
Petter Adolf Karsten was a Finnish mycologist, the foremost expert on the fungi of Finland in his day, and known in consequence as the "father of Finnish mycology".
Scutula is a genus of lichenicolous fungi in the family Ramalinaceae.

The Chaetothyriales are an order of ascomycetous fungi in the class Eurotiomycetes and within the subclass Chaetothyriomycetidae. The order was circumscribed in 1987 by mycologist Margaret Elizabeth Barr-Bigelow.
Geltingia is a fungal genus in the family Helicogoniaceae. It is monotypic, containing the single lichenicolous species Geltingia associata. The genus was circumscribed in 1990 by mycologists Vagn Alstrup and David Leslie Hawksworth. The genus name honours Danish scientist Paul Gelting.

Unguiculariopsis is a genus of lichenicolous fungi in the family Cordieritidaceae. It has 29 species.
Endococcus is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) in the family Lichenotheliaceae. It has 44 species. The genus was circumscribed by the Finnish botanist William Nylander in 1855. Although at least one source places the genus in the Verrucariaceae, a 2016 study of the type species, Endococcus rugulosus, determined that it should instead be placed in the family Lichenotheliaceae of the order Dothideales; this classification echoes a placement proposed in 1979 by David Hawksworth.

Abrothallus is a genus of lichenicolous fungi. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Abrothallaceae, which itself is the sole taxon in the order Abrothallales.
Skyttella is a genus of lichenicolous fungi in the family Cordieritidaceae. It contains two species. The genus was circumscribed in 1988 by David Leslie Hawksworth and Rolf Santesson, with Skyttella mulleri assigned as the type species. This species, which parasitizes the lobes of foliose lichens in the genus Peltigera, was previously classified in the genus Phacopsis. Skyttella stictae, an Ecuadorian species that grows on Sticta, was added to the genus in 2017.

Skyttea is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi in the family Cordieritidaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1981 by lichenologists Martha Allen Sherwood, David L. Hawksworth, and Brian J. Coppins, with Skyttea nitschkei assigned as the type species.

Nesolechia is a genus of parasitic fungi in the family Parmeliaceae. All three species in the genus grow on lichens. Nesolechia probably evolved from a lichen ancestor, as it is closely related to many lichenized species of fungi.

Phacopsis is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi. They are parasites of members of the large lichen family Parmeliaceae, of which they are also a member. Originally proposed by Edmond Tulasne in 1852 to contain 3 species, Phacopsis now contains 10 species, although historically, 33 taxa have been described in the genus. Many of the species are poorly known, some of them having been documented only from the type specimen.
Dacampia is a genus of fungi in the family Dacampiaceae. It contains 15 species. The genus was circumscribed in 1853 by Italian lichenologist Abramo Bartolommeo Massalongo, with Dacampia hookeri assigned as the type species. The genus name honours Italian naturalist Benedetto de Dacampo (1787–1851).

Ovicuculispora is a genus of lichenicolous fungi in the family Bionectriaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Javier Etayo in 2010, with O. parmeliae assigned as the type species. This species had formerly been placed in the genera Nectria in 1981, and later (2001) in Nectriopsis.

Cordieritidaceae is a family of fungi in the order Cyttariales. Species in this family are saprobes or lichenicolous.

Polycoccum is a genus of lichenicolous fungi in the family Polycoccaceae. It has about 60 species.
Intralichen is a genus of lichenicolous fungi of uncertain classification in the class Ascomycota. It has four species. The genus was circumscribed by David Leslie Hawksworth and Mariette S. Cole in 2002, with Intralichen christiansenii as the type species.
Pyrenidium is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi. It is the only genus in the family Pyrenidiaceae. It has 13 species.
Gemmaspora is a single-species fungal genus of uncertain familial placement in the order Verrucariales. It contains Gemmaspora lecanorae, a lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungus that parasitises the lichen genus Aspicilia. The genus was proposed in 2007 by David Hawksworth and Gökhan Halici to contain the fungus formerly known as Adelococcus lecanorae. This species, originally described by Roger-Guy Werner in 1963, occurs in Syria and Turkey.
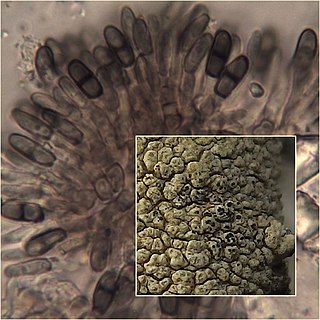
Minutoexcipula is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi of uncertain familial placement in the order Chaetothyriales. It has eight species. The genus was circumscribed in 1994 by M. Violeta Atienza Tamarit and David Leslie Hawksworth, with Minutoexcipula tuckerae assigned as the type species. The genus is characterized both by its black convex sporodochia-like conidiomata, as well as the well-differentiated exciple on these structures.

Hobsonia is a genus of fungi in the family Phleogenaceae. The genus is currently monotypic, with a single recognized species, Hobsonia mirabilis. The type species, H. gigaspora, and H. ackermannii are considered to be synonyms and additional lichenicolous species have now been transferred to the ascomycete genera Hobsoniopsis and Illosporiopsis. Hobsonia mirabilis is only known in its anamorph form, which is whitish, gelatinous, pustular, and occurs on dead woody plant remains. Microscopically, it produces coiled or spiralled conidia. The species was formerly of uncertain disposition, but molecular research, based on cladistic analysis of DNA sequences, has shown that it belongs within the Atractiellales. Though originally described from New York, the species is more commonly found in the tropics and subtropics.










