
A tilting train is a train that has a mechanism enabling increased speed on regular rail tracks. As a train rounds a curve at speed, objects inside the train experience centrifugal force. This can cause packages to slide about or seated passengers to feel squashed by the outboard armrest, and standing passengers to lose their balance, or in such excessive speeds, could even cause the train to derail. Tilting trains are designed to counteract this by tilting the carriages towards the inside of the curve, thus compensating for the g-force. The train may be constructed such that inertial forces cause the tilting, or it may have a computer-controlled powered mechanism.

Pendolino is an Italian family of high-speed tilting trains used in Italy, Spain, Germany, Poland, Portugal, Slovenia, Finland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, the UK, the US, Switzerland, China, and Greece. It was also used in Russia from December 12, 2010 until March 26, 2022. Based on the design of the Italian ETR 401, it was further developed and manufactured by Fiat Ferroviaria, which was taken over by Alstom in 2000.

The Chungbuk Line is a railway line serving North Chungcheong Province in South Korea. The line connects Jochiwon on the Gyeongbu Line to Bongyang on the Jungang Line, serving the major cities of Cheongju and Chungju en route. Cheongju International Airport is located near the rail line.
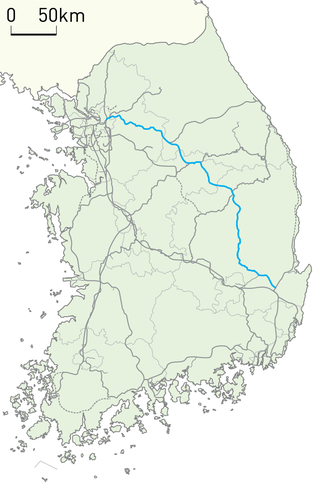
The Jungang line is a railway line connecting Cheongnyangni in Seoul to Moryang in Gyeongju in South Korea, traversing central South Korea from the northwest to the southeast. It is also referred to as the rail line of the Seoul Metropolitan Subway from Yongsan station to Jipyeong station. The section from Cheongnyangni to Dodam was designated as a semi-high-speed railway.
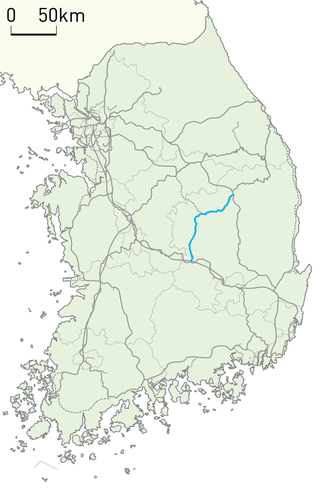
The Gyeongbuk Line is a railway line serving North Gyeongsang Province in South Korea. The line runs from Gimcheon on the Gyeongbu Line via Sangju, Jeomchon, and Yecheon to Yeongju on the Jungang Line.

Korea Train eXpress (Korean: 한국고속철도), often known as KTX, is South Korea's high-speed rail system, operated by Korail. Construction began on the high-speed line from Seoul to Busan in 1992. KTX services were launched on April 1, 2004.

The Yeongdong Line is a line of Korail. It connects Yeongju in North Gyeongsang Province with Gangneung in Gangwon Province. From Yeongju, it crosses the Taebaek Mountains and reaches the Sea of Japan at Donghae, thence proceeding north to Gangneung.

The Mugunghwa-ho (Korean: 무궁화호) is a class of train operated by Korail, the main railway operator of South Korea. Mugunghwa trains are Korail's slowest tier of trains stopping at a number of towns and villages, and operating over a number of lines that are not served by other trains. Journey times are generally twice that of KTX trains and 25% longer than ITX express trains.

Cheongnyangni Station (Korean: 청량리역) is a major railway station located at Dongdaemun District, Seoul, South Korea. It serves as a terminus for passenger trains serving the eastern part of South Korea. KTX, ITX-Cheongchun, and Mugunghwa-ho trains terminates or stops at this station. Several Seoul Metropolitan Subway lines serve the station. These are: Seoul Subway Line 1, the Gyeongchun Line, the Suin–Bundang Line and the Gyeongui–Jungang Line.
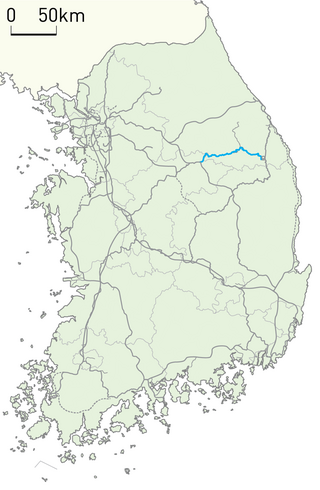
Taebaek Line is a single-track electrified railway mainline connecting Jecheon station to Baeksan station in South Korea. At its two ends, the Taebaek Line connects to the Jungang Line and Yeongdong Line. The line was originally two spur lines, which were built across difficult mountainous terrain in stages, before a connection was built. The line includes the steepest section of the South Korean network, a short parallel line that is operated as a second track on the section includes South Korea's longest spiral tunnel. The centerpiece of the last-built section west of Taebaek, is a tunnel that was the longest in South Korea at the time of its construction, and Chujeon Station at the eastern end of the tunnel is the highest altitude in South Korea at 855 m (2,805 ft). In passenger traffic, the line is served by cross-country passenger trains connecting the capital Seoul with Korea's east coast. In freight traffic, while coal transport declined, the line carries significant cement transport. In the winter, regular special trains take tourists along the scenic route.

