Teesta Bazaar is a village located 4 km (2.5 mi) downstream from the town of Melli on the right bank of Teesta River in the Kalimpong I CD block in the Kalimpong subdivision of Kalimpong district of the state of West Bengal, India.
Jaldhaka is a small town in the Gorubathan CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India. It lies on the bank of Jaldhaka River.
Loleygaon is a village in the Kalimpong II CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the Indian state of West Bengal.

Suntalekhola or Suntaley Khola is a village and a tourist spot in the Gorubathan CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of Kalimpong District in the state of West Bengal, India.
Bindu is a village in the Gorubathan CD block in the Kalimpong subdivision of the Kalimpong district in West Bengal, India. Bindu lies in the Indo-Bhutan border, India's second oldest dam is situated at Bindu on River Jaldhaka. It is located 121 Km from Kalimpong Town, 103 Km from Siliguri City and 85 km from Jalpaiguri city. It takes around 4hrs from Siliguri to reach Bindu. Roadway is the only option to reach Bindu. The roads are good for most part of the journey but during the last 15-20 Km it's mostly off road. As of 2023, a road is under construction by the Border Road Organization and is due to connect Bindu and surrounding area with NH17.
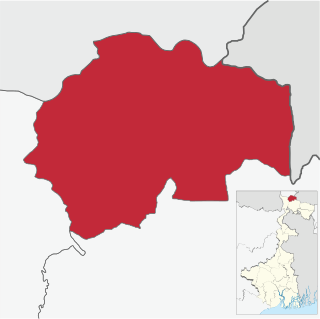
The Kalimpong subdivision is the sole subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India. It was initially formed as a subdivision of the Darjeeling district in 1916 under British India. On 14 February 2017 the subdivision was promoted to a district, becoming an independent Kalimpong district. The subdivision has its headquarters at Kalimpong Town and consists of the hilly areas annexed from Bhutan at the end of the Anglo-Bhutanese War in 1865.

Jholung or Jholong is a village in the Gorubathan CD block in the Kalimpong subdivision of the Kalimpong district in West Bengal, India.
Bich Kagay is a village in the Kalimpong II CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in West Bengal, India
Sillery Gaon is a village in the Kalimpong II CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India.

Rishyap is a village in the Kalimpong II CD block in the Kalimpong subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the Indian state of West Bengal.
Kolakham is a village in the Kalimpong II CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India.
Ramdhura is a village in Kalimpong II CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India.

Teesta Low Dam - IV Hydropower Plant is a run-of-the-river hydroelectric station built on the Teesta River at Kalijhora, Kalimpong district, West Bengal.
Kumai Tea Garden is a village in the Gorubathan CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India.
Samabiyong Tea Garden is a village in the Gorubathan CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India.
Rambi Bazar is an urban village lying near Teesta River in the Kalimpong I CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India. The town lies on the National Highway 10 connecting Siliguri and Gangtok. Teesta Low Dam - III Hydropower Plant and Riyang railway station lies in Rambi. Rambi bazaar is famous for Mushroom, there are around 30 to 40 mushroom shops and stalls in the market area where different types of edible mushrooms are available for sale.
Dungra is a census town in the Kalimpong I CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India.
Rongo is a village in the Gorubathan CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India.
Bhalukhop is a village in the Kalimpong I CD block in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India.
Kalijhora is an urban village in the Kalimpong I CD block that lies on the bank of River Teesta, in the Kalimpong Sadar subdivision of the Kalimpong district in the state of West Bengal, India. National Highway 10 connecting Siliguri and Gangtok passes through Kalijhora. Teesta Low Dam - IV Hydropower Plant Dam lies in Kalijhora.