Fuelleborn's squeaker is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to Tanzania where it is found in Lake Rukwa and the Rufiji River basin. It was first described by Franz Martin Hilgendorf and Paul Pappenheim in 1903, from a specimen collected at Lake Rukwa. The species name fuelleborni is named in honor of Prof. Dr. F. Fülleborn, who collected the original sample.
Synodontis ruandae is a species of upside-down catfish native to Rwanda, Burundi, and Tanzania where it is found in the Kagera River system. It was first described by Belgian ichthyologist Hubert Matthes in 1959, based upon holotypes discovered in the Kagera River at Rusumo, Rwanda. The specific name "ruandae" is derived from its type locality, Rwanda.

Synodontis angelicus is a species of upside-down catfish commonly named polkadot squeaker, black clown catfish, whitespotted squeaker, pearl squeaker, or angel squeaker. This species is native to the Congo Basin in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. It was originally described in 1891 by Belgian ichthyologist Louise Schilthuis after its discovery in the Malebo Pool of the Congo River. The specific name "angelicus" means heavenly or divine, since juveniles of this species are remarkable for their bright coloring.

Synodontis acanthomias is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Congo Basin of Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. It was originally discovered by George Albert Boulenger in 1899 in Boma, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The original specimen resides in the Natural History Museum in London. The species Synodontis pfefferi, described by Franz Steindachner in 1912 was found to be the same species. The specific name "acanthomias" means "very spiny", a reference to spines found on the side of the fish's body.
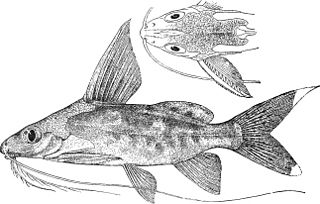
Synodontis alberti, the bigeye squeaker, Albert's syno, bigspotted squeaker, or high-fin synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Congo Basin of Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. It was originally described in 1891 by Belgian ichthyologist Louise Schilthuis after its discovery in the Malebo Pool of the Congo River.

Synodontis batesii is a species of upside-down catfish native to rivers of Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea and Gabon. It was first collected by G. L. Bates and described by Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1907, based upon holotypes discovered in the Dja River, near Bitye in Cameroon. The specific name "batesii" refers to the name of the collector of the first specimen.

Synodontis congicus is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo where it occurs in the upper and middle Congo Basin. It was first described by Belgian ichthyologist Max Poll in 1971. The first specimen was found near the town of Gangala-na-Bodio, Democratic Republic of the Congo, in the Dungu River. The meaning of the specific name "congicus" is "From the Congo".

Synodontis depauwi is a species of upside-down catfish that is endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo where it can be found in Stanley Pool. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, from specimens collected in Stanley Pool, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The species name depauwi is in honour of the "conservateur des collections de l'Université libre de Bruxelles", Louis De Pauw.

Synodontis flavitaeniatus, known as the orangestriped squeaker, the chocolatestriped squeaker, the yellowstriped squeaker, and the pyjama Syno, is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo where it is found in the lower and central Congo Basin. It was first described by Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1919. The holotype was collected from the Ruki River at Eala, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The meaning of the specific name "flavitaeniatus" is "yellow stripes".

Synodontis greshoffi is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Congo Basin of Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. It was first collected by M.A. Greshoff in Pool Malebo on the upper Congo River, and the species was named for him by the author of the first paper written about the species, Belgian ichthyologist Louise Schilthuis, in 1891.

Synodontis longirostris, known as the eyespot synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Democratic Republic of the Congo where it occurs in the Congo Basin. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1902, from specimens obtained in the Ubangi River at Banzyville. The species name longirostris comes from the Latin word longus, meaning "long", and the Latin word rostrum, meaning snout, referring to the long snout on this species.

Synodontis nigromaculatus, known as the spotted squeaker, the blackspotted squeaker, or the speckled squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is found widely in southern Africa. It has been identified in Angola, Botswana, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1905, from specimens collected in Lake Bangweulu in Zambia.

Synodontis notatus, known as the onespot squeaker, the one-spot synodontis, or the domino syno, is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Congo Basin of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Republic of the Congo. It was first described by French zoologist Léon Vaillant in 1893. The specific name "notatus" comes from the Latin word for "marked", as with a spot.
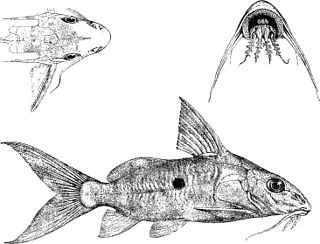
Synodontis nummifer, known as the two spot synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Congo Basin of Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. It was first described by the Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, based upon a holotype discovered in Léopoldville, Belgian Congo. The specific name "nummifer" comes from the Latin for "to bear a coin", which refers to the large spots on its sides.
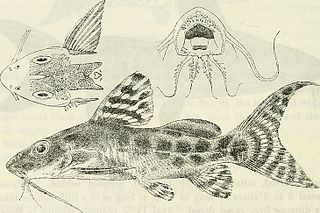
Synodontis ornatipinnis, known as the barfin synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Congo Basin of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, from specimens collected in Mbandaka, on the Congo River in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The species name ornatipinnis means "ornate fins".

Synodontis pardalis is a species of upside-down catfish that is endemic to Cameroon where it occurs in the Dja River drainage. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1908, from specimens collected in the Dja River in southern Cameroon. The species name pardalis is derived from the Greek word pardalis, which means "leopard", which refers to the spotted pattern on the fish.
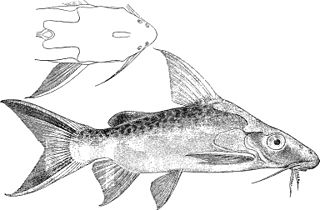
Synodontis pleurops, known as the Congo squeaker, the bigeye squeaker, or the bug eyed synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish native to the upper Congo Basin of Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. It was first described by the Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, based upon a holotype discovered at the Boyoma Falls, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Synodontis serratus, known as the shield-head squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Nile basin of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia and Sudan. It was first described by German naturalist and explorer Eduard Rüppell in 1829, from specimens obtained near Cairo, Egypt. The species name serratus comes from the Latin word serra, meaning "saw", which refers to the serrated pectoral spines of the species.

Synodontis smiti, known as the longtail Synodontis, or Smit's Synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo where it is found in the middle and upper Congo Basin. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1902, from specimens obtained in the Ubangi River at Banzyville. The species name smiti is named for Pierre Jacques Smit, who illustrated the plates in Boulenger's works.

Synodontis soloni, known as the scissortail synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo where it is found in the Ubangi River and the rapids just below Stanley Pool. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, from the Congo River in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The species name soloni is a patronym and in memory of Alexandre Solon, who assisted with the collection of fish.



















