 70 petals and 150 to 200 stamens.

The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region. This land is sometimes called the Chaco Plain.

The ringed teal is a small duck of South American forests. It is the only species of the genus Callonetta. Usually placed with the dabbling ducks (Anatinae), this species may actually be closer to shelducks and belong in the subfamily Tadorninae; its closest relative is possibly the maned duck.
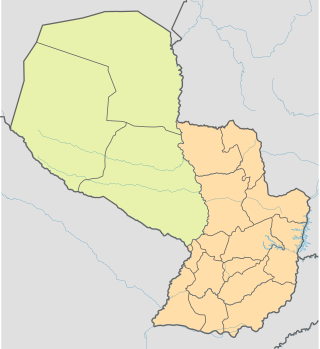
The Paraguayan Chaco or Región Occidental is a semi-arid region in Paraguay, with a very low population density. The area is being rapidly deforested. Consisting of more than 60% of Paraguay's land area, but with less than 3% of the population, the Chaco is one of the most sparsely inhabited areas in South America.

Brasiliopuntia is a genus in the cactus family, Cactaceae. It contains only one species, Brasiliopuntia brasiliensis.

The genus Helwingia consists of shrubs or rarely small trees native to eastern Asia, the Himalayas, and northern Indochina. It is the only genus in the family Helwingiaceae.
Priogymnanthus is a genus of three species of flowering plants in the family Oleaceae native to tropical South America, in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Argentina and Paraguay.
The Mascoian languages, also known as Enlhet–Enenlhet, Lengua–Mascoy, or Chaco languages, are a small, closely related language family of Paraguay.

Harrisia bonplandii is a species of cactus. The cactus plants in the Gran Chaco are generally called tuna and this specific variety reina de la noche. Fruits and roots are edible and well known to the native nations of the Gran Chaco.

Butia paraguayensis is a species of Butia palm tree found in the cerrado region of South America. Its natural range runs from Mato Grosso do Sul and São Paulo in southern Brazil through Paraguay to northern Argentina and Uruguay. It was given the name dwarf yatay palm in English by 2000, and it is locally known as yata'i in Guaraní in Paraguay, or butiá-do-cerrado in Portuguese in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.

Indigenous peoples in Paraguay, or Native Paraguayans, include 17 ethnic groups belonging to five language families. While only a 1.7% of Paraguay's population is fully indigenous, 75% of the population identifies as being partially of indigenous descent; however, the majority do not identify as being indigenous but as Mestizos. Most of the native population lives in the northwestern part of the country, the Gran Chaco.
Maskoy, or Toba-Maskoy, is one of several languages of the Paraguayan Chaco called Toba. It is spoken on a reservation near Puerto Victoria. Toba-Maskoy is currently a threatened language at risk of becoming an extinct language, due to the low number of native speakers.

Lyropteryx is a genus of butterflies of the family Riodinidae. Species of this genus are widespread in the tropical areas of the South America.
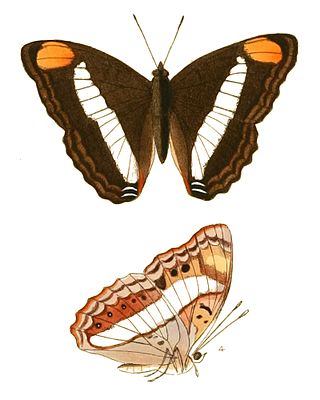
Doxocopa pavon, the Pavon emperor or Pavon, is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. They can be found from Paraguay in South America up to Texas in the southern United States. They are generally brown in their overall coloration, with two bands of white straddling the middle of the upper surfaces of the wings, and a patch of orange on the tips of their forewings. The upper surfaces of the wings of the males are overlaid by an iridescent blue-purple sheen. The females of the species closely resemble members of the unrelated genus Adelpha.
Enlhet (Eenlhit), or Northern Lengua, is a language of the Paraguayan Chaco, spoken by the northern Enxet people. It is also known as Vowak and Powok.

Cecropia pachystachya, commonly known as Ambay pumpwood, is a species of tree in the family Urticaceae. It is native to Argentina, Paraguay and Brazil where it grows near the edges of moist forests.
















