
The brook trout is a species of freshwater fish in the char genus Salvelinus of the salmon family Salmonidae. It is native to Eastern North America in the United States and Canada, but has been introduced elsewhere in North America, as well as to Iceland, Europe, and Asia. In parts of its range, it is also known as the eastern brook trout, speckled trout, brook charr, squaretail, brookie or mud trout, among others. A potamodromous population in Lake Superior, is known as coaster trout or, simply, as coasters. Anadromous populations which are found in coastal rivers from Long Island to Hudson Bay are sometimes referred to as salters. The brook trout is the state fish of nine U.S. states: Michigan, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Vermont, Virginia, and West Virginia, and the Provincial Fish of Nova Scotia in Canada.

The Arctic char or Arctic charr is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes, as well as Arctic and subarctic coastal waters in the Holarctic.

Sea trout is the common name usually applied to anadromous (sea-run) forms of brown trout, and is often referred to as Salmo trutta morpha trutta. Other names for anadromous brown trout are bull trout, sewin (Wales), peel or peal, mort, finnock (Scotland), white trout (Ireland), Dollaghan (Northern Ireland and salmon trout.

The silver trout is an extinct char species or subspecies that inhabited a few waters in New Hampshire in the United States prior to 1939, when a biological survey conducted on the Connecticut watershed by the New Hampshire Fish and Game Department found none.

Salvelinus is a genus of salmonid fish often called char or charr; some species are called "trout". Salvelinus is a member of the subfamily Salmoninae within the family Salmonidae. The genus has a northern circumpolar distribution, and most of its members are typically cold-water fish that primarily inhabit fresh waters. Many species also migrate to the sea.

The giant bully, tītarakura, or tīpokopoko (Māori), is a species of fish in the family Eleotridae endemic to New Zealand.

The upland bully is a species of fish in the family Eleotridae endemic to freshwater habitats in New Zealand. Both sexes have distinctive orange-brown dots all over the head. Adults generally reach a length of 8–10 cm (3.1–3.9 in).

Cran's bully is a species of fish in the family Eleotridae endemic to New Zealand, where it is only found in fresh waters. This species can reach a length of 9 cm (3.5 in).

The bluegill bully is a fish in the family Eleotridae that is endemic to New Zealand. It lives in shallow, fast-flowing riffles and torrents, where it forages and shelters amongst the gravels. It has a similar distribution to the other endemic riffle specialist, the torrentfish. It can be found up to 100 kilometres (62 mi) inland, and from sea level up to an elevation of 480 metres (1,570 ft). The bluegill bully is the smallest of the Eleotrids, commonly reaching only 60–70 mm (2.4–2.8 in).

The redfin bully is a species of freshwater fish in the family Eleotridae endemic to New Zealand. Being amphidromous, it spends part of its life cycle at sea. Males have distinctive bright red patterns and stripes on their fins. Adults grow to an average of 80–100 mm (3.1–3.9 in) total length, with a maximum of 120 mm (4.7 in).
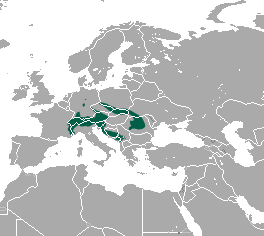
The alpine shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in the alpine meadows and coniferous forests of central and southern European mountain ranges.

Gerald Stokell was a New Zealand amateur ichthyologist.

Coregonus alpinus is a species of freshwater whitefish in the family Salmonidae. It is endemic to Lake Thun, in Switzerland's Interlaken region, where it is found in deep water. The maximum length recorded for this species is 25 centimetres (9.8 in). It feeds on chironomids and other bottom-dwelling invertebrates. It is known as the kropfer, a name also applied to the probably extinct species Coregonus restrictus.
Salvethymus svetovidovi, also called the long-finned charr, is a species of salmonid fish. It is endemic to Elgygytgyn Lake in Chukotka, Far East of Russia, together with another species, the small-mouth char Salvelinus elgyticus. A third char species in the same lake is Salvelinusboganidae, the Boganid char.
Salvelinus inframundus, also known as Orkney charr is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae which is endemic to Scotland.

Salvelinus killinensis, also known as Haddy charr is a variety of charr found in certain lakes in Scotland.

Salvelinus umbla, also known as lake char, is a species of char found in certain lakes of the region of the Alps in Europe.

Gobiomorphus is a genus of fishes in the family Eleotridae native to New Zealand and Australia. They are typically small, benthic fishes with large, rounded fins and two dorsal fins. Many have an amphidromous lifecycle: the eggs are laid in fresh water, but the fry are dispersed to sea soon after hatching, and grow there for several months before returning to fresh water.

Gobiomorphus australis, the striped gudgeon, is a fish in the family Eleotridae, native to eastern Australia. It can be found in a wide variety of habitats from clear streams with rapid currents to muddy stillwaters such as ponds and waterholes. Juveniles are common in estuaries near rocks, submerged logs and among vegetation. They are good climbers and are able to clamber over wet rocky surfaces such as rapids and waterfalls.
The Coomsaharn char is a species of lacustrine char fish in the family Salmonidae.
