HSR-350x, alternatively called G7, KHST or NG-KTX, is a South Korean experimental high-speed train. It was developed and built in a joint project of government research institutes, universities and private companies that started in 1996, which aimed to reduce import dependence in high-speed rail technology. New components developed for the HSR-350x included motors, electronics, and the carbody of passenger cars. Test runs were conducted between 2002 and 2008. The experimental train achieved the South Korean rail speed record of 352.4 km/h (219.0 mph) in 2004. The HSR-350x was the basis for Korail's KTX-II (KTX-Sancheon) commercial high-speed trains.

The Korail Class 8200 is a South Korean electric locomotive operated by Korail. This locomotive has head-end power capabilities in place of a dynamo car, which could be used with up to 12 passenger cars.

The Gyeongbu high-speed railway, also known as Gyeongbu HSR, is South Korea's first high-speed rail line from Seoul to Busan. KTX high-speed trains operate three sections of the line: on 1 April 2004, the first between a junction near Geumcheon-gu Office station, Seoul and a junction at Daejeonjochajang station north of Daejeon, and a second between a junction at Okcheon station, southeast of Daejeon, and a junction near Jicheon station, north of Daegu entered service; then on 1 November 2010, the third section, between a junction west of Daegu and Busan became operational. The missing gaps across the urban areas of Daejeon and Daegu were in construction for an expected opening in 2014, separate tracks into Seoul Station were also planned. The temporary ends of the three sections were connected to the parallel conventional Gyeongbu Line by tracks that will serve as interconnector branches upon the completion of the entire line. On 1 August 2015, construction on urban areas of Daejeon and Daegu were completed; all the sections of HSR line were connected.

Osong station is a train station on the Honam and Gyeongbu high-speed railways in Cheongju City, North Chungcheong Province, South Korea. It is located at the intersection of the Gyeongbu KTX high-speed rail line, the conventional Chungbuk Line and, since April 2015, the Honam high-speed railway. KTX trains began calling there from November 1, 2010, bringing high-speed rail service to the nearby city of Cheongju.

The KTX-Sancheon is a South Korean high-speed train built by Hyundai Rotem in the second half of the 2000s and operated by Korail since March 2010. With a top speed of 305 km/h (189.5 mph), the KTX-Sancheon is the second commercial high-speed train operated in South Korea and the first domestic high-speed train that is designed and developed in South Korea.

The KTX-I, also known as the TGV-K or Korail Class 100000, is a South Korean high speed train class based on the French TGV Réseau. The 20-car formation of the trainsets without a restaurant car is optimized for high capacity. The 46 trainsets were built partly in France and partly in South Korea in the framework of a technology transfer agreement, which was the basis for further domestic high-speed train development in South Korea.

In South Korea, speed limits are controlled at the national level by Article 19 of the Enforcement Regulations of the Road Traffic Act, although speed limits can be lowered if deemed necessary, or if they are going through cities, towns, villages, or school zones. In some cases, the speed on some expressways is limited to 80 km/h, so there are some expressways with speeds that are strictly limited to the level of automobile-only roads such as South Korea's Olympic-daero, Gangbyeon-buk-ro, and Beonyeong-ro. These speed limits are as follows:

HEMU-430X is a South Korean high-speed train intended for a maximum speed of 430 km/h (267 mph). On 31 March 2013, it achieved 421.4 km/h (261.8 mph) in a test run, making South Korea the world's fourth country after France, Japan and China to develop a high-speed train running above 420 km/h (261 mph). The main new feature of the train compared to older South Korean high-speed trains is distributed traction. The commercial versions of the trains, tentatively named the EMU-260 and EMU-320, were delivered to Korail from 2020 to 2021.
High-speed rail service in South Korea began with the construction of a high-speed line from Seoul to Busan in 1992, and was inspired by Japan's Shinkansen. The first commercial high-speed rail service was launched on 1 April 2004. Currently, South Korea hosts two high-speed rail operators: Korea Train eXpress (KTX) and Super Rapid Train (SRT).

Nuriro (Korean: 누리로) is a class of train operated by Korail, the national railroad of South Korea, it was introduced on June 1, 2009, to replace the short-range Mugunghwa-ho. The train was introduced as a replacement for the Bidulgi-ho/Tongil-ho/Mugunghwa-ho operating system between Seoul and Onyangoncheon, and will replace the short-range Mugunghwa-ho when a new train comes in. However, due to various problems, it is currently operating in Yeongdong Line and Jungang Line as a replacement for Mugunghwa-ho.


















