
The chlorarachniophytes are a small group of exclusively marine algae widely distributed in tropical and temperate waters. They are typically mixotrophic, ingesting bacteria and smaller protists as well as conducting photosynthesis. Normally they have the form of small amoebae, with branching cytoplasmic extensions that capture prey and connect the cells together, forming a net. These extensions are dependent on the presence of light and polymerization of the actin cytoskeleton. They may also form flagellate zoospores, which characteristically have a single subapical flagellum that spirals backwards around the cell body, and walled coccoid cells.

Bryopsidales is an order of green algae, in the class Ulvophyceae.

Chlorococcaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlamydomonadales. They are mostly soil-dwelling algae. Many members of this group produce lipids and secondary carotenoids.

Characium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is very commonly found in freshwater habitats, where it is attached to phytoplankton or zooplankton.

Chlamydocapsa is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae.

Cylindrocapsa is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats.
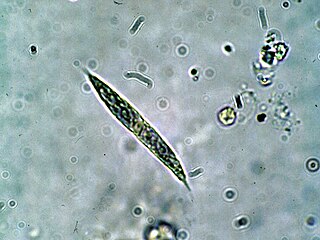
Quadrigula is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats as phytoplankton.

Schroederia is a genus of green algae in the family Schroederiaceae. Schroederiaceae is a monotypic taxon; Schroederia is its only genus.

Tetraedron is a genus of green algae in the family Hydrodictyaceae. It may also be spelled as Tetraëdron.
Vitreochlamys is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. It is sometimes known by the name Sphaerellopsis, published by Aleksandr Arkadievich Korshikov. However, that name is an illegitimate later homonym, preceded by SphaerellopsisM.C.Cooke. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats.

Cosmarium is a large genus of desmids (Desmidiaceae), a group of green algae closely related to the land plants (Embryophyta). Members of this genus are microscopic and found in freshwater habitats around the world.
Gilbertsmithia is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae, containing the single species Gilbertsmithia grandis. It was named after the American botanist Gilbert Morgan Smith. This remarkable alga has only been recorded once from a muddy rainwater pool in Madras, India.
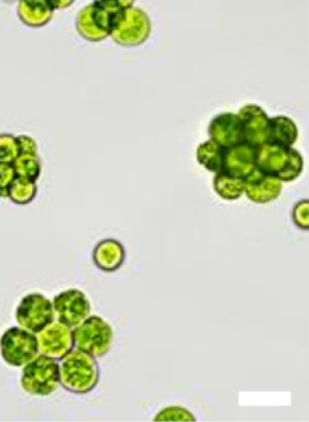
Deasonia is a genus of green algae, in the family Actinochloridaceae. It is found in soils.
Deuterocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, attached to algae or detritus. It is rare and has only been recorded from Europe.
Lanceola is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae, containing a single species, Lanceola spatulifera. It is found in freshwater habitats.

Chlorotetraedron is a genus of green algae, in the family Neochloridaceae. The name may also be written as Chlorotetraëdon. It is found as freshwater plankton or in soil.
Follicularia is a genus of green algae, in the family Schizochlamydaceae. It is found in terrestrial habitats, mainly soil.

Chlorokybus is a multicellular (sarcinoid) genus of basal green algae or charophyte. It has been classified as the sole member of the family Chlorokybaceae, which is the sole member of the order Chlorokybales, in turn the sole member of the class Chlorokybophyceae. It grows on soil and rock surfaces, and is rare.

Klebsormidium is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae comprising 20 species. The name was proposed in 1972 to resolve confusion in application and status of Hormidium and was given for the German botanist Georg Albrecht Klebs.
Ilsteria is a genus of algae from the yellow-green algae class. It is a colonial organism, generally consisting of four or – sometimes – two cells. This genus is named after a Latvian botanist, teacher and poet Jānis Ilsters (1851–1889).













