
Histone acetyltransferase p300 also known as p300 HAT or E1A-associated protein p300 also known as EP300 or p300 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the EP300 gene. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription of genes via chromatin remodeling by allowing histone proteins to wrap DNA less tightly. This enzyme plays an essential role in regulating cell growth and division, prompting cells to mature and assume specialized functions (differentiate), and preventing the growth of cancerous tumors. The p300 protein appears to be critical for normal development before and after birth.

P300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF), also known as K(lysine) acetyltransferase 2B (KAT2B), is a human gene and transcriptional coactivator associated with p53.

Histone H3.1t is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST3H3 gene.

RuvB-like 2 , also known as RUVBL2, is a human gene coding for a protein belonging to the AAA+ family of proteins.
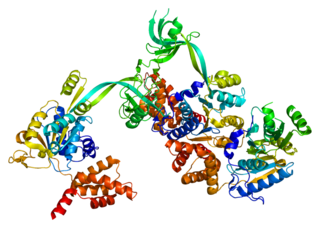
RuvB-like 1 , also known as RUVBL1 and TIP49, is a human gene. RUVBL1 can form a hexamer. The hexamer can form a dodecamer with RUVBL2 protein. Possesses single-stranded DNA-stimulated ATPase and ATP-dependent DNA helicase activity; hexamerization is thought to be critical for ATP hydrolysis and adjacent subunits in the ring-like structure contribute to the ATPase activity.

Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFYB gene.

Histone acetyltransferase KAT2A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KAT2A gene.
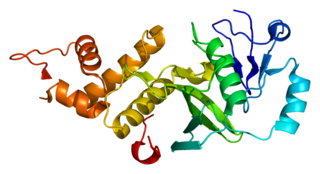
Histone acetyltransferase KAT5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KAT5 gene. It is also commonly identified as TIP60.

MAX is a gene that in humans encodes the MAX transcription factor.

TAF9 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 32kDa, also known as TAF9, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAF9 gene.

Actin-like protein 6A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTL6A gene.

Transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAF2 gene.

DNA methyltransferase 1-associated protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DMAP1 gene.

Splicing factor 3B subunit 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SF3B3 gene.

Transcription initiation protein SPT3 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SUPT3H gene.

E1A-binding protein p400 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EP400 gene.

Transcriptional adapter 2-alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TADA2A gene.

TAF5-like RNA polymerase II p300/CBP-associated factor-associated factor 65 kDa subunit 5L is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TAF5L gene.

Biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 1 subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BLOC1S1 gene.
The NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex is a protein complex that has histone acetylase activity on chromatin, as well as ATPase, DNA helicase and structural DNA binding activities. The complex is thought to be involved in double-strand DNA break repair. Subunits of the human complex include HTATIP/TIP60, TRRAP, RUVBL1, RUVBL2, beta-actin and BAF53/ACTL6A. In yeast, the complex has 13 subunits, including the catalytic subunit Esa1.























