
The Vanuatu rain forests are tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion which includes the islands of Vanuatu, as well as the Santa Cruz Islands group of the neighboring Solomon Islands. It is part of the Australasian realm, which includes neighboring New Caledonia and the Solomon Islands, as well as Australia, New Guinea, and New Zealand.
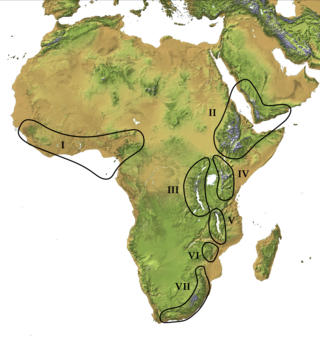
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.
The Torricelli Mountains are a mountain range in Sandaun Province, north-western Papua New Guinea. The highest peak in the range is Mount Sulen at 1650 meters. The Bewani Mountains are located to the west, and the Prince Alexander Mountains are located to the east. To the north, the mountains slope down to the Pacific Ocean, and to the south lies the basin of the Sepik River. Named after the Italian physicist and mathematician Evangelista Torricelli during the German colonial period.

Castanopsis acuminatissima is an evergreen tree native to Southeast Asia and New Guinea. It is known by a variety of common names over its range, including white oak, New Guinea oak, Papua New Guinea oak, ki riung, ko-duai, ko-soi, ko-mat, meranak, and riung anak.

The Huon Peninsula montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the mountains of northeastern New Guinea's Huon Peninsula.

The Samoan tropical moist forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Samoan Islands of the Pacific Ocean.

Ilex mitis is a tall, dense, evergreen tree that is indigenous to Sub-Saharan Africa and Madagascar. It makes an excellent fast-growing hedge for gardens - growing tall, straight and dense.

The Guinean montane forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of West Africa.

The Vogelkop–Aru lowland rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Indonesia. The ecoregion covers the peninsular lowlands of western New Guinea, along with the Aru Islands and other nearby islands.

The Vogelkop montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in western New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the mountains of western New Guinea's Bird's Head and Bomberai peninsulas.

The New Britain–New Ireland montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Papua New Guinea. The ecoregion includes the mountain rain forests on the islands of New Britain and New Ireland, which lie northeast of New Guinea.

The Northern New Guinea montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in northern New Guinea. The ecoregion covers several separate mountain ranges lying north of New Guinea's Central Range and south of the Pacific Ocean.

The Southeastern Papuan rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in southeastern New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the mountainous center and coastal lowlands of the Papuan Peninsula.

Syzygium claviflorum is a tree in the Myrtaceae family. It is native to the north of the Australian continent and in tropical and subtropical Asia. It is used for timber, as fuel, as human and cattle food, and for dye. Stunted specimens can be found on the top of the plateau of Bokor National Park, Cambodia.
A tree in the Anacardiaceae family, Buchanania macrocarpa is native to an area in the southwest Pacific from the Solomon Islands to the northern Maluku Islands.
Campnosperma brevipetiolatum is a species of tree in the Anacardiaceae family. It is native to an area in the west Pacific and Malesia from the Santa Cruz Islands to the Caroline Islands and Sulawesi. It is commonly used for its timber, including for canoe making, but also for oil-production and medicine. It has been used as an indicator species to identify 19th century sites of indigenous occupation in the Solomon Islands.
Nothofagus carrii is a species of tree in the family Nothofagaceae. It is endemic to New Guinea.
Nothofagus starkenborghiorum is a species of tree in the family Nothofagaceae. It is native to New Guinea and New Britain. It grows in montane rain forests, and occasionally in lowland rain forests.

Syzygium puberulum, commonly known as white satinash or downy satinash, is a plant in the family Myrtaceae which is native to rainforests of Cape York Peninsula, Queensland, and Papua New Guinea. It was first described in 1942.
Nepenthes calcicola is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to the northern Gulf Province in Papua New Guinea. Nepenthes calcicola was compared to Nepenthes neoguineensis. The species is characterized from N. neoguineensis by its stem that grows beneath the leaf litter, with rosettes of leaves producing erect pitchers which are sometimes half-buried in the litter, a much shorter stem, terete and recurved spur, the peduncle of the female inflorescence 160–190 mm by 3–4 mm, and the obovate to broadly obovate shape of the tepals. On the contrary, N. neoguineensis has stem that grow above the leaf litter, absence of rosettes of pitchers, dorsiventrally flattened and non-recurved spur, a much shorter peduncle of female inflorescence measuring only 120–150 mm by 2-2.5 mm and orbicular-elliptic shape of tepals. The species grows on closed forest over limestone karsts and is assessed as Vulnerable based on IUCN criteria.















