
John Calvin was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of Christian theology later called Calvinism, including its doctrines of predestination and of God's absolute sovereignty in the salvation of the human soul from death and eternal damnation. Calvinist doctrines were influenced by and elaborated upon the Augustinian and other Christian traditions. Various Congregational, Reformed and Presbyterian churches, which look to Calvin as the chief expositor of their beliefs, have spread throughout the world.

Jan Hus, sometimes anglicized as John Hus or John Huss, and referred to in historical texts as Iohannes Hus or Johannes Huss, was a Czech theologian and philosopher who became a Church reformer and the inspiration of Hussitism, a key predecessor to Protestantism, and a seminal figure in the Bohemian Reformation. Hus is considered to be the first Church reformer, even though some designate the theorist John Wycliffe. His teachings had a strong influence, most immediately in the approval of a reformed Bohemian religious denomination and, over a century later, on Martin Luther.
The terms Old Catholic Church, Old Catholics, Old-Catholic churches, or Old Catholic movement, designate "any of the groups of Western Christians who believe themselves to maintain in complete loyalty the doctrine and traditions of the undivided church but who separated from the see of Rome after the First Vatican council of 1869–70".
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation and the European Reformation, was a major theological movement or period or series of events in Western Christianity in 16th-century Northwestern Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and the authority of the Catholic Church. Towards the end of the Renaissance, the Reformation marked the beginning of Protestantism and in turn resulted in a major schism within Western Christianity.
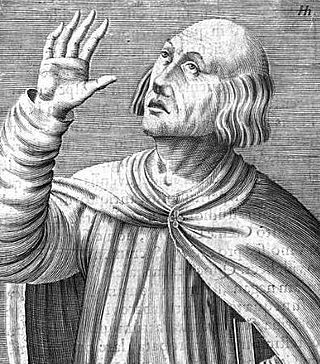
Berengar of Tours, in Latin Berengarius Turonensis, was an 11th-century French Christian theologian and archdeacon of Angers, a scholar whose leadership of the cathedral school at Chartres set an example of intellectual inquiry through the revived tools of dialectic that was soon followed at cathedral schools of Laon and Paris. Berengar of Tours was distinguished from mainline Catholic theology by two views: his assertion of the supremacy of Scripture and his denial of transubstantiation.

Peter Waldo was the leader of the Waldensians, a Christian spiritual movement of the Middle Ages.

Beeldenstorm in Dutch and Bildersturm in German are terms used for outbreaks of destruction of religious images that occurred in Europe in the 16th century, known in English as the Great Iconoclasm or Iconoclastic Fury. During these spates of iconoclasm, Catholic art and many forms of church fittings and decoration were destroyed in unofficial or mob actions by Calvinist Protestant crowds as part of the Protestant Reformation. Most of the destruction was of art in churches and public places.

The Waldensians, also known as Waldenses, Vallenses, Valdesi, or Vaudois, are adherents of a church tradition that began as an ascetic movement within Western Christianity before the Reformation. Originally known as the Poor of Lyon in the late twelfth century, the movement spread to the Cottian Alps in what is today France and Italy. The founding of the Waldensians is attributed to Peter Waldo, a wealthy merchant who gave away his property around 1173, preaching apostolic poverty as the way to perfection.

Norbert of Xanten, O. Praem (Gennep-Magdeburg), also known as Norbert Gennep, was Archbishop of Magdeburg, founder of the Premonstratensian order of canons regular, and is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church. Norbert was canonized by Pope Gregory XIII in the year 1582, and his statue appears above the Piazza colonnade of St. Peter's Square in Rome.
Peter of Bruys was a medieval French religious teacher. He was called a heresiarch by the Roman Catholic Church because he opposed infant baptism, the erecting of churches and the veneration of crosses, the doctrine of transubstantiation and prayers for the dead. An angry Roman Catholic mob murdered him in or around 1131.

William Sawtrey, also known as William Salter was an English Roman Catholic priest and Lollard martyr. He was executed for heresy.
Henry of Lausanne was a French heresiarch of the first half of the 12th century. His preaching began around 1116 and he died imprisoned around 1148. His followers are known as Henricians.
Heresy in Christianity denotes the formal denial or doubt of a core doctrine of the Christian faith as defined by one or more of the Christian churches.

Reformed Christianity originated with the Reformation in Switzerland when Huldrych Zwingli began preaching what would become the first form of the Reformed doctrine in Zürich in 1519.

St. Norbert Abbey is a Roman Catholic monastery of Canons Regular of Premontre, located in De Pere, Wisconsin. The Abbey is named after Saint Norbert of Xanten, the founder of the order, after whom, members are known as, "Norbertines". St. Norbert Abbey was established in 1898 by Norbertines from Berne Abbey in the Netherlands. St. Norbert's is the oldest religious community of its kind in the United States, serving as the Mother Canonry to Norbertines across North America.

Daylesford Abbey is a Roman Catholic monastery of Canons Regular of Premontre, located in Chester County, Pennsylvania, about 20 miles west of Philadelphia. The Abbey is named after Daylesford, Pennsylvania, where the Norbertine Fathers established the foundation that developed into the Abbey.

In the history of Belgium, the period from 1789 to 1914, dubbed the "long 19th century" by the historian Eric Hobsbawm, includes the end of Austrian rule and periods of French and Dutch rule over the region, leading to the creation of the first independent Belgian state in 1830.
Johannes Saliger was a sixteenth century radical Lutheran theologian and controversialist. He was a leading protagonist in "the Saliger Controversy" which bears his name.
Apostolici, Apostolic Brethren, or Apostles, are the names given to various Christian heretics, whose common doctrinal feature was an ascetic rigidity of morals, which made them reject property and marriage.

Proto-Protestantism, also called pre-Protestantism, refers to individuals and movements that propagated various ideas later associated with Protestantism before 1517, which historians usually regard as the starting year for the Reformation era. The relationship between medieval sects and Protestantism is an issue that has been debated by historians.














