
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.

Chlamydomonadaceae is a family of algae within the order Chlamydomonadales. Traditionally, it has been defined as containing single-celled flagellates with a cell wall.

Asterococcus is a genus of green algae in the order Chlamydomonadales. It is planktonic in freshwater ponds and lakes, or benthic within mires and swamps. It is a common and widespread genus, but is rarely abundant.

Bracteacoccus is a genus of green algae, the sole genus of the family Bracteacoccaceae. It is a terrestrial alga commonly found in soils, from the tropics to the poles.
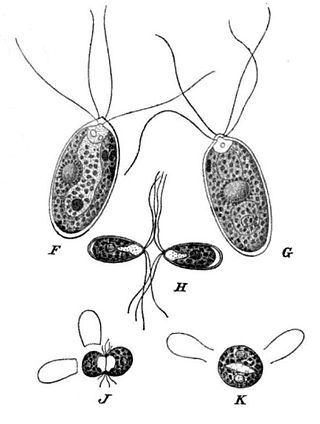
Carteria is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. Carteria are similar in morphology to the common genus Chlamydomonas and differ by having four, rather than two, flagella at the vegetative stage.
Characiochloris is a genus of green algae in the family Characiochloridaceae. Characiochloris is epiphytic on freshwater algae, or found in soil.
Characiopodium is a genus of green algae in the family Sphaeropleaceae. It occurs in soils.

Characium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is very commonly found in freshwater habitats, where it is attached to phytoplankton or zooplankton.
Dictyochloris is a genus of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. It is the sole genus of the family Dictyochloridaceae. It is commonly found in terrestrial and subaerial habitats.

Neochloris is a genus of green algae in the family Neochloridaceae. It is found in freshwater aquatic and terrestrial soil habitats.
Palmellopsis is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Palmellopsidaceae. They are either planktonic or attached to substrates in fresh water, or in aeroterrestrial habitats.

Planktosphaeria is a genus of Chlorophyceae of the green algae. It was first described by the phycologist Gilbert Morgan Smith in 1918, with Planktosphaeria gelatinosa as its type species. Species of Planktosphaeria are commonly found in freshwater plankton around the world.

Schroederia is a genus of green algae in the family Schroederiaceae. Schroederiaceae is a monotypic taxon; Schroederia is its only genus.
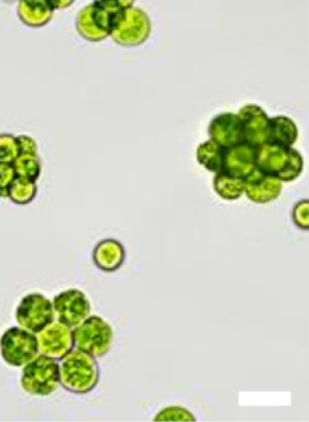
Actinochloridaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlamydomonadales.

Characiaceae is a family of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales. It contains epiphytic or planktonic algae that are unicellular or colonial. The cells are heteropolar, with basal and apical ends having different shapes. The daughter cells are often retained in the cell wall of the old mother cell, whose cell wall becomes gelatinized.
Follicularia is a genus of green algae, in the family Schizochlamydaceae. It is found in terrestrial habitats, mainly soil.
Pseudodictyochloris is a genus of green algae, in the family Actinochloridaceae. It is found in soils.
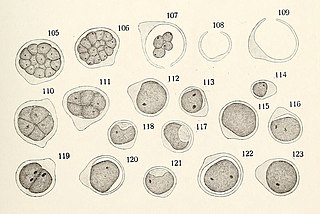
Myrmecia is a genus of green algae that is associated with lichens.
Bracteamorpha is a genus of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales, and is the only genus in the family Bracteamorphaceae. It contains a single species, Bracteamorpha trainorii.

Chlorosarcinaceae is a family of chlorophyte green algae, in the order Chlamydomonadales. Members of this genus are found in soils.











