
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.

Chlamydomonadales, also known as Volvocales, are an order of flagellated or pseudociliated green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae. Chlamydomonadales can form planar or spherical colonies. These vary from Gonium up to Volvox. Each cell has two flagella, and is similar in appearance to Chlamydomonas, with the flagella throughout the colony moving in coordination.

Characiochloridaceae is a family of green algae in the order Chlamydomonadales.

Selenastraceae is a family of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales. Members of this family are common components of the phytoplankton in freshwater habitats worldwide. A few species have been found in brackish and marine habitats, such as in the Baltic Sea.
Characiosiphon is a genus of green algae in the family Characiosiphonaceae. It contains a single species, Characiosiphon rivularis.

Dimorphococcus is a genus of fresh water green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae. It is found as a component of the phytoplankton of freshwater ponds, lakes, and peat bogs. It is widespread, but usually not very common.

Kirchneriella is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, as phytoplankton or metaphyton.
Lobocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiosiphonaceae. It contains the single species Lobocharacium coloradoense. It has been isolated from a pond in Colorado, United States.

Schroederia is a genus of green algae in the family Schroederiaceae. Schroederiaceae is a monotypic taxon; Schroederia is its only genus.

Schroederiella is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae.
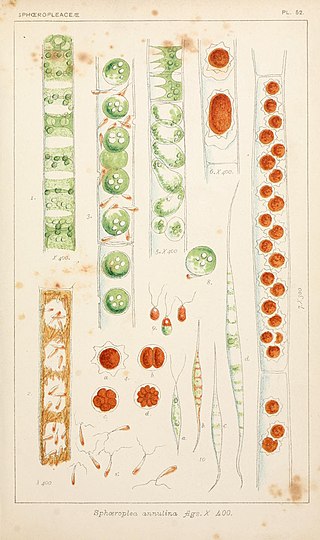
Sphaeroplea is a genus of green algae in the family Sphaeropleaceae. It was first circumscribed by the Swedish botanist Carl Adolph Agardh in 1824.

Tetraedron is a genus of green algae in the family Hydrodictyaceae. It may also be spelled as Tetraëdron.
Gilbertsmithia is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae, containing the single species Gilbertsmithia grandis. It was named after the American botanist Gilbert Morgan Smith. This remarkable alga has only been recorded once from a muddy rainwater pool in Madras, India.
Actinochloridaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlamydomonadales.
Deuterocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, attached to algae or detritus. It is rare and has only been recorded from Europe.

Marthea is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae, containing the single species Marthea tetras. It is an extremely rare genus; it has only been recorded once, as freshwater phytoplankton from its original locality in the Bohemian Forest region of the Czech Republic.
Chlorotetraedron is a genus of green algae, in the family Neochloridaceae. The name may also be written as Chlorotetraëdon. It is found as freshwater plankton or in soil.
Korshikoviella is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae.

Chlorokybus is a multicellular (sarcinoid) genus of basal green algae or charophyte. It has been classified as the sole member of the family Chlorokybaceae, which is the sole member of the order Chlorokybales, in turn the sole member of the class Chlorokybophyceae. It grows on soil and rock surfaces, and is rare.
Bracteamorpha is a genus of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales, and is the only genus in the family Bracteamorphaceae. It contains a single species, Bracteamorpha trainorii.











