
Mato Grosso is one of the states of Brazil, the third largest by area, located in the Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.9% of the Brazilian GDP.

Mato Grosso do Sul is one of Brazil's 27 federal units, located in the southern part of the Central-West Region, bordering five Brazilian states: Mato Grosso, Goiás and Minas Gerais (northeast), São Paulo (east) and Paraná (southeast); and two South American countries: Paraguay and Bolivia (west). It is divided into 79 municipalities and covers an area of 357,145.532 square kilometers, which is about the same size as Germany. With a population of 2,839,188 inhabitants in 2021, Mato Grosso do Sul is the 21st most populous state in Brazil.

The white-bellied woolly mouse opossum is a small pouchless marsupial of the family Didelphidae. It was formerly assigned to the genus Micoureus, which was made a subgenus of Marmosa in 2009. The specific epithet was given in honour of Constance Sladen, wife of the naturalist Percy Sladen. She funded the 1902 expedition which collected the type specimen.

The Pantanal is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area, and the world's largest flooded grasslands. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, but it extends into Mato Grosso and portions of Bolivia and Paraguay. It sprawls over an area estimated at between 140,000 and 195,000 km2. Various subregional ecosystems exist, each with distinct hydrological, geological, and ecological characteristics; up to 12 of them have been defined.
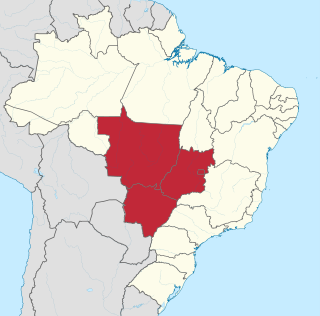
The Central-West or Center-West Region of Brazil is composed of the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul; along with Distrito Federal, where Brazil's national capital, Brasília, is situated. The region comprises 18.86% of the national territory, and is the least populated in Brazil.

Corumbá is a municipality in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, 425 km northwest of Campo Grande, the state's capital. It has a population of approximately 112,000 inhabitants, and its economy is based mainly on agriculture, animal husbandry, mineral extraction, and tourism, being the gateway to the biggest wetlands of the world, the Pantanal. Due to its border with Bolivia, Bolivians in Brazil constitute a significant portion of the city's population, forming a distinct cultural community. The city is served by Corumbá International Airport.

The hoary fox or hoary zorro, also known as raposinha-do-campo in Brazil, is a species of zorro or "false" fox endemic to Brazil. Unlike many other foxes, it feeds primarily on small invertebrates such as insects.

The buff-bellied hermit is a species of bird in the family Trochilidae, the hummingbirds. It is found in Bolivia and Brazil.

Rhinella scitula is a species of toads in the family Bufonidae. It is found in the southwestern Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, and in the adjacent southeastern Paraguay.
Ameerega braccata, formerly Epipedobates braccatus, is a species of frog in the family Dendrobatidae. It is endemic to the Central-West Region of Brazil and is known from southern Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, and southwestern Goiás states; however, it is likely that its true range extends into adjacent Bolivia and Paraguay.

Phyllomedusa boliviana is a species of frog in the subfamily Phyllomedusinae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, and Brazil. It has been observed between 200 and 1800 meters above sea level.

Physalaemus albonotatus is a species of frog in the family Leptodactylidae. It is found in Brazil, Paraguay, and Chacoan Argentina and Bolivia.

The blue-eyed ground dove is a species of bird in the family Columbidae. It is endemic to the Cerrado region of Brazil.

The Mato Grosso antbird is a species of bird in subfamily Thamnophilinae of family Thamnophilidae, the "typical antbirds". It is found in Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay.
Nectandra matogrossensis is a species of plant in the family Lauraceae.

Lobelia siphilitica, the great blue lobelia, great lobelia, or blue cardinal flower, is a plant species within the family Campanulaceae. It is an herbaceous perennial dicot native to eastern and central Canada and United States. There are two recognized varieties of Lobelia siphilitica, var. siphilitica and var. ludoviciana. Blooming from August to October, it is short-lived, lasting only for a few years.
Taiamã Ecological Station is an ecological station in the Mato Grosso state of Brazil.

Spix's red-handed howler is a species of Howler monkey native to the southeastern Amazon in Brazil. It is threatened by deforestation and hunting.

Tabernaemontana pandacaqui, known as windmill bush and banana bush, is a species of plant in the dogbane family Apocynaceae.

Tabernaemontana rupicola is a species of plant in the family Apocynaceae.


















