Las Choapas is a city and its surrounding municipality in the southeastern extremes of the Mexican state of Veracruz. It is bordered by the municipalities of Uxpanapa, Minatitlán, Moloacán, and Agua Dulce in Veracruz, Huimanguillo in Tabasco, Cintalapa and Tecpatán in Chiapas, and Santa María Chimalapa in Oaxaca. Its major products are cattle breeding, corn, oil, fruit, sugar, and rubber. In the past it had a rice miller. It is one of the largest municipalities in Veracruz, with an area of 2,851.2 km². At the 2005 census the city had a population of 40,773 inhabitants, while the municipality had a population of 70,092. It is a very hot place, as temperature reaches up to 40 degrees Celsius. It has had some tornadoes in the past. It is connected to the communities of Raudales-Ocozocoautla in Chiapas through the Chiapas bridge.
The Ferrocarril del Istmo de Tehuantepec, also known as Tren Interoceánico, Line Z, Ferrocarril Transístmico or simply Ferroistmo, is part of the Interoceanic Corridor of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, owned by the Mexican government, that crosses the Isthmus of Tehuantepec between Puerto Mexico, Veracruz, and Salina Cruz, Oaxaca. It is leased to Ferrocarril del Sureste FERROSUR.

Acapetahua is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas, in southern Mexico. As of 2010, the municipality had a total population of 27,580, up from 14,189 in 2005.

Juárez is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.
Tonalá is a municipality in the state of Chiapas in southern Mexico.

Ciudad Hidalgo is a city in the Mexican state of Chiapas. It serves as the municipal seat of the surrounding municipality of Suchiate which is the southernmost in Mexico. In the 2010 INEGI Census, it reported a population of 14,606 inhabitants.
Cuichapa is a municipality in the Mexican state of Veracruz.
Jáltipan is a municipality in the Mexican state of Veracruz.

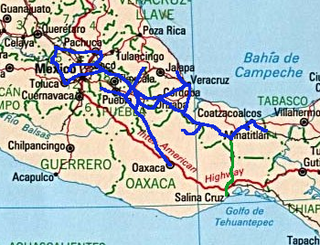
The Interoceanic Corridor of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, abbreviated as CIIT, is a trade and transit route in Southern Mexico, under the control of the Mexican Secretariat of the Navy, which connects the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans through a railway system, the Railway of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec , for both cargo and passengers, crossing through the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. This project also consists on the modernization and growth of local seaports, particularly the ports of Salina Cruz (Oaxaca) and Coatzacoalcos (Veracruz), and of the Minatitlán oil refinery and the Salina Cruz oil refinery. In addition, it plans to attract private investors through the creation of 10 industrial parks in the Isthmus area, as well as two other parks in Chiapas. The project has the goal of developing the economy and industry of the Mexican South through encouraging economic investment, both national and international, and facilitate commerce and transportation of goods internationally.

The Coatzacoalcos–Pakal Ná (Palenque) Line, also known as the FA Line, is a railroad owned by the Mexican government, connecting Coatzacoalcos, Veracruz, and Palenque, Chiapas. It was leased to the Ferrocarriles Chiapas-Mayab company.
Roberto Ayala railway station is a railway station in Huimanguillo, Tabasco.
Palenque railway station (Spanish: Estación de Palenque, referred to as Pakal Ná by Tren Interoceánico, is a railway station located between the towns of Palenque and Pakal Ná in Chiapas, Mexico. The station was built on the territory of a former airport. It is the southern terminus of the Tren Maya.
Line K, also known as the Ixtepec–Ciudad Hidalgo Line, is a railroad owned by the Mexican government that connects Ixtepec, Oaxaca with Ciudad Hidalgo, Chiapas. It was leased to the Ferrocarril Chiapas-Mayab. President Andrés Manuel López Obrador announced that the Mexican government will rehabilitate the line from Ixtepec, Oaxaca to Ciudad Hidalgo, Chiapas.
Pijijiapan is a former and future railway station in Pijijiapan, Chiapas.
Mapastepec is a former and future railway station in Mapastepec, Chiapas.
Villa Comaltitlán is a former and future railway station in Villa Comaltitlán, Chiapas.
Tapachula is a former and future railway station in Tapachula, Chiapas.
Salto de Agua railway station, also known since 2024 as the Pino Suárez railway station, is a train station in Salto de Agua, Chiapas.
Huixtla is a former and future railway station in Huixtla, Chiapas. The building is unique to this region, because it is made from bricks and mud tile roof.

The Interoceanic Train of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec is a government-owned railway system in Mexico that has 3 lines. It seeks to become a global logistics network focused on the manufacture and movement of goods between the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean through the Isthmus of Tehuantepec.









