
The Chinese mantis is a species of mantis native to Asia and the nearby islands. In 1896, this species was accidentally introduced by a nursery tender at Mt. Airy near Philadelphia, United States. Tenodera sinensis often is erroneously referred to as Tenodera aridifolia sinensis because it was at first described as a subspecies of Tenodera aridifolia, but Tenodera sinensis is now established as a full species.

Extatosoma tiaratum, commonly known as the spiny leaf insect, the giant prickly stick insect, Macleay's spectre, or the Australian walking stick, is a large species of Australian stick insect. The species has the Phasmid Study Group number PSG9.

Iris oratoria, known by the common name Mediterranean mantis, due to humans first studying it in lands around the Mediterranean Sea, is a species of praying mantis. Its range is expanding in the Middle East, Western Asia and the United States.

Creobroter is a genus of flower mantises in the tribe Hymenopodini; species are concentrated in Asia. The name comes from the Greek kreo-, meaning "flesh") and broter" meaning "eating", therefore, "flesh-eating", an apt name for a predatory insect. Both sexes have long wings and are capable fliers. Full-grown males are about 3 to 4 cm in length; females are about 4 to 5 cm.

Flower mantises are praying mantises that use a special form of camouflage referred to as aggressive mimicry, which they not only use to attract prey, but avoid predators as well. These insects have specific colorations and behaviors that mimic flowers in their surrounding habitats.

Phyllocrania paradoxa, common name ghost mantis, is a small species of mantis from Africa remarkable for its leaf-like body. It is one of the three species in the genus Phyllocrania. It is known for its distinct and exclusive camouflaged appearance of a dry weathered leaf.

Brunneria borealis, common name Brunner's mantis, Brunner's stick mantis, or northern grass mantis, is a species of praying mantis native to the southern United States. It is the only mantis species known to reproduce solely through parthenogenesis; there are no males.

Sphodromantis viridis is a species of praying mantis that is kept worldwide as a pet. Its common names include African mantis, giant African mantis, and bush mantis.
Deroplatys desiccata, known by the common name giant dead leaf mantis, is a praying mantis from Southeast Asia. This is the type species of genus Deroplatys.

Popa spurca, also known as the African twig mantis, is a species of mantis native to Africa. It takes its common name from its resemblance to twig from a woody plant and grows up to 8 centimetres (3.1 in) long if female or 7 cm (2.8 in) long if male.

Dead leaf mantis is a common name given to various species of praying mantis that mimic dead leaves. It is most often used in reference to species within genus Deroplatys because of their popularity as exotic pets. Examples include D. desiccata, D. lobata, and D. philippinica. Other species to which the term may apply include Acanthops falcataria, A. falcata, and Phyllocrania paradoxa.

Brunneria is a genus of praying mantises in family Mantidae. They are often called stick mantis for their slender shape and the species of the genus are native to the Americas.

Idolomantis is a monotypic genus of praying mantises in the family Empusidae. It contains the single species, Idolomantis diabolica, commonly known as the devil's flower mantis or giant devil's flower mantis. It is one of the largest species of praying mantises, and is possibly the largest that mimics flowers
Parasphendale agrionina species of praying mantis in the family Miomantidae. It has been given the common name budwing mantis for its vestigial wings. Females are incapable of flight.
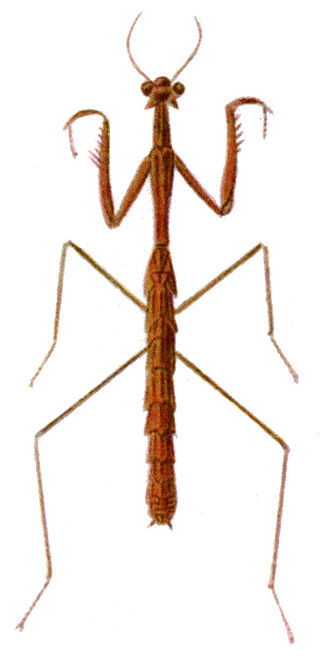
Stick mantis and twig mantis are common names applied to numerous species of mantis that mimic sticks or twigs as camouflage. Often the name serves to identify entire genera such as is the case with:

Pseudoharpax virescens, common name Gambian spotted-eye flower mantis, is a species of praying mantis native to western, central and eastern Africa. It takes its name from two eye spots on the dorsal side of the abdomen of adult females.

Sphodromantis is a large genus of praying mantises concentrated in Africa, sometimes considered a synonym of the genus Hierodula: from the same tribe, Paramantini. Outside their range especially, many share the common name African Mantis.

The red triangle slug is a species of large air-breathing land slug, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Athoracophoridae, the leaf-veined slugs.

Veltheimia capensis is one of two species of flowering plants belonging to the genus Veltheimia, of the family Asparagaceae. It is a tender bulbous perennial reaching a height of 46 cm (18 in), with flowers varying in color from white with red spots to pink with green or red markings.

Eurycantha calcarata is a species of phasmid endemic to Australasia.


















