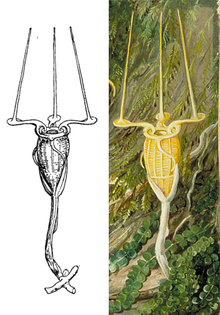
Rafflesia, or stinking corpse lily, is a genus of parasitic flowering plants in the family Rafflesiaceae. The species have enormous flowers, the buds rising from the ground or directly from the lower stems of their host plants; one species has the largest flower in the world. Plants of the World Online lists up to 41 species from this genus; all of them are found throughout Southeast Asia.

The Pleurothallidinae are a neotropical subtribe of plants of the orchid family (Orchidaceae) including 29 genera in more than 4000 species.

Nepenthes is a genus of carnivorous plants, also known as tropical pitcher plants, or monkey cups, in the monotypic family Nepenthaceae. The genus includes about 170 species, and numerous natural and many cultivated hybrids. They are mostly liana-forming plants of the Old World tropics, ranging from South China, Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines; westward to Madagascar and the Seychelles (one); southward to Australia (four) and New Caledonia (one); and northward to India (one) and Sri Lanka (one). The greatest diversity occurs on Borneo, Sumatra, and the Philippines, with many endemic species. Many are plants of hot, humid, lowland areas, but the majority are tropical montane plants, receiving warm days but cool to cold, humid nights year round. A few are considered tropical alpine, with cool days and nights near freezing. The name "monkey cups" refers to the fact that monkeys were once thought to drink rainwater from the pitchers.
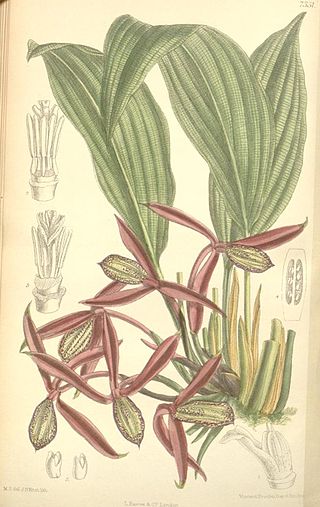
Orchidantha is a genus of flowering plants. In the APG III system, it is placed in the family Lowiaceae, as the sole genus. It includes the plants in the formerly recognised genera Lowia and Protamomum.

Dipterocarpaceae is a family of flowering plants with 22 genera and about 695 known species of mainly lowland tropical forest trees. Their distribution is pantropical, from northern South America to Africa, the Seychelles, India, Indochina, Indonesia, Malaysia and Philippines. The greatest diversity of Dipterocarpaceae occurs in Borneo.

Odoardo Beccari was an Italian botanist famous for his discoveries in Indonesia, New Guinea, and Australia. He has been called the greatest botanist to ever study Malesia. The standard author abbreviation Becc. is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.

Nepenthes gracilis, or the slender pitcher-plant, is a common lowland pitcher plant that is widespread in the Sunda region. It has been recorded from Borneo, Cambodia, Peninsular Malaysia, Singapore, Sulawesi, Sumatra, and Thailand. The species has a wide altitudinal distribution of 0 to 1100 m above sea level, although most populations are found below 100 m and plants are rare above 1000 m. Despite being a widespread plant, natural hybrids between N. gracilis and other species are quite rare.
Ctenolophon is the only genus in the flowering plant family Ctenolophonaceae. It has two recognized species:

Nepenthes hurrelliana is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo, where it has been recorded from northern Sarawak, southwestern Sabah, and Brunei. It is of putative hybrid origin; its two original parent species are thought to be N. fusca and N. veitchii. A thick indumentum of rusty-brown hairs covers the entire plant, a characteristic presumably inherited from the latter.

Hanguana is a genus of flowering plants with a dozen known species. It is the only genus in the family Hanguanaceae.

The wildlife of Malaysia is diverse, with Malaysia being a megadiverse country. Most of the country is covered in rainforest, which hosts a huge diversity of plant and animal species. There are approximately 361 mammal species, 694 bird species, 250 reptile species, and 150 frog species found in Malaysia. Its large marine territory also holds a great diversity of life, with the country's coastal waters comprising part of the Coral Triangle.

Thismia is a genus of myco-heterotrophic plants in family Burmanniaceae, first described as a genus in 1845. It is native to East and Southeast Asia, New Guinea, Australia, New Zealand, and the Americas.

Alastair S. Robinson is a taxonomist and field botanist specialising in the carnivorous plant genus Nepenthes, for which he is regarded as a world authority. He is currently Manager Biodiversity Services at the National Herbarium of Victoria, Royal Botanic Gardens Melbourne, where he oversees identification and field botany services, the Victorian Conservation Seedbank, the Library and Artwork components of the State Botanical Collection, and the botanical journal Muelleria, a peer-reviewed scientific journal on botany published by the Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria, for which he is Editor in Chief.

Thismia americana, known as thismia or banded Trinity was a species of flowering plant that was first discovered in 1912 by Norma Etta Pfeiffer in the wetlands surrounding Chicago's Lake Calumet, and described by her in 1914. The type specimen was found in what was then a wet-mesic sand prairie at 119th Street and Torrence Avenue in what would become the industrial neighborhood of South Deering. The plant has not been seen since 1916, and the ground where it was observed has since been extensively altered by industrial development. The species is believed to be extinct. Several extensive searches have not uncovered any living specimens of the vanished species.

Sciaphila is a genus of mycoheterotrophic plants in the family Triuridaceae. These plants receive nutrition from fungi and neighboring trees and have less need for photosynthesis. It is widespread in tropical and subtropical regions, found in Africa, China, Japan, the Indian Subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Latin America and on various islands Pacific Islands. The most noteworthy feature of the genus is the number of the various flower parts 99.9 percent of Monocots are trimerous, but Sciaphila spp. can have eight or even ten parts in a whorl.

The Batu Tinagat Lighthouse is a lighthouse on Batu Tinagat of Tawau District, Tawau Division in Sabah, Malaysia. It is located approximately 10 kilometres from the Tawau town centre.

Thismia kobensis is a species of flowering plant from the Thismia genus in the myco-heterotrophic family Burmanniaceae.