This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(February 2025) |
| Tetrated dodecahedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Near-miss Johnson solid |
| Faces | 4 equilateral triangles 12 isosceles triangles 12 pentagons |
| Edges | 54 |
| Vertices | 28 |
| Vertex configuration | 4 (5.5.5) 12 (3.5.3.5) 12 (3.3.5.5) |
| Symmetry group | Td |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
 | |


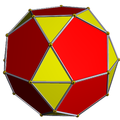
In geometry, the tetrated dodecahedron is a near-miss Johnson solid. It was first discovered in 2002 by Alex Doskey. It was then independently rediscovered in 2003, and named, by Robert Austin. [1]
Contents
It has 28 faces: twelve regular pentagons arranged in four panels of three pentagons each, four equilateral triangles (shown in blue), and six pairs of isosceles triangles (shown in yellow). All edges of the tetrated dodecahedron have the same length, except for the shared bases of these isosceles triangles, which are approximately 1.07 times as long as the other edges. This polyhedron has tetrahedral symmetry.
Topologically, as a near-miss Johnson solid, the four triangles corresponding to the face planes of a tetrahedron are always equilateral, while the pentagons and the other triangles only have reflection symmetry.