Philyra is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1841. It contains only one known species, Philyra brasiliensis, native to Brazil, Paraguay, and northeastern Argentina.
Romanoa tamnoides is a species of plant of the family Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus Romanoa, first described in 1824. It is native to Brazil and Paraguay.
Micrandropsis is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1973. It contains only one known species, Micrandropsis scleroxylon, endemic to the State of Amazonas in northwestern Brazil.
Rhodothyrsus is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae, first described as a genus in 1999. It is native to South America.
- Rhodothyrsus hirsutusEsser - Colombia, NW Venezuela
- Rhodothyrsus macrophyllus(Ducke) Esser - Guyana, Suriname, Colombia, Peru, N Brazil

Algernonia is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1858. It is native to Peru and Brazil.

Dracontium is a genus of flowering plants similar to those of Amorphophallus. Unlike Amorphophallus which is found in the Old World, this genus has a New World distribution and is native to South America, Central America, southern Mexico, and the West Indies.
Syagrus macrocarpa is a rare species of palm found only as scattered isolated individuals and small groups in the east of the Brazilian states of Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais and Rio de Janeiro. It grows to 4-10m tall, with 8-20 leaves to 2m long. The leaves are bent at the end, with very hairy margins near the trunk, and consist of 180-320 slightly coiled leaflets irregularly arranged in several planes on the rake. The fruit are oval, greenish-yellow, 6–9 cm long. It is grown in cultivation. Seeds are difficult to germinate, with low rates of germination. Common names for it in Minas Gerais are baba-de-boi-grande and maria-rosa.

Blepharocalyx is a genus of plant in family Myrtaceae first described as a genus in 1854. It is native to South America and the West Indies.
- Blepharocalyx cruckshanksii(Hook. & Arn.) Nied. - Chile
- Blepharocalyx eggersii(Kiaerskou) L.R.Landrum - Lesser Antilles, Venezuela, Guyana, Peru, Brazil
- Blepharocalyx myriophyllus Mattos - Minas Gerais
- Blepharocalyx salicifolius(Kunth.) O.Berg - Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Paraguay, Uruguay, N Argentina

Syngonanthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Eriocaulaceae. It is native to tropical Africa and to Latin America.

Schoeneoplectus californicus is a species of sedge known by the common names California bulrush, southern bulrush and giant bulrush. It is also sometimes called "tule", but the closely related Schoenoplectus acutus is the species most often referred to by that name.

Lytocaryum is a monoecious genus of flowering plant in the palm family endemic to the Atlantic coast of Brazil, where 4 species are known. Palms once classified as Microcoelum are herein included; the genus is closely related to Syagrus, from which it is differentiated only by abundant tomentum, strongly versatile anthers, and slight epicarp, mesocarp, and endocarp differences. The name is Greek for "loose" and "nut".

Asterostigma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to Brazil and Argentina. The leaves are pinnate and the plant is tuberous.
- Asterostigma cryptostylumBogner - Brasília, Goiás, Minas Gerais
- Asterostigma cubense(A.Rich.) K.Krause ex Bogner - São Paulo
- Asterostigma lividum(G.Lodd.) Engl. - southern Brazil; Misiones Province of Argentina
- Asterostigma lombardiiE.G.Gonç. - Minas Gerais, Espírito Santo
- Asterostigma luschnathianumSchott - southern Brazil
- Asterostigma reticulatumE.G.Gonç - southern Brazil
- Asterostigma riedelianum(Schott) Kuntze - eastern Brazil
- Asterostigma tweedieanumSchott - Santa Catarina in southern Brazil

Urospatha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae that consists of 11 known species. They are found growing in South America and Central America in swamps, wet savannahs, and brackish water. The leaves of the species in this genus are upward pointing and sagittate (arrow-shaped). The inflorescences are quite unique; the spathe is mottled and elongated with a spiral twist at the end. The seeds are distributed by water and have a texture similar to cork that allows them to float. They also quickly germinate in water.
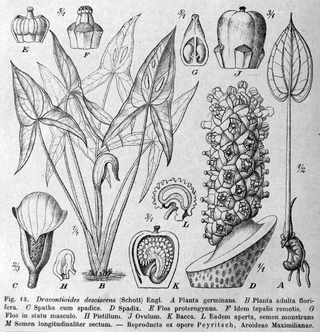
Dracontioides is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It was long thought to contain only a single species until a second species was described in 2005. Both are endemic to Brazil.
Mangonia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. The genus contains only two known species native to southern Brazil and Uruguay.
- Mangonia tweedieanaSchott. - Rio Grande do Sul, Uruguay
- Mangonia uruguaya(Hicken) Bogner - Cerro Largo in Uruguay

Taccarum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is endemic to South America. The genus tends to grow in rocky areas.
- Taccarum caudatumRusby - Bolivia, Peru, Acre State in western Brazil
- Taccarum crassispathumE.G.Gonç. - central Brazil
- Taccarum peregrinum(Schott) Engl. - Paraguay, southern Brazil, Misiones Province of Argentina
- Taccarum uleiEngl. & K.Krause - eastern Brazil
- Taccarum warmingiiEngl. - southern Brazil
- Taccarum weddellianumBrongn. ex Schott - Bolivia, Peru, Paraguay, central and western Brazil

Butia yatay, the jelly palm or yatay palm, is a Butia palm native to southern Brazil, Uruguay and northern Argentina. It is known as the butiá-jataí in Portuguese in the south of Brazil, as well as simply jataí or butiá. It is sometimes cultivated as an ornamental in Europe and the United States. It is the tallest of all the species in the genus Butia. The fruit is edible with a sweet flavour.
Monochilus is a genus of plants in the mint family, Lamiaceae, first described in 1835. It contains two known species, both endemic to Brazil.
- Monochilus gloxinifoliusFisch. & C.A.Mey. - Rio de Janeiro
- Monochilus obovatusP.D.Cantino - Goiás

Siderasis is a genus of monocotyledonous flowering plants in the dayflower family, first described in 1837. It consists of a single known species, Siderasis fuscata, endemic to the State of Rio de Janeiro in southeastern Brazil, though it is also naturalized on the Island of Java in Indonesia.

Butia stolonifera was an oddly growing palm assigned to the genus Butia found only once in Uruguay in the 19th century, but which now is considered to be uncertain as a valid species.















