The Dinaric race, also known as the Adriatic race, were pseudoscientific terms used by certain physical anthropologists in the early to mid-20th century to describe the perceived predominant phenotype of the contemporary ethnic groups of southeast Europe. According to the discredited theories of physical anthropologist Carleton Coon, the Dinaric race was most commonly found among the populations in the Balkans and Carpathians, such as Montenegrins, Serbs, Bosniaks, Croats, Ghegs, Slovaks, Romanians, Hungarians, Western Ukrainians, and Southern Poles. Additionally, in Northern Europe, the South Germans were also identified as having Dinaric characteristics.
The concept of race as a categorization of anatomically modern humans has an extensive history in Europe and the Americas. The contemporary word race itself is modern; historically it was used in the sense of "nation, ethnic group" during the 16th to 19th centuries. Race acquired its modern meaning in the field of physical anthropology through scientific racism starting in the 19th century. With the rise of modern genetics, the concept of distinct human races in a biological sense has become obsolete. In 2019, the American Association of Biological Anthropologists stated: "The belief in 'races' as natural aspects of human biology, and the structures of inequality (racism) that emerge from such beliefs, are among the most damaging elements in the human experience both today and in the past."
The Caucasian race is an obsolete racial classification of humans based on a now-disproven theory of biological race. The Caucasian race was historically regarded as a biological taxon which, depending on which of the historical race classifications was being used, usually included ancient and modern populations from all or parts of Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa.
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscientific belief that the human species is divided into biologically distinct taxa called "races", and that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racial discrimination, racial inferiority, or racial superiority. Before the mid-20th century, scientific racism was accepted throughout the scientific community, but it is no longer considered scientific. The division of humankind into biologically separate groups, along with the assignment of particular physical and mental characteristics to these groups through constructing and applying corresponding explanatory models, is referred to as racialism, race realism, or race science by those who support these ideas. Modern scientific consensus rejects this view as being irreconcilable with modern genetic research.
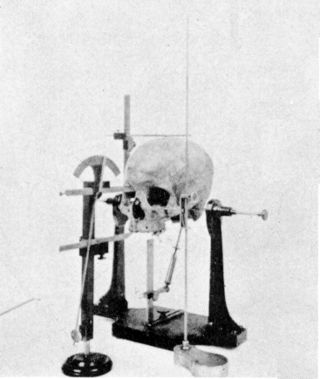
Craniometry is measurement of the cranium, usually the human cranium. It is a subset of cephalometry, measurement of the head, which in humans is a subset of anthropometry, measurement of the human body. It is distinct from phrenology, the pseudoscience that tried to link personality and character to head shape, and physiognomy, which tried the same for facial features.

Joseph Yegorovich Deniker was a Russian-French naturalist and anthropologist, known primarily for his attempts to develop highly detailed maps of race in Europe.

