
Hawaii is an island state in the Western United States, about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) from the U.S. mainland in the Pacific Ocean. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only one which is an archipelago, and the only one in the tropics.
Hawaiian is a Polynesian language of the Austronesian language family that takes its name from Hawaiʻi, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the US state of Hawaii. King Kamehameha III established the first Hawaiian-language constitution in 1839 and 1840.

Hawaii is the largest island in the United States, located in the state of Hawaii. It is the southeasternmost of the Hawaiian Islands, a chain of volcanic islands in the North Pacific Ocean. With an area of 4,028 square miles (10,430 km2), it has 63% of the Hawaiian archipelago's combined landmass. However, it has only 13% of the archipelago's population. The island of Hawaiʻi is the third largest island in Polynesia, behind the north and south islands of New Zealand.

The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major volcanic islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaiʻi in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll. Formerly called the Sandwich Islands, the present name for the archipelago is derived from the name of its largest island, Hawaiʻi.

The governor of Hawaii is the head of government of the U.S. state of Hawaii and its various agencies and departments, as provided in the Hawaii State Constitution Article V, Sections 1 through 6. It is a directly elected position, votes being cast by popular suffrage of residents of the state.

Channa striata, the striped snakehead, is a species of snakehead fish. It is also known as the common snakehead, chevron snakehead, or snakehead murrel and generally referred simply as mudfish. It is native to South and Southeast Asia, and has been introduced to some Pacific Islands. Reports from Madagascar and Hawaii are misidentifications of C. maculata.

Hydrocotyle, also called floating pennywort, water pennywort, Indian pennywort, dollar weed, marsh penny, thick-leaved pennywort and white rot, is a genus of prostrate, perennial aquatic or semi-aquatic plants formerly classified in the family Apiaceae, now in the family Araliaceae.

Aeromonas is a genus of Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, bacteria that morphologically resemble members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Most of the 14 described species have been associated with human diseases. The most important pathogens are A. hydrophila, A. caviae, and A. veronii biovar sobria. The organisms are ubiquitous in fresh and brackish water.

Aeromonas hydrophila is a heterotrophic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium mainly found in areas with a warm climate. This bacterium can be found in fresh or brackish water. It can survive in aerobic and anaerobic environments, and can digest materials such as gelatin and hemoglobin. A. hydrophila was isolated from humans and animals in the 1950s. It is the best known of the species of Aeromonas. It is resistant to most common antibiotics and cold temperatures and is oxidase- and indole-positive. Aeromonas hydrophila also has a symbiotic relationship as gut flora inside of certain leeches, such as Hirudo medicinalis.

Euglandina rosea, the rosy wolfsnail or cannibal snail, is a species of medium-sized to large predatory air-breathing land snail, a carnivorous terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Spiraxidae.

Achatina achatina, commonly known as the giant African snail, also known as the giant tiger land snail, and gigantocochlea, is a species of large, air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Achatinidae. The name "Achatina" is from "achates", Greek for agate. It shares the common name "giant African snail" with other species of snails such as Lissachatina fulica and Archachatina marginata.

Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875. Much of the harbor and surrounding lands are now a United States Navy deep-water naval base. It is also the headquarters of the United States Pacific Fleet. The U.S. government first obtained exclusive use of the inlet and the right to maintain a repair and coaling station for ships here in 1887. The surprise attack by the Imperial Japanese Navy on December 7, 1941, led the United States to declare war on the Empire of Japan, making the attack on Pearl Harbor the immediate cause of the United States' entry into World War II.
Tamsica is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.
Aeromonas infections include skin infections such as cellulitis, pustules, and furuncles. Aeromonas species can also cause gastroenteritis.

Allium tuncelianum is a species of wild onion which is endemic to the Munzur Valley in Tunceli, in eastern Turkey.It usually produces a single-bulb white onion, unlike garlic, which has multiple bulbs. It has a garlic odor and taste and is used locally like garlic. Its common names include Tunceli garlic and Ovacik garlic. Botanists have suggested this species may be a close relative of garlic, and perhaps an ancestor of garlic, but genetic analysis shows that it is actually more closely related to leek. The plant is collected from the wild for use in cooking, a phenomenon that threatens the plant with extinction. It is known that Tunceli garlic shows higher antiradical activity and contains more total phenolic compounds than normal garlic. In addition, it is possible to say that Tunceli garlic is a better natural antioxidant than Kastamonu garlic. Tunceli garlic is single-toothed, has small tooth-like formations between its shells, has the familiar taste and aroma of garlic, unlike others, it can flower and give seeds. It has a chance to be used in consumption as well as in industry, due to its features such as being single-toothed, the number of shells being less compared to the cultivated garlic, and the storage of the head parts. It is stored for a long time at 18-20"C. It is collected from the mountains in the region and sold under the name of 'Rock garlic' and used as commercial goods. In an experiment conducted at Malatya Turgut Özal University, the effect of intraperitoneal injection of 1% and 10% doses of Tunceli garlic oil on some immunological factors of rainbow trout was evaluated. Rohu pups were fed a garlic supplemented diet for 60 days. This fish was then exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila by IP injection. Rainbow trout fry were fed garlic to groups for 14 days prior to intraperitoneal injection challenge with Aeromonas hydrophila per fish. In both of these studies, it was noted that fish fed garlic showed increased serum lysozyme and bactericidal activities and higher serum total protein.
Tamsica hyacinthina is a moth of the family Crambidae. It is endemic to the Hawaiian islands of Oahu and Hawaii.

In molecular biology, aerolysin is a cytolytic pore-forming toxin exported by Aeromonas hydrophila, a Gram-negative bacterium associated with diarrhoeal diseases and deep wound infections. It is also produced by the caterpillar of the moth Megalopyge opercularis, sometimes called the Tree Asp. The mature toxin binds to eukaryotic cells and aggregates to form holes leading to the destruction of the membrane permeability barrier and osmotic lysis. The structure of proaerolysin has been determined to 2.8A resolution and shows the protoxin to adopt a novel fold. Images of an aerolysin oligomer derived from electron microscopy have helped to construct a model of the protein in its heptameric conformation, and to outline a mechanism by which this assembly might insert into lipid bilayers to form ion channels.
Aeromonas dhakensis is a Gram-negative bacterium first isolated from aquariums in Portugal in 2005. The species is globally distributed in aquatic environments, like other species in the genus Aeromonas.
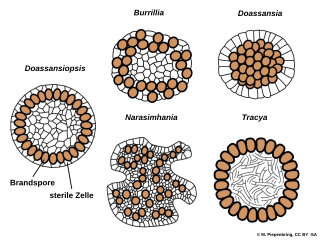
Doassansiopsis is a genus of smut fungi belonging to the monotypic family DoassansiopsidaceaeBegerow, R.Bauer & Oberw., 1998, within the class Ustilaginomycetes and order Urocystidales.

Peltigera hydrophila is a species of foliose lichen in the family Peltigeraceae. First described in 2020, it distinguishes itself through a distinct, hairless thallus that turns deep blue-violet when it becomes wet. Found primarily in the Magallanes Region of Chile, this small leafy lichen clings closely to mosses and other substrates. Distinctive features include the always-present reddish-brown to dark brown apothecia and the Peltigera-type ascospores that contain three internal partitions, or septa. Despite sharing a habitat with similar species like P. aubertii and P. frigida, P. hydrophila sets itself apart through its unique thallus surface texture and colour. This semi-aquatic lichen primarily thrives in humid forests, shrubby and herbaceous vegetation in southern Chile, particularly near waterfalls, streams, and other wet environments.