Jan Czekanowski was a Polish anthropologist, statistician, ethnographer, traveller, and linguist. He was one of the first persons to use quantitative methods in linguistics.
The Nordic race is an obsolete racial concept which originated in 19th-century anthropology. It was once considered a race or one of the putative sub-races into which some late-19th to mid-20th century anthropologists divided the Caucasian race, claiming that its ancestral homelands were Northwestern and Northern Europe, particularly to populations such as Anglo-Saxons, Germanic peoples, Balts, Baltic Finns, Northern French, and certain Celts, Slavs and Ghegs. The supposed physical traits of the Nordics included light eyes, light skin, tall stature, and dolichocephalic skull; their psychological traits were deemed to be truthfulness, equitability, a competitive spirit, naivete, reservedness, and individualism. In the early 20th century, the belief that the Nordic race constituted the superior branch of the Caucasian race gave rise to the ideology of Nordicism.
The Mediterranean race is an obsolete racial classification of humans based on the now-disproven theory of biological race. According to writers of the late 19th to mid-20th centuries it was a sub-race of the Caucasian race. According to various definitions, it was said to be prevalent in the Mediterranean Basin and areas near the Mediterranean and Black Sea, especially in Southern Europe, Eastern Europe, North Africa, most of West Asia, the Middle East or Near East; western Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and parts of the Horn of Africa. To a lesser extent, certain populations of people in Ireland, western parts of Great Britain, and Southern Germany, despite living far from the Mediterranean, were thought to have some minority Mediterranean elements in their population, such as Bavaria, Wales, and Cornwall.
Nordicism is an ideology which views the historical race concept of the "Nordic race" as an endangered and superior racial group. Some notable and influential Nordicist works include Madison Grant's book The Passing of the Great Race (1916); Arthur de Gobineau's An Essay on the Inequality of the Human Races (1853); the various writings of Lothrop Stoddard; Houston Stewart Chamberlain's The Foundations of the Nineteenth Century (1899); and, to a lesser extent, William Z. Ripley’s The Races of Europe (1899). The ideology became popular in the late-19th and 20th centuries in Germanic-speaking Europe, Northwestern Europe, Central Europe, and Northern Europe, as well as in North America and Australia.
The Alpine race is an obsolete racial classification of humans based on a now-disproven theory of biological race. It was defined by some late 19th-century and early 20th-century anthropologists as one of the sub-races of the Caucasian race. The origin of the Alpine race was variously identified. Ripley argued that it migrated from Central Asia during the Neolithic Revolution, splitting the Nordic and Mediterranean populations. It was also identified as descending from the Celts residing in Central Europe in Neolithic times. The Alpine race was described as having moderate stature, neotenous features, and specific cranial measurements, such as a high cephalic index.
The Armenoid race was a supposed sub-race in the context of a now-outdated model of dividing humanity into different races which was developed originally by Europeans in support of colonialism. The Armenoid race was variously described as a "sub-race" of the "Aryan race" or the "Caucasian race".
William Zebina Ripley was an American economist, lecturer at Columbia University, professor of economics at MIT, professor of political economy at Harvard University, and anthropologist of race. Ripley was famous for his criticisms of American railroad economics and American business practices in the 1920s and 1930s, and later for his tripartite racial theory of Europe. His contribution to the anthropology of race was later taken up by racial physical anthropologists, eugenicists, white supremacists, Nordicists, and racists in general, and it was considered a valid academic work at the time, although today it is considered to be a prime example of scientific racism and pseudoscience.

The Passing of the Great Race: Or, The Racial Basis of European History is a 1916 racist and pseudoscientific book by American lawyer, anthropologist, and proponent of eugenics Madison Grant (1865–1937). Grant expounds a theory of Nordic superiority, claiming that the "Nordic race" is inherently superior to other human "races". The theory and the book were praised by Adolf Hitler and other Nazis.

Count Georges Vacher de Lapouge was a French anthropologist and a theoretician of eugenics and scientific racism. He is known as the founder of anthroposociology, the anthropological and sociological study of race as a means of establishing the superiority of certain peoples.
Various attempts have been made, under the British Raj and since, to classify the population of India according to a racial typology. After independence, in pursuance of the government's policy to discourage distinctions between communities based on race, the 1951 Census of India did away with racial classifications. Today, the national Census of independent India does not recognise any racial groups in India.
The Irano-Afghan race or Iranid race is an obsolete racial classification of human beings based on a now-disproven theory of biological race. Some anthropologists of the 20th century classified the populations native to the Iranian plateau as belonging to this race, which was usually seen as a subrace of the Caucasian race or the Mediterranean racial subtype of that race, depending on the authority consulted.
Negroid is an obsolete racial grouping of various people indigenous to Africa south of the area which stretched from the southern Sahara desert in the west to the African Great Lakes in the southeast, but also to isolated parts of South and Southeast Asia (Negritos). The term is derived from now-disproven conceptions of race as a biological category.
The Atlantid race or North-Atlantid is an obsolete racial classification of human beings based on a now-disproven theory of biological race. In the early 20th century, it was described as one of the sub-races of the Caucasoid race, a blend of the Nordic and Mediterranean races.
The history of anthropometry includes its use as an early tool of anthropology, use for identification, use for the purposes of understanding human physical variation in paleoanthropology and in various attempts to correlate physical with racial and psychological traits. At various points in history, certain anthropometrics have been cited by advocates of discrimination and eugenics often as part of novel social movements or based upon pseudoscience.






